Volume 23, Number 4—April 2017
Research
Three Divergent Subpopulations of the Malaria Parasite Plasmodium knowlesi
Figure 4
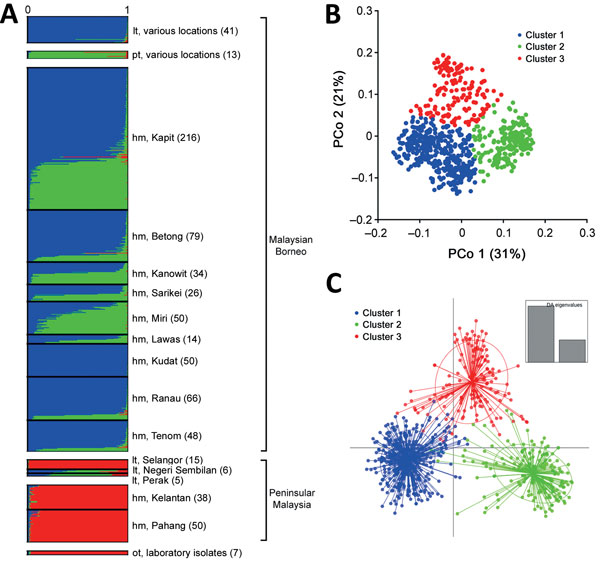
Figure 4. Population genetic structure of combined 751 P. knowlesi infections across Malaysia and 7 laboratory isolates. A) The inference of genetic clusters on complete 10-locus genotype dataset using the STRUCTURE analysis with LOCPRIOR model (22) showed 3 major subpopulation structures (K = 3, ΔK = 98.73), corresponding to those shown in Figure 3. Numbers in parentheses indicate number of isolates. B, C) Using a priori K = 3, individual genotypes were assigned to the most probable subpopulation clusters using independent genetic distance matrix inferred by the principal coordinate analysis (B) and discriminant analysis of principal component (DAPC) (C). In DAPC, clusters depicted as ellipses indicated the variance within the clusters and centered by K-means. hm, human; lt, long-tailed macaque; PCo, principal coordinate; pt, pig-tailed macaque.
References
- Singh B, Daneshvar C. Human infections and detection of Plasmodium knowlesi. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2013;26:165–84. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Setiadi W, Sudoyo H, Trimarsanto H, Sihite BA, Saragih RJ, Juliawaty R, et al. A zoonotic human infection with simian malaria, Plasmodium knowlesi, in Central Kalimantan, Indonesia. Malar J. 2016;15:218. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Yusof R, Lau YL, Mahmud R, Fong MY, Jelip J, Ngian HU, et al. High proportion of knowlesi malaria in recent malaria cases in Malaysia. Malar J. 2014;13:168. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- William T, Rahman HA, Jelip J, Ibrahim MY, Menon J, Grigg MJ, et al. Increasing incidence of Plasmodium knowlesi malaria following control of P. falciparum and P. vivax Malaria in Sabah, Malaysia. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013;7:e2026. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fornace KM, Nuin NA, Betson M, Grigg MJ, William T, Anstey NM, et al. Asymptomatic and submicroscopic carriage of Plasmodium knowlesi malaria in household and community members of clinical cases in Sabah, Malaysia. J Infect Dis. 2016;213:784–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Vythilingam I, Wong ML, Wan-Yussof WS. Current status of Plasmodium knowlesi vectors: a public health concern? Parasitology. 2016;1–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lee KS, Divis PC, Zakaria SK, Matusop A, Julin RA, Conway DJ, et al. Plasmodium knowlesi: reservoir hosts and tracking the emergence in humans and macaques. PLoS Pathog. 2011;7:e1002015. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Vythilingam I, Noorazian YM, Huat TC, Jiram AI, Yusri YM, Azahari AH, et al. Plasmodium knowlesi in humans, macaques and mosquitoes in peninsular Malaysia. Parasit Vectors. 2008;1:26. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Divis PC, Singh B, Anderios F, Hisam S, Matusop A, Kocken CH, et al. Admixture in humans of two divergent Plasmodium knowlesi populations associated with different macaque host species. PLoS Pathog. 2015;11:e1004888. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ahmed MA, Fong MY, Lau YL, Yusof R. Clustering and genetic differentiation of the normocyte binding protein (nbpxa) of Plasmodium knowlesi clinical isolates from Peninsular Malaysia and Malaysia Borneo. Malar J. 2016;15:241. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ahmed AM, Pinheiro MM, Divis PC, Siner A, Zainudin R, Wong IT, et al. Disease progression in Plasmodium knowlesi malaria is linked to variation in invasion gene family members. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014;8:e3086. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pinheiro MM, Ahmed MA, Millar SB, Sanderson T, Otto TD, Lu WC, et al. Plasmodium knowlesi genome sequences from clinical isolates reveal extensive genomic dimorphism. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0121303. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fong MY, Lau YL, Chang PY, Anthony CN. Genetic diversity, haplotypes and allele groups of Duffy binding protein (PkDBPαII) of Plasmodium knowlesi clinical isolates from Peninsular Malaysia. Parasit Vectors. 2014;7:161. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fong MY, Rashdi SA, Yusof R, Lau YL. Distinct genetic difference between the Duffy binding protein (PkDBPαII) of Plasmodium knowlesi clinical isolates from North Borneo and Peninsular Malaysia. Malar J. 2015;14:91. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Yusof R, Ahmed MA, Jelip J, Ngian HU, Mustakim S, Hussin HM, et al. Phylogeographic evidence for 2 genetically distinct zoonotic Plasmodium knowlesi parasites, Malaysia. Emerg Infect Dis. 2016;22:1371–80. