Volume 25, Number 11—November 2019
Dispatch
Non-Leishmania Parasite in Fatal Visceral Leishmaniasis–Like Disease, Brazil
Figure 1
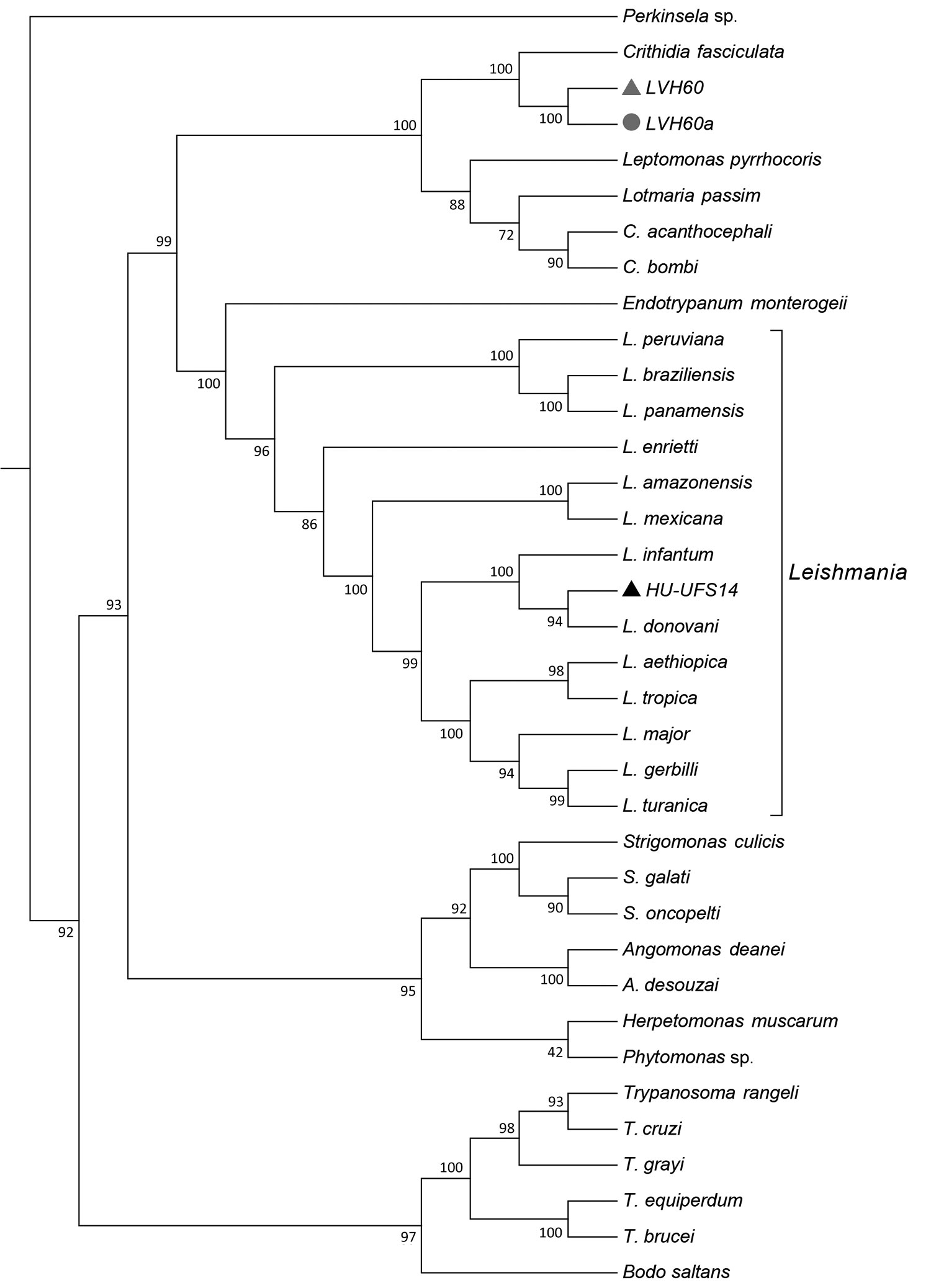
Figure 1. Phylogenomic analysis of genomewide orthologous coding sequences from LVH60 and LVH60a clinical isolates from a 64-year-old man with fatal visceral leishmaniasis–like illness, Brazil, and 33 Trypanosomatida species. Dendrogram shows the genetic relationships among all species investigated in the current study. Hierarchical clustering was performed with a set of ≈6,400 orthologous genes across 33 trypanosomatids, designated as the total orthologous median matrix. HU-UFS14 (black triangle; L. infantum laboratory reference strain) is placed in the same branch with L. infantum and L. donovani, whereas the LVH60 and LVH60a clinical isolates are placed in sister positions with Crithidia fasciculata. LVH60 was isolated from bone marrow (gray triangle), LVH60a from a skin lesion (gray circle) biopsy, both from the same patient. Numbers next to the branches represent the percentages of approximate unbiased support probabilities for 10,000 bootstraps, calculated using the pvclust R package (https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/pvclust). Branch relationships were defined by their median amino acid evolutionary distance (Appendix).
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
2Current affiliation: Universidade de São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil.
3These senior authors contributed equally to this article.