Volume 24, Number 11—November 2018
Research
Effects of Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine on Genotypic Penicillin Resistance and Serotype Changes, Japan, 2010–2017
Figure 3
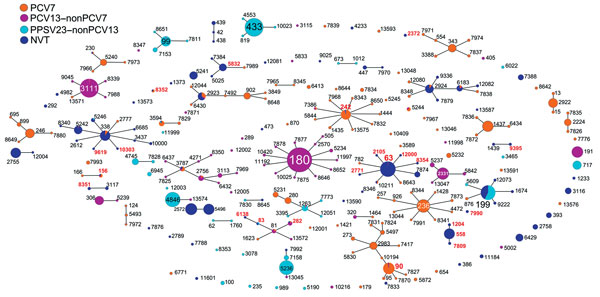
Figure 3. An eBURST (http://eburst.mlst.net/) diagram displaying pneumococcal sequence types (STs) causing invasive pneumococcal disease across patients of all age groups in Japan. All 2,849 strains are distinguished by colors to indicate PCV7, PCV13–nonPCV7, PPSV23–nonPCV13, and NVT. Size of each circle reflects the number of strains. ST numbers shown in red represent genotypes for penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae confirmed among PPSV23–nonPCV13 and NVT as follows: 15B (n = 2), ST242 and ST83; 6C (n = 2), ST8352 and ST5832; 6D (n = 2), ST90 and ST282; 13 (n = 1), ST10303; 15A (n = 77), ST63 (n = 73), ST2105, ST2771, ST8354, and ST12000; 15C (n = 2), ST83 and ST6138; 16F (n = 4), ST8351; 23A (n = 1), ST9619; 23B (n = 1), ST2372; 34 (n = 1), ST9395; 35B (n = 55), ST558 (n = 49), ST1204, ST7809, ST7990, and ST156. NVT, nonvaccine serotype; PCV7, 7-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine; PCV13, 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine; PPSV23, 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine.