Volume 24, Number 3—March 2018
CME ACTIVITY - Synopsis
Epidemiology of Recurrent Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease, China, 2008–2015
Figure 1
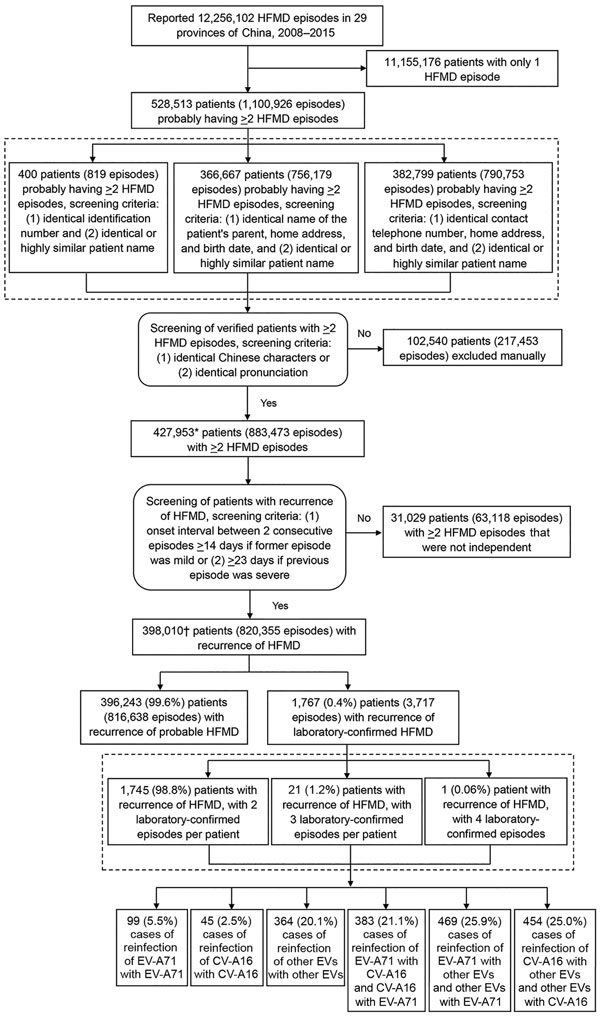
Figure 1. Flowchart showing screening for and analysis of patients with recurrent HFMD from the national HFMD surveillance database, 29 provinces of China, 2008–2015. Percentages do not equal 100% because of rounding. *The number of patients (427,953) with >2 HFMD episodes is higher than expected (528,513 – 102,540 = 425,973) because of improved patient matching. In some situations, the number of patients with >2 episodes did not change; for example, a patient initially identified with 3 episodes might have been determined to have only 2 episodes, with the third episode being attributed to a different patient. In other situations, the number of patients with >2 episodes decreased; for example, a patient initially identified as having 3 episodes might have been determined to be 3 different patients with 3 different episodes. Therefore, the reduced number of patients (528,513 – 427,953 = 100,560) with >2 HFMD episodes is smaller than the number of patients (102,540) excluded manually. †The number of patients (398,010) with recurrence of HFMD is higher than expected (427,953 – 31,029 = 396,924) because some patients needed to be excluded and included. In some situations, patients were completely included or excluded from the recurrent HFMD patient population sample; for example, all 3 episodes of a patient could have been determined to not be independent from each other. In other situations, patients were included and excluded from the recurrent HFMD patient population sample; for example, a patient with 3 episodes might have had 2 episodes that were not independent from each other. In these cases, the patient had 2 episodes included and 1 episode excluded; therefore, the number of included patients plus excluded patients (398,010 + 31,029 = 429,039) exceeded the starting population number (427,953). CV-A16, coxsackievirus A16; EV-A71, enterovirus A71; HFMD, hand, foot and mouth disease; other EVs, other non–EV-A71 and non–CV-A16 enteroviruses.
1These first authors contributed equally to this article.
2These senior authors contributed equally to this article.