Volume 26, Number 9—September 2020
Research Letter
Acute Cerebral Stroke with Multiple Infarctions and COVID-19, France, 2020
Cite This Article
Citation for Media
Abstract
We describe 2 cases in coronavirus disease patients in France involving presumed thrombotic stroke that occurred during ongoing anticoagulation treatment for atrial fibrillation stroke prophylaxis; 1 patient had positive antiphospholipid antibodies. These cases highlight the severe and unique consequences of coronavirus disease–associated stroke.
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Evidence increasingly shows that SARS-CoV-2 is not always confined to the respiratory tract but can induce neurologic diseases (1). Several studies have reported that acute ischemic stroke can develop in COVID-19 patients (1–6). We describe 2 COVID-19 patients who had multiple cerebral infarctions; 1 patient had positive antiphospholipid antibodies.
On March 25, 2020, an 84-year-old man with a history of diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, coronary heart disease, peripheral arterial disease, and atrial fibrillation (treated with apixaban [2.5 mg orally 2×/d]) sought care for respiratory symptoms, including dyspnea and cough. At admission, physical examination revealed a blood pressure of 120/70 mm Hg, irregular heartbeat (100 beats/min), fever (39°C), and bilateral crackling sounds on pulmonary auscultation. Laboratory findings revealed low leukocyte count and lymphopenia (Appendix). Chest radiograph showed a bilateral interstitial infiltrate. Real-time reverse transcription PCR on a nasopharyngeal swab specimen confirmed COVID-19.
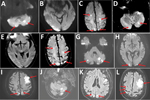
Supportive treatment began (oxygen support, antimicrobial drugs [ceftriaxone 1 g by intravenous (IV) infusion/d], and hydroxychloroquine [200 mg orally 2×/d]), and the same dosage of apixaban was continued. On April 3 (day 9 of hospitalization), dysarthria, left hemiplegia, and alteration of consciousness developed. Brain magnetic resonance imaging revealed acute ischemic stroke in multiple vascular areas (Figure). We switched the anticoagulation medication from apixaban to IV unfractionated heparin [18 UI/kg/h]). On April 6 (day 12), the patients Glasgow coma scale score was 3/15 (eye opening = 1, motor response = 1, verbal response = 1), and severe acute respiratory distress developed. No neurologic recovery occurred, and the patient did not undergo subsequent brain imaging. Mechanical ventilation was not possible (high Charlson comorbidity index), and the patient died on April 12 (day 18).
On April 3, a 74-year-old man with a history of multiple cardiovascular diseases, such as atrial fibrillation treated with rivaroxaban (20 mg orally 1×/d), sought care for influenza-like illness and confusion. His work colleagues had noticed disorientation during his activity as a truck driver. At admission, physical examination revealed hypertension (230/70 mm Hg) and irregular heartbeat (86 beats/min). He was febrile (38.3°C) and had crackling sounds on pulmonary auscultation. Neurologic examination showed nonfluent aphasia. COVID-19 was diagnosed from results of real-time reverse transcription PCR, microbiologic testing, and computed tomographic thoracic imaging (Appendix). Brain computed tomographic scan revealed many recent ischemic infarctions in different vascular areas, and magnetic resonance imaging of the brain confirmed this finding (Figure). As with patient 1, this patient had no non–central nervous system thrombotic events (e.g., pulmonary embolisms, abdominal visceral infarction). Treatment began with IV unfractionated heparin (18 UI/kg/h), hydroxychloroquine (200 mg orally 2×/d), and antimicrobial drugs (ceftriaxone 1g by IV infusion/d). The patient’s aphasia regressed, and he was discharged on April 20.
Several factors can cause acute ischemic stroke, but the primary ones are arterial and cardiac embolism, arterial wall disease, and variants of those conditions. Both of these patients had concurrent cardiovascular conditions, particularly atrial fibrillation, although both were adequately treated with anticoagulants. Hematologic derangements, including lymphopenia and leukopenia, are associated with ischemic stroke and are predictors of worse prognosis with stroke (7). A systematic review and meta-analysis identified lymphopenia as one of the most prevalent laboratory results described in COVID-19 (35%–72%) (8), and we observed it in these 2 patients. Many infectious agents have been implicated as potential causes of cerebral stroke, such as herpes simplex virus, varicella zoster virus, Treponema pallidum, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and Aspergillus spp.; acute bacterial meningitis has also been implicated (9). Multiple brain localizations have previously been described with other viruses that lead to cerebrovascular complications through various mechanisms, including multifocal vasculopathy, focal infiltrative vasculitis and vasospasm, and direct vessel wall invasion and thrombus formation (10).
