Volume 20, Number 5—May 2014
Research
Streptococcus mitis Strains Causing Severe Clinical Disease in Cancer Patients
Figure 4
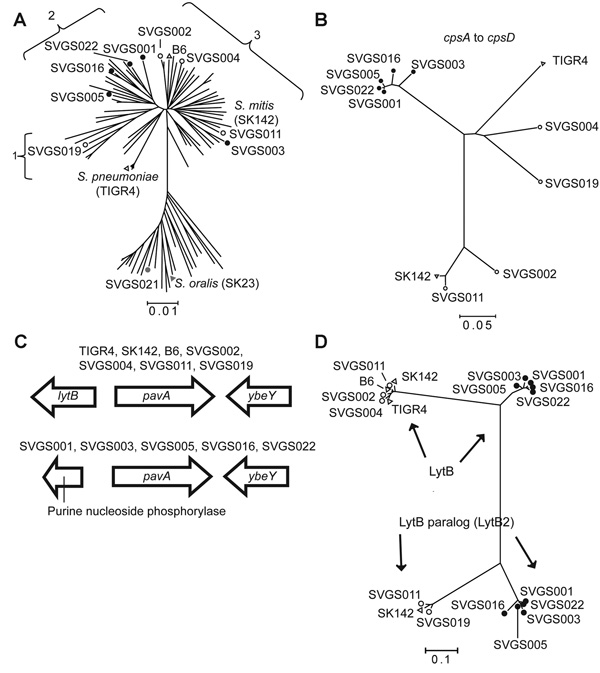
Figure 4. Selected data from whole-genome analysis of viridans group streptococci (VGS) strainsA) Neighbor-joining tree generated by multilocus sequence analysis (MLSA) of Streptococcus mitis and Soralis strains, showing locations of VGS strains selected for whole-genome analysisNumbers 1–3 refer to Smitis clusters (defined in Figure 3)MLSA locations are also shown for the Smitis and Soralis type strains (SK142 and SK23, respectively) and fully sequenced Smitis strain B6 and Spneumoniae strain TIGR4B) SVGS004 mouse challenge dataNeighbor-joining tree of first 4 genes of the capsular polysaccharide encoding operon (cpsA–cpsD)TIGR4 and SK142 are included for reference purposesStrain B6 is not included because it lacks a cps operonNote tight clustering of 5 VGS strains (black dots)C) Genetic arrangement surrounding the pavA gene, which encodes a fibronectin-binding proteinTwo distinct gene arrangements are present 5′ of the pavA gene, with the arrangement for particular strains as indicatedD) Neighbor-joining tree of LytB protein, which is involved in cell-wall turnover, from fully sequenced Smitis strainsSome Smitis strains possess a gene encoding a second LytB-like protein, which we have named LytB2 (ZP_07643922 from strain SK142)Note tight clustering of the same 5 VGS strains (black dots) for the LytB and LytB2 proteins as was observed for the cpsA–cpsD analysis in panel BA, B, D) SVGS, Shelburne VGSScale bars indicate genetic distances.