Volume 25, Number 11—November 2019
Dispatch
Non-Leishmania Parasite in Fatal Visceral Leishmaniasis–Like Disease, Brazil
Figure 2
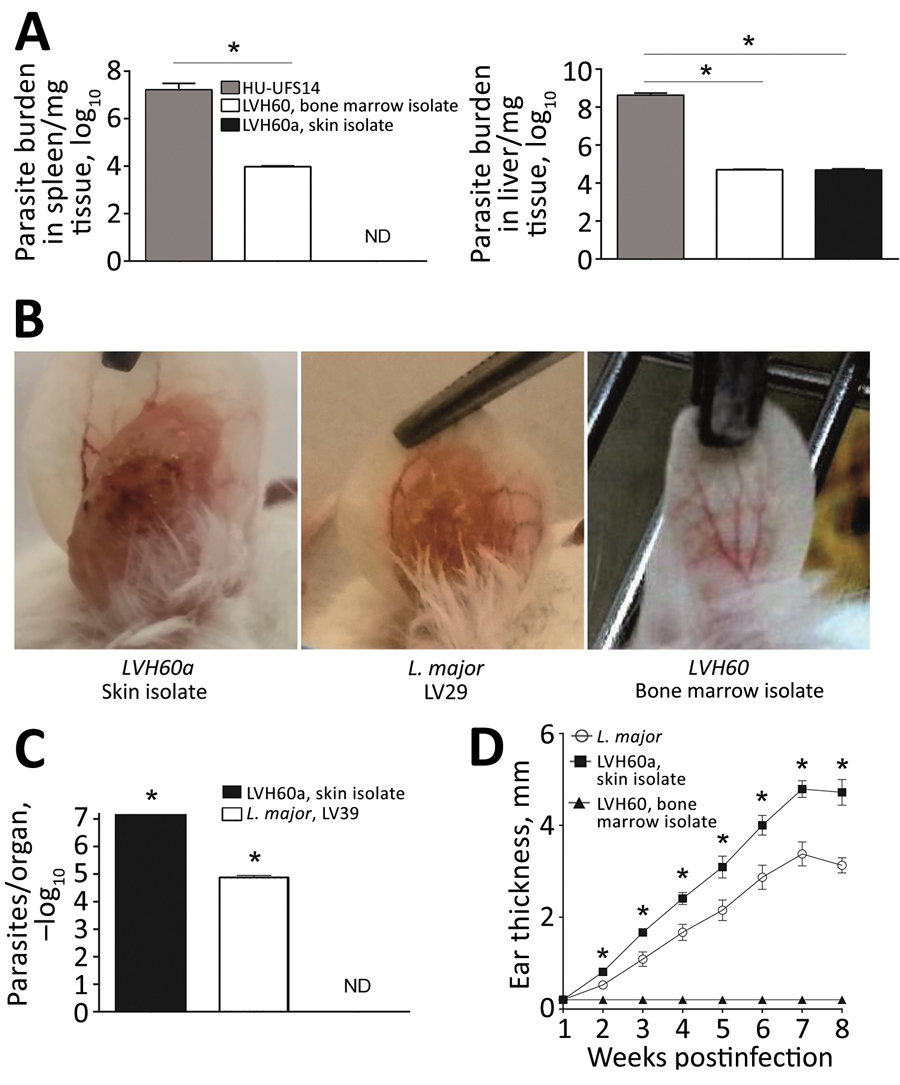
Figure 2. Experimental infection of BALB/c mice with LVH60 and LVH60a clinical isolates obtained from a 64-year-old man with fatal visceral leishmaniasis–like illness, Brazil. LVH60 was isolated from bone marrow, LVH60a from a skin lesion biopsy. Female BALB/c mice were infected intravenously with 107 stationary-phase promastigotes. After 4 weeks of infection, spleen and liver samples were collected. Parasite loads were determined by a limiting dilution assay of spleen and liver homogenates and are expressed as the mean ± SD. A) LVH60 strain infection in mice resulted in parasite detection in the spleen and liver; the LVH60a strain was not detected in the spleen. B) For cutaneous infection, BALB/c mice were injected subcutaneously in the right ear dermis with 106 stationary phase promastigotes. Infected ears were collected and imaged. C) Parasite burden in ears was assessed by a limiting dilution assay. D) Ear thickness was measured weekly with a digital caliper. The HU-UFS14 strain (L. infantum) was used as a positive control for experimental visceral leishmaniasis (A), whereas the LV29 strain (L. major) was used as a positive control for experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis. The results represent 3 independent experiments. Error bars indicate SD. ND, not detected. *p<0.05.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
2Current affiliation: Universidade de São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil.
3These senior authors contributed equally to this article.