Volume 24, Number 2—February 2018
Research
New Parvovirus Associated with Serum Hepatitis in Horses after Inoculation of Common Biological Product
Figure 2
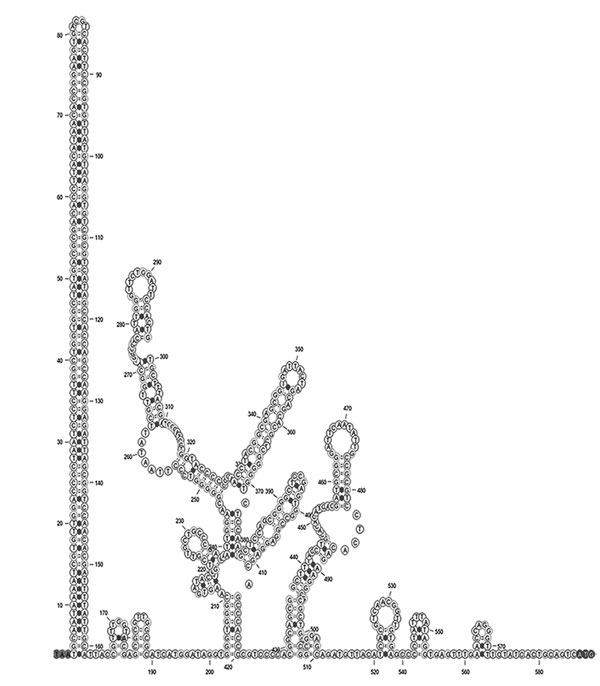
Figure 2. EqPV-H DNA secondary structure of the 583-nt intergenic region predicted using mFOLD (25). EqPV-H, equine parvovirus hepatitis.
References
- Theiler A. Acute liver atrophy and parenchymatous hepatitis in horses. Reports of the Director of Veterinary Research. 1918;5&6:7–99.
- Marsh H. Losses of undetermined cause following an outbreak of equine encephalomyelitis. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1937;91:88–93.
- Rose JA, Immenschuh RD, Rose EM. Serum hepatitis in the horse. Proceedings of the Twentieth Annual Conference of the American Association of Equine Practitioners. Lexington (KY): American Association of Equine Practitioners; 1974. p. 175–85.
- Step DL, Blue JT, Dill SG. Penicillin-induced hemolytic anemia and acute hepatic failure following treatment of tetanus in a horse. Cornell Vet. 1991;81:13–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Messer NT IV, Johnson PJ. Idiopathic acute hepatic disease in horses: 12 cases (1982-1992). J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1994;204:1934–7.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Guglick MA, MacAllister CG, Ely RW, Edwards WC. Hepatic disease associated with administration of tetanus antitoxin in eight horses. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1995;206:1737–40.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chandriani S, Skewes-Cox P, Zhong W, Ganem DE, Divers TJ, Van Blaricum AJ, et al. Identification of a previously undescribed divergent virus from the Flaviviridae family in an outbreak of equine serum hepatitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110:E1407–15. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Aleman M, Nieto JE, Carr EA, Carlson GP. Serum hepatitis associated with commercial plasma transfusion in horses. J Vet Intern Med. 2005;19:120–2. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Burbelo PD, Dubovi EJ, Simmonds P, Medina JL, Henriquez JA, Mishra N, et al. Serology-enabled discovery of genetically diverse hepaciviruses in a new host. J Virol. 2012;86:6171–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kapoor A, Simmonds P, Cullen JM, Scheel TK, Medina JL, Giannitti F, et al. Identification of a pegivirus (GB virus-like virus) that infects horses. J Virol. 2013;87:7185–90. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Scheel TK, Simmonds P, Kapoor A. Surveying the global virome: identification and characterization of HCV-related animal hepaciviruses. Antiviral Res. 2015;115:83–93. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pfaender S, Cavalleri JM, Walter S, Doerrbecker J, Campana B, Brown RJ, et al. Clinical course of infection and viral tissue tropism of hepatitis C virus-like nonprimate hepaciviruses in horses. Hepatology. 2015;61:447–59. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Scheel TK, Kapoor A, Nishiuchi E, Brock KV, Yu Y, Andrus L, et al. Characterization of nonprimate hepacivirus and construction of a functional molecular clone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112:2192–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ramsay JD, Evanoff R, Wilkinson TE Jr, Divers TJ, Knowles DP, Mealey RH. Experimental transmission of equine hepacivirus in horses as a model for hepatitis C virus. Hepatology. 2015;61:1533–46. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lyons S, Kapoor A, Schneider BS, Wolfe ND, Culshaw G, Corcoran B, et al. Viraemic frequencies and seroprevalence of non-primate hepacivirus and equine pegiviruses in horses and other mammalian species. J Gen Virol. 2014;95:1701–11. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kapoor A, Kumar A, Simmonds P, Bhuva N, Singh Chauhan L, Lee B, et al. Virome analysis of transfusion recipients reveals a novel human virus that shares genomic features with hepaciviruses and pegiviruses. MBio. 2015;6:e01466–15. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kapoor A, Hornig M, Asokan A, Williams B, Henriquez JA, Lipkin WI. Bocavirus episome in infected human tissue contains non-identical termini. PLoS One. 2011;6:e21362. