Molecular Characterization of Canine Rabies Virus, Mali, 2006–2013
Abdallah Traoré, Evelyne Picard-Meyer, Stephanie Mauti, Melanie Biarnais, Oliver Balmer, Kassim Samaké, Badian Kamissoko, Saïdou Tembely, Amadou Sery, Abdel K. Traoré, Amy P. Coulibaly, Emmanuelle Robardet, Jakob Zinsstag, and Florence Cliquet

Author affiliations: Central Veterinary Laboratory, Bamako, Mali (A. Traoré, K. Samaké, B. Kamissoko, S. Tembely, A. Sery, A.P. Coulibaly); French Agency for Food, Environmental, and Occupational Health and Safety, Malzéville, France (E. Picard-Meyer, M. Biarnais, E. Robardet, F. Cliquet); Swiss Tropical and Public Health Institute, Basel (S. Mauti, O. Balmer, J. Zinsstag); University of Basel, Basel, Switzerland (S. Mauti, O. Balmer, J. Zinsstag); Faculty of Medicine and Odontostomatology, Bamako (A.K. Traoré)
Main Article
Figure 2
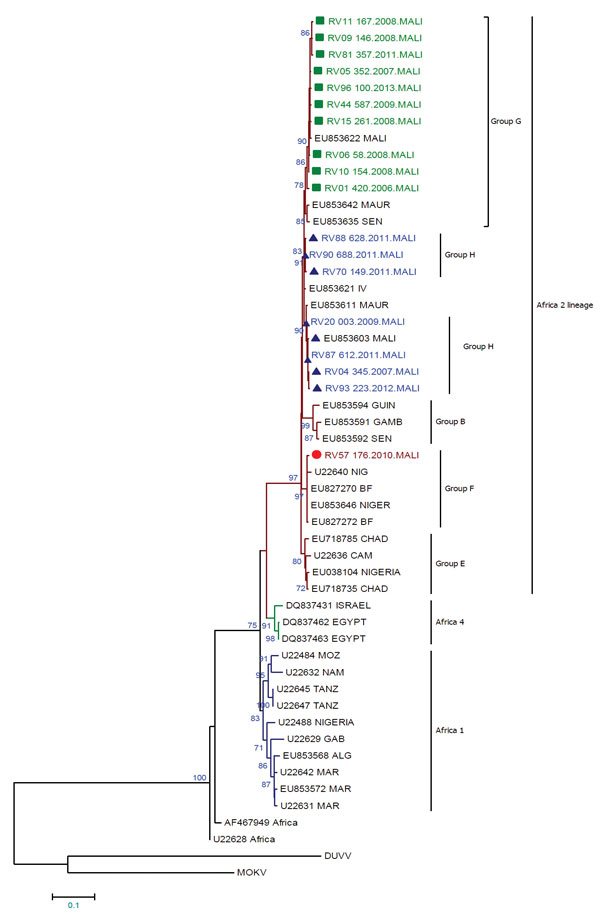
Figure 2. Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree based on a 564-nt sequence of nucleoprotein genes of 18 rabies virus sequences from Mali, 2002–2013, and representative sequences from Mali (n = 2), northern Africa (n = 6), South Africa (n = 2), West Africa (n = 32), and central Africa (n = 5). Sequences obtained in this study are identified in green, blue, and red. Green squares indicate genotype G, blue triangles indicate genotype H, and red circles indicate genotype F. The tree is rooted with 2 bat isolates used as outgroups Duvenhage virus (DUVV) (U22848) and Mokola virus (MOKV) (U22843). Bootstrap values (100 replicates) >70% are shown next to nodes. Alg, Algeria; BF, Burkina Faso; Cam, Cameroon; Gab, Gabon; Gamb, Gambia; Guin, Guinea; Maur, Mauritania; Mar, Morocco; Moz, Mozambique; Nig, Niger; Sen, Senegal; Tanz, Tanzania. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
Main Article
Page created: April 13, 2016
Page updated: April 13, 2016
Page reviewed: April 13, 2016
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
