Volume 25, Number 4—April 2019
Research
Sand Fly–Associated Phlebovirus with Evidence of Neutralizing Antibodies in Humans, Kenya
Figure 5
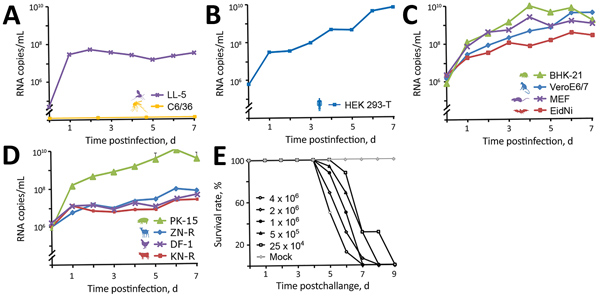
Figure 5. In vitro growth kinetics of novel sand fly–associated phlebovirus Ntepes virus from Kenya in different cell lines. A) Insects: LL-5, sand fly; C6/36, mosquito. B) Human: HEK293-T. C) Peridomestic wildlife: hamster, BHK-21; primate, VeroE6/7; mouse, MEF; bat, EidNi. D) Livestock: swine, PK-15; goat, ZN-R; chicken, DF-1; cattle, KN-R. Cells were infected with a multiplicity of infection of 0.1; supernatants were collected every 24 h for 7 d postinfection. Viral genome copies were measured at indicated timepoints by real-time reverse transcription PCR. E) Pathogenicity of Ntepes virus infection in mice. Litters of 2-day-old Swiss Albino suckling mice (8 mice/litter) were intracerebrally inoculated using the indicated virus titers or cell culture media as a control. Animals were monitored daily for signs of disease. Titers are shown in PFU/mL.
1Current affiliation: Biotest AG, Dreieich, Germany.
2These authors contributed equally to this article.