Clinical and Molecular Epidemiology of Invasive Group B Streptococcus Disease among Infants, China
Wenjing Ji , Haiying Liu

, Shabir A. Madhi, Marianne Cunnington, Zilu Zhang, Ziyaad Dangor, Haijian Zhou, Xiaoping Mu, Zhengjiang Jin, Aimin Wang, Xiaosong Qin, Chunyan Gao, Yuning Zhu, Xiaodan Feng, Shangyang She, Shuhua Yang, Jing Liu, Jine Lei, Lan Jiang, Zeshi Liu, Gang Li, Qiuhong Li, Qiulian Deng, Kankan Gao, and Yu Fang

Author affiliations: Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an, China (W. Ji, Y. Fang); Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, China (H. Liu, Q. Deng, K. Gao); University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa (S.A. Madhi, Z. Dangor); GlaxoSmithKline Plc, London, UK (M. Cunnington); Harvard Medical School and Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute, Boston, Massachusetts, USA (Z. Zhang); Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Beijing, China (H. Zhou); Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou (X. Mu); Hubei Maternal and Child Health Hospital, Wuhan, China (Z. Jin); Children’s Hospital of Fudan University, Shanghai, China (A. Wang); China Medical University, Shenyang, China (X. Qin); Tangshan Maternal and Child Health Care Hospital, Tangshan, China (C. Gao); Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China (Y. Zhu); Nanjing Maternity and Child Health Care Hospital, Nanjing, China (X. Feng); Maternal and Child Health Hospital of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, Nanjing (S. She); Tianjin Central Hospital of Gynecology Obstetrics, Tianjin, China (S. Yang); Tsinghua University Hospital, Beijing (J. Liu); The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an (J. Lei); Maternal and Child Health Care Hospital of Uygur Autonomous Region, Urumqi, China (L. Jiang); The Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an (Z. Liu); General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan, China (G. Li); Chongqing Health Center for Women and Children, Chongqing, China (Q. Li)
Main Article
Figure 6
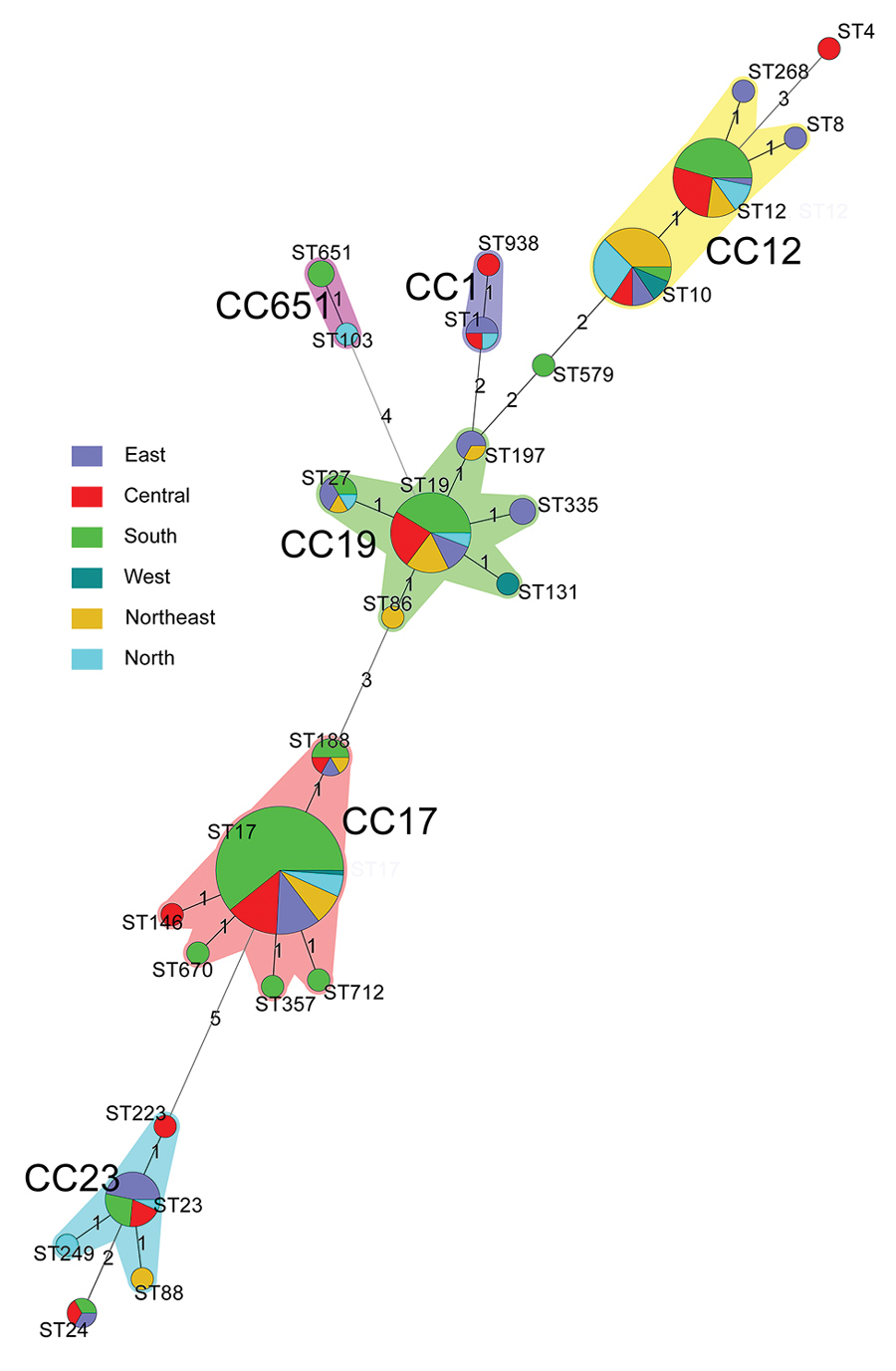
Figure 6. Minimum spanning tree analysis of invasive group B Streptococcus isolates showing the relationship between ST and CCs by region in China. Circles represent STs; size of each circle indicates the number of isolates within the specific type. The ST with the greatest number of single-locus variants is the founder ST. Regions appear as different colors; shading denotes STs belonging to the same CC. CC, clonal complex; ST, sequence type.
Main Article
Page created: October 15, 2019
Page updated: October 15, 2019
Page reviewed: October 15, 2019
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
