Volume 21, Number 12—December 2015
Dispatch
Japanese Macaques (Macaca fuscata) as Natural Reservoir of Bartonella quintana
Figure 1
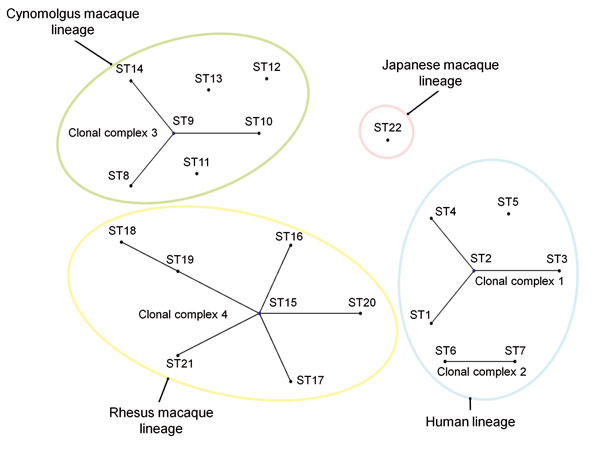
Figure 1. Phylogenetic relationship among 1 to 22 sequence types (STs) of Bartonella quintana strains based on eBURST analysis (http://eburst.mlst.net/default.asp). Black dots indicate ST numbers of B. quintana strains. A clonal complex was defined as a group of STs that had 8 identical alleles. Clonal complexes 1, 2, 3, and 4 consist of STs 1–4, STs 6–7, STs 8–10 and 14, and STs 15–21, respectively. A lineage was defined as a group of STs that had ≥7 identical alleles. Color circles show 4 lineages classified by host species.
Page created: November 17, 2015
Page updated: November 17, 2015
Page reviewed: November 17, 2015
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.