In this rapidly emerging epidemic, several cases have reported strokes in SARS-CoV-2–infected patients (1–6). However, the unique feature in the patients we report is multiple simultaneous strokes. These cases involved presumed thrombotic stroke that occurred during ongoing anticoagulation for atrial fibrillation stroke prophylaxis. Given the increasing realization that COVID-19 might be associated with hypercoagulability, the concurrent presence of anticoagulation with direct oral anticoagulants should not be reassuring as preventive.
Other authors suggest that the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies, such as anticardiolipin antibodies, as well as anti–β2-glycoprotein I antibodies might rarely lead to multiple thrombotic cerebral events (5). In the patients we report, subsequent serologic testing showed anticardiolipin antibodies (IgM) in patient 1. We did not conduct functional testing (such as dilute Russell viper venom time). However, antiphospholipid antibody syndrome in cases of stroke cannot be diagnosed until positive antibodies persist after multiple months.
The association between cerebral stroke and COVID-19 requires more attention. Coagulability dysfunction and possibly antiphospholipid antibody syndrome may contribute to thromboembolic events in the central nervous system. Further investigation is required to determine the prognostic role of the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies in COVID-19.
Dr Zayet is a specialist in the Infectious Diseases Department of Nord Franche-Comte Hospital, France. His primary research interests focus on hepatitis and tuberculosis, especially in HIV-infected patients.
Acknowledgment
We thank Vincent Gendrin for English language editing and his support and valuable feedback.
References
- Mao L, Jin H, Wang M, Hu Y, Chen S, He Q, et al. Neurologic manifestations of hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan, China. JAMA Neurol. 2020 Apr 10 [Epub ahead of print].
- Oxley TJ, Mocco J, Majidi S, Kellner CP, Shoirah H, Singh IP, et al. Large-vessel stroke as a presenting feature of covid-19 in the young. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:
e60 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Klok FA, Kruip MJHA, van der Meer NJM, Arbous MS, Gommers DAMPJ, Kant KM, et al. Incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19. Thromb Res. 2020; [Epub ahead of print]. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Lodigiani C, Iapichino G, Carenzo L, Cecconi M, Ferrazzi P, Sebastian T, et al.; Humanitas COVID-19 Task Force. Venous and arterial thromboembolic complications in COVID-19 patients admitted to an academic hospital in Milan, Italy. Thromb Res. 2020;191:9–14. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zhang Y, Xiao M, Zhang S, Xia P, Cao W, Jiang W, et al. Coagulopathy and antiphospholipid antibodies in patients with covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:
e38 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Griffin DO, Jensen A, Khan M, Chin J, Chin K, Parnell R, et al. Arterial thromboembolic complications in COVID-19 in low risk patients despite prophylaxis. Br J Haematol. 2020;
bjh.16792 ; Epub ahead of print. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Ren H, Liu X, Wang L, Gao Y. Lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio: a novel predictor of the prognosis of acute ischemic stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2017;26:2595–602. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rodriguez-Morales AJ, Cardona-Ospina JA, Gutiérrez-Ocampo E, Villamizar-Peña R, Holguin-Rivera Y, Escalera-Antezana JP, et al. Latin American Network of Coronavirus Disease 2019-COVID-19 Research (LANCOVID-19). Electronic address: https://www.lancovid.org. Clinical, laboratory and imaging features of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2020;34:101623.
- Shulman JG, Cervantes-Arslanian AM. Infectious etiologies of stroke. Semin Neurol. 2019;39:482–94. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lin C-F, Hong C-T, Lee W-H, Wu D, Hu C-J, Chung C-C. Disseminated cutaneous herpes zoster and multiple cerebral infarcts in an adult with diabetes mellitus. J Neurovirol. 2020;26:130–2. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Figure
Cite This ArticleOriginal Publication Date: May 26, 2020
Table of Contents – Volume 26, Number 9—September 2020
| EID Search Options |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Please use the form below to submit correspondence to the authors or contact them at the following address:
Souheil Zayet, Department of Infectious Disease, Nord Franche-Comte Hospital, 100 Route de Moval, 90400 Trevenans, France
Top