Volume 27, Number 5—May 2021
Research
Serologic Screening of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection in Cats and Dogs during First Coronavirus Disease Wave, the Netherlands
Figure 2
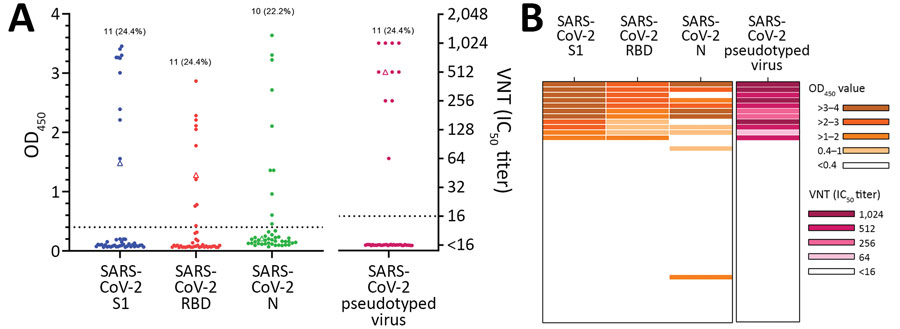
Figure 2. Serologic analyses of cat and dog serum samples from SARS-CoV-2–exposed cohort, the Netherlands. A) ELISA against SARS-CoV-2 S1, RBD, and N proteins, and VN analysis with SARS-CoV-2 pseudotyped virus. Dots indicate cat serum samples (n = 44) and triangle indicates dog sample (n = 1). B) Combination