Volume 20, Number 5—May 2014
Research
Streptococcus mitis Strains Causing Severe Clinical Disease in Cancer Patients
Figure 2
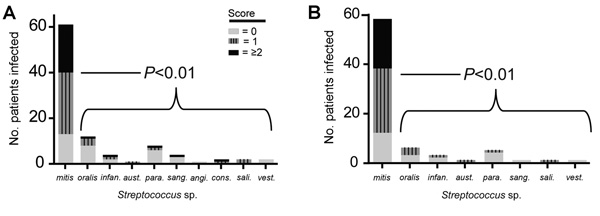
Figure 2. A) Pitt bacteremia scores for cancer patients infected with particular VGS species, showing that more clinically severe disease is caused by Streptococcus mitis strains than other viridans group streptococci (VGS) speciesB) Pitt bacteremia scores for only those cancer patients with neutropeniap values refer to Mann-Whitney U comparison of Pitt bacteremia scores for patients infected with Smitis strains versus those infected with non–Smitis strainsinfan., infantis; aust., australis; para., parasanguinis; sang., sanguinus; angi., anginosus; cons., constellatus; sali., salivarius; vest., vestibularis.
Page created: April 16, 2014
Page updated: April 16, 2014
Page reviewed: April 16, 2014
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.