Volume 23, Number 1—January 2017
Dispatch
Host-Associated Absence of Human Puumala Virus Infections in Northern and Eastern Germany
Figure 1
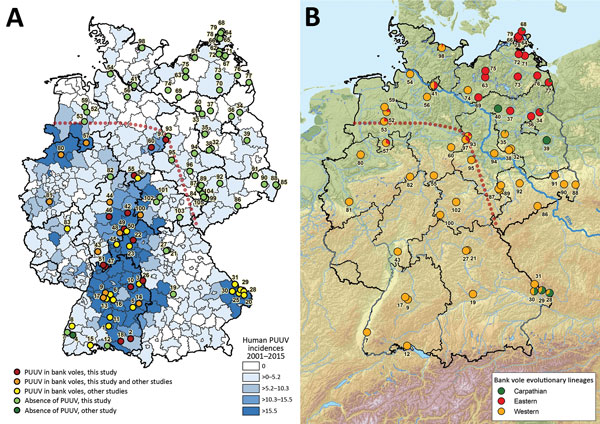
Figure 1. Geographic distribution of Puumala virus (PUUV)–positive and PUUV-negative bank voles in Germany (A) and assignment of bank voles to the evolutionary lineages Western, Eastern, and Carpathian (B). The coloration of the map in panel A was generated on the basis of the human PUUV incidence per district (2). PUUV detection in previous studies was extracted from (3–7). The identification of the bank vole evolutionary lineages shown in panel B was determined by using partial cytochrome b gene sequences (see Figure 2). The red dotted line illustrates the hypothetical current edge of the range of PUUV-positive bank voles.
References
- Heyman P, Ceianu CS, Christova I, Tordo N, Beersma M, João Alves M, et al. A five-year perspective on the situation of haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome and status of the hantavirus reservoirs in Europe, 2005-2010. Euro Surveill. 2011;16:977–86.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ettinger J, Hofmann J, Enders M, Tewald F, Oehme RM, Rosenfeld UM, et al. Multiple synchronous outbreaks of Puumala virus, Germany, 2010. Emerg Infect Dis. 2012;18:1461–4.DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Weber de Melo V, Sheikh Ali H, Freise J, Kühnert D, Essbauer S, Mertens M, et al. Spatiotemporal dynamics of Puumala hantavirus associated with its rodent host, Myodes glareolus. Evol Appl. 2015;8:545–59.DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Essbauer SS, Schmidt-Chanasit J, Madeja EL, Wegener W, Friedrich R, Petraityte R, et al. Nephropathia epidemica in metropolitan area, Germany. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13:1271–3.DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mertens M, Kindler E, Emmerich P, Esser J, Wagner-Wiening C, Wölfel R, et al. Phylogenetic analysis of Puumala virus subtype Bavaria, characterization and diagnostic use of its recombinant nucleocapsid protein. Virus Genes. 2011;43:177–91.DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Faber M, Wollny T, Schlegel M, Wanka KM, Thiel J, Frank C, et al. Puumala virus outbreak in Western Thuringia, Germany, 2010: epidemiology and strain identification. Zoonoses Public Health. 2013;60:549–54.DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Castel G, Couteaudier M, Sauvage F, Pons JB, Murri S, Plyusnina A, et al. Complete genome and phylogeny of Puumala hantavirus isolates circulating in France. Viruses. 2015;7:5476–88.DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Schilling S, Emmerich P, Klempa B, Auste B, Schnaith E, Schmitz H, et al. Hantavirus disease outbreak in Germany: limitations of routine serological diagnostics and clustering of virus sequences of human and rodent origin. J Clin Microbiol. 2007;45:3008–14.DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mertens M, Essbauer SS, Rang A, Schröder J, Splettstoesser WD, Kretzschmar C, et al. Non-human primates in outdoor enclosures: risk for infection with rodent-borne hantaviruses. Vet Microbiol. 2011;147:420–5.DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Morger J, Råberg L, Hille SM, Helsen S, Štefka J, Al-Sabi MM, et al. Distinct haplotype structure at the innate immune receptor toll-like receptor 2 across bank vole populations and lineages in Europe. Biol J Linn Soc Lond. 2015;116:124–33. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Ali HS, Drewes S, Sadowska ET, Mikowska M, Groschup MH, Heckel G, et al. First molecular evidence for Puumala hantavirus in Poland. Viruses. 2014;6:340–53.DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wójcik JM, Kawałko A, Marková S, Searle JB, Kotlík P. Phylogeographic signatures of northward post-glacial colonization from high-latitude refugia: a case study of bank voles using museum specimens. J Zool (Lond). 2010;281:249–62.
- Filipi K, Marková S, Searle JB, Kotlík P. Mitogenomic phylogenetics of the bank vole Clethrionomys glareolus, a model system for studying end-glacial colonization of Europe. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2015;82(Pt A):245–57.DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kotlík P, Deffontaine V, Mascheretti S, Zima J, Michaux JR, Searle JB. A northern glacial refugium for bank voles (Clethrionomys glareolus). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:14860–4.DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
1Current affiliation: Seramun Diagnostica GmbH, Heidesee, Germany.
2Current affiliation: Stiftung Tierärztliche Hochschule Hannover, Hannover, Germany.