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kapoor A, Mehta N, Dubovi EJ, Simmonds P, Govindasamy L, Medina JL, et al. Characterization of novel canine bocaviruses and their association with respiratory disease. J Gen Virol. 2012;93:341–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kapoor A, Mehta N, Esper F, Poljsak-Prijatelj M, Quan PL, Qaisar N, et al. Identification and characterization of a new bocavirus species in gorillas. PLoS One. 2010;5:e11948. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kapoor A, Lipkin WI. Virus discovery in the 21st century. Chichester (UK): John Wiley & Sons; 2014. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30:2725–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zuker M. Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31:3406–15. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Burbelo PD, Ragheb JA, Kapoor A, Zhang Y. The serological evidence in humans supports a negligible risk of zoonotic infection from porcine circovirus type 2. Biologicals. 2013;41:430–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Burbelo PD, Ching KH, Morse CG, Alevizos I, Bayat A, Cohen JI, et al. Altered antibody profiles against common infectious agents in chronic disease. PLoS One. 2013;8:e81635. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Burbelo PD, Ching KH, Esper F, Iadarola MJ, Delwart E, Lipkin WI, et al. Serological studies confirm the novel astrovirus HMOAstV-C as a highly prevalent human infectious agent. PLoS One. 2011;6:e22576. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hartlage AS, Cullen JM, Kapoor A. The strange, expanding world of animal hepaciviruses. Annu Rev Virol. 2016;3:53–75. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kapoor A, Simmonds P, Dubovi EJ, Qaisar N, Henriquez JA, Medina J, et al. Characterization of a canine homolog of human Aichivirus. J Virol. 2011;85:11520–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Li L, Giannitti F, Low J, Keyes C, Ullmann LS, Deng X, et al. Exploring the virome of diseased horses. J Gen Virol. 2015;96:2721–33. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kailasan S, Agbandje-McKenna M, Parrish CR. Parvovirus family conundrum: what makes a killer? Annu Rev Virol. 2015;2:425–50. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bihari C, Rastogi A, Saxena P, Rangegowda D, Chowdhury A, Gupta N, et al. Parvovirus B19 associated hepatitis. Hepat Res Treat. 2013;2013:472027.
- Hatakka A, Klein J, He R, Piper J, Tam E, Walkty A. Acute hepatitis as a manifestation of parvovirus B19 infection. J Clin Microbiol. 2011;49:3422–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Caruso C, Gobbi E, Biosa T, Andra’ M, Cavallazzi U, Masoero L. Evaluation of viral inactivation of pseudorabies virus, encephalomyocarditis virus, bovine viral diarrhea virus and porcine parvovirus in pancreatin of porcine origin. J Virol Methods. 2014;208:79–84. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Roberts PL, Hart H. Comparison of the inactivation of canine and bovine parvovirus by freeze-drying and dry-heat treatment in two high purity factor VIII concentrates. Biologicals. 2000;28:185–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mani B, Gerber M, Lieby P, Boschetti N, Kempf C, Ros C. Molecular mechanism underlying B19 virus inactivation and comparison to other parvoviruses. Transfusion. 2007;47:1765–74. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Blümel J, Stühler A, Dichtelmüller H. Kinetics of inactivating human parvovirus B19 and porcine parvovirus by dry-heat treatment. Transfusion. 2008;48:790–1. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Qualls CW, Gribble DH. Equine serum hepatitis: a morphologic study. Lab Invest. 1976;34:330.
- Robinson M, Gopinath C, Hughes DL. Histopathology of acute hepatitis in the horse. J Comp Pathol. 1975;85:111–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
1Deceased.
Page created: January 17, 2018
Page updated: January 17, 2018
Page reviewed: January 17, 2018
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.