Volume 24, Number 6—June 2018
Research
Genomic Epidemiology of Global Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacter spp., 2008–2014
Figure 1
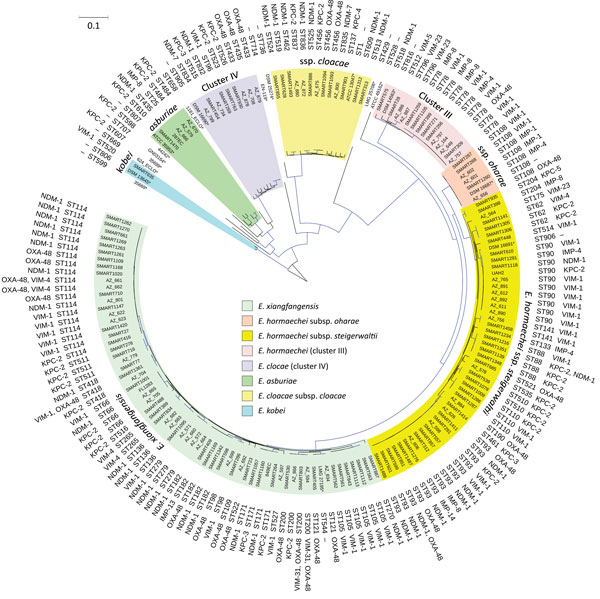
Figure 1. Phylogenetic tree of the different species and sequence types among 160 Enterobacter cloacae complex isolates identified from Enterobacter spp. isolates collected in the Merck Study for Monitoring Antimicrobial Resistance Trends, 2008–2014, and the AstraZeneca global surveillance program, 2012–2014. The tree is rooted with E. cloacae complex Hoffmann cluster IX (Chavda group R) strain 35,699. A total of 369,123 core single-nucleotide polymorphisms were found; 4,010 were used to draw the tree (after phages and recombination sites were excluded). KPC, Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase; NDM, New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase; OXA, oxacillin; ST, sequence type; –, information missing; *, isolate identified in another study. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
1These co-authors contributed equally to this article.
2Current affiliation: Jackson Laboratory for Genomic Medicine, Farmington, Connecticut, USA.