Volume 20, Number 4—April 2014
Research
Novel Betacoronavirus in Dromedaries of the Middle East, 2013
Figure 4
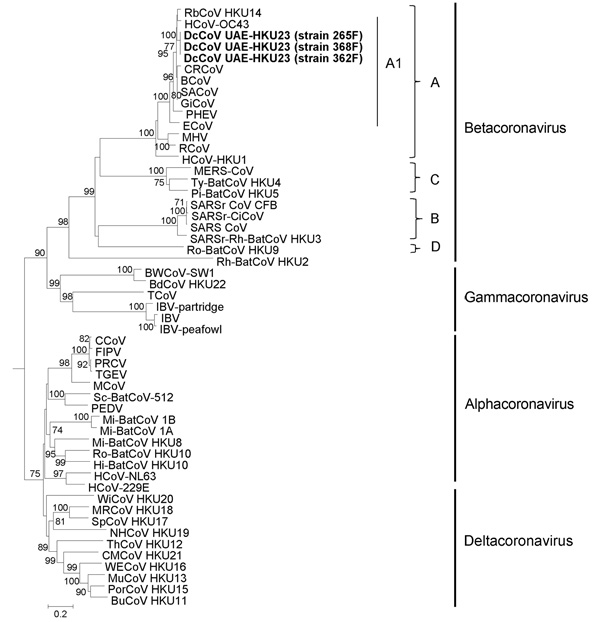
Figure 4. . . . . . Phylogenetic analyses of spike protein of dromedary camel coronavirus (DcCoV) UAE-HKU23from dromedaries of the Middle East, 2013.The tree was constructed by the neighbor-joining method, using Jones-Taylor-Thornton substitution model with gamma distributed rate variation and bootstrap values calculated from 1,000 trees. Bootstrap values of <70% are not shown. A total of 1,366 aa positions in spike protein were included in the analysis. The tree was rooted to Breda virus (GenBank accession no. AY_427798).Betacoronavirus lineages A1 and A–D are indicated on the right. Boldface indicates the 3 strains of DcCoV UAE-HKU23 characterized in this study. Virus definitions and GenBank accession numbers (in parentheses) follow: RbCoV HKU14, rabbit CoV HKU14 (JN874559); HCoV-OC43, human CoV OC43 (NC_005147); CRCoV, canine respiratory CoV (JX860640); BCoV, bovine CoV (NC_003045); SACoV, sable antelope CoV (EF424621); GiCoV, giraffe CoV (EF424622); PHEV, porcine hemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus (NC_007732); ECoV, equine CoV (NC_010327); MHV, murine hepatitis virus (NC_001846); RCoV, rat CoV (NC_012936); HCoV-HKU1, human CoV HKU1 (NC_006577); MERS-CoV, Middle East respiratory syndrome CoV (JX869059); Ty-BatCoV HKU4, tylonycteris bat CoV HKU4 (NC_009019); Pi-BatCoV HKU5, pipistrellus bat CoV HKU5 (NC_009020); SARSrCoV CFB, SARS-related Chinese ferret badger CoV (AY545919); SARSr-CiCoV, SARS-related palm civet CoV (AY304488); SARS-CoV, severe acute respiratory syndrome–associated human CoV (NC_004718); SARSr-Rh-BatCoV HKU3, SARS-related rhinolophus bat CoV HKU3 (DQ022305); Ro-BatCoV HKU9, rousettus bat CoV HKU9 (NC_009021); RhBatCoV HKU2, rhinolophus bat CoV HKU2 (EF203064); BWCoV-SW1, Beluga whale CoV SW1 (NC_010646); BdCoV HKU22, bottlenose dolphin CoV HKU22 (KF793824); TCoV, turkey CoV (NC_010800); IBV-partridge, partridge CoV (AY646283); IBV, infectious bronchitis virus (NC_001451); IBV-peafowl, peafowl CoV (AY641576); CCoV, canine CoV (GQ477367); FIPV, feline infectious peritonitis virus (AY994055); PRCV, porcine respiratory CoV (DQ811787); TGEV, transmissible gastroenteritis virus (DQ811789); MCoV, mink CoV (HM245925); Sc-BatCoV-512, scotophilus bat CoV 512 (NC_009657); PEDV, porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (NC_003436); Mi-BatCoV 1B, miniopterus bat CoV 1B (NC_010436); Mi-BatCoV 1A, miniopterus bat CoV 1A (NC_010437); Mi-BatCoV HKU8, miniopterus bat CoV HKU8 (NC_010438); Ro-BatCoV HKU10, rousettus bat CoV HKU10 (JQ989270); Hi-BatCoV HKU10, hipposideros bat CoV HKU10 (JQ989266); HCoV-NL63, human CoV NL63 (NC_005831); HCoV-229E, human CoV 229E (NC_002645); WiCoV HKU20, wigeon CoV HKU20 (JQ065048); MRCoV HKU18, magpie–robin CoV HKU18 (JQ065046); SpCoV HKU17, sparrow CoV HKU17 (JQ065045); NHCoV HKU19, night-heron CoV HKU19 (JQ065047); ThCoV HKU12, thrush CoV HKU12 (FJ376621); CMCoV HKU21, common-moorhen CoV HKU21 (JQ065049); WECoV HKU16, white-eye CoV HKU16 (JQ065044); MunCoV HKU13, munia CoV HKU13 (FJ376622); PorCoV HKU15, porcine CoV HKU15 (JQ065042); BuCoV HKU11, bulbul CoV HKU11 (FJ376619). Numbers at nodes represent bootstrap values. Scale bar indicates the estimated number of substitutions per 5 aa.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.