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Assefa S, Lim C, Preston MD, Duffy CW, Nair MB, Adroub SA, et al. Population genomic structure and adaptation in the zoonotic malaria parasite Plasmodium knowlesi. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112:13027–32. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kocken CH, Ozwara H, van der Wel A, Beetsma AL, Mwenda JM, Thomas AW. Plasmodium knowlesi provides a rapid in vitro and in vivo transfection system that enables double-crossover gene knockout studies. Infect Immun. 2002;70:655–60. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, et al.; 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:2078–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Danecek P, Auton A, Abecasis G, Albers CA, Banks E, DePristo MA, et al.; 1000 Genomes Project Analysis Group. The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics. 2011;27:2156–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rutherford K, Parkhill J, Crook J, Horsnell T, Rice P, Rajandream MA, et al. Artemis: sequence visualization and annotation. Bioinformatics. 2000;16:944–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics. 2000;155:945–59.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hubisz MJ, Falush D, Stephens M, Pritchard JK. Inferring weak population structure with the assistance of sample group information. Mol Ecol Resour. 2009;9:1322–32. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Earl DA, vonHoldt BM. STRUCTURE HARVESTER: a website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv Genet Resour. 2012;4:359–61. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study. Mol Ecol. 2005;14:2611–20. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jakobsson M, Rosenberg NA. CLUMPP: a cluster matching and permutation program for dealing with label switching and multimodality in analysis of population structure. Bioinformatics. 2007;23:1801–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Peakall R, Smouse PE. GENALEX 6: genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Mol Ecol Resour. 2006;6:288–95. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Jombart T, Devillard S, Balloux F. Discriminant analysis of principal components: a new method for the analysis of genetically structured populations. BMC Genet. 2010;11:94. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Goudet J. FSTAT (Version 1.2): A computer program to calculate F-statistics. J Hered. 1995;86:485–6. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Haubold B, Hudson RR. LIAN 3.0: detecting linkage disequilibrium in multilocus data. Linkage Analysis. Bioinformatics. 2000;16:847–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Putaporntip C, Kuamsab N, Jongwutiwes S. Sequence diversity and positive selection at the Duffy-binding protein genes of Plasmodium knowlesi and P. cynomolgi: Analysis of the complete coding sequences of Thai isolates. Infect Genet Evol. 2016;44:367–75. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Liedigk R, Kolleck J, Böker KO, Meijaard E, Md-Zain BM, Abdul-Latiff MA, et al. Mitogenomic phylogeny of the common long-tailed macaque (Macaca fascicularis fascicularis). BMC Genomics. 2015;16:222. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Voris HK. Maps of Pleistocene sea levels in Southeast Asia: shorelines, river systems and time durations. J Biogeogr. 2000;27:1153––67. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Esselstyn JA, Widmann P, Heaney LR. The mammals of Palawan Island, Philippines. Proc Biol Soc Wash. 2004;117:271–302.
- Meijaard E. Mammals of south-east Asian islands and their Late Pleistocene environments. J Biogeogr. 2003;30:1245–57. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Smith DG, Ng J, George D, Trask JS, Houghton P, Singh B, et al. A genetic comparison of two alleged subspecies of Philippine cynomolgus macaques. Am J Phys Anthropol. 2014;155:136–48. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Muehlenbein MP, Pacheco MA, Taylor JE, Prall SP, Ambu L, Nathan S, et al. Accelerated diversification of nonhuman primate malarias in Southeast Asia: adaptive radiation or geographic speciation? Mol Biol Evol. 2015;32:422–39. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ziegler T, Abegg C, Meijaard E, Perwitasari-Farajallah D, Walter L, Hodges JK, et al. Molecular phylogeny and evolutionary history of Southeast Asian macaques forming the M. silenus group. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2007;42:807–16. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Moyes CL, Shearer FM, Huang Z, Wiebe A, Gibson HS, Nijman V, et al. Predicting the geographical distributions of the macaque hosts and mosquito vectors of Plasmodium knowlesi malaria in forested and non-forested areas. Parasit Vectors. 2016;9:242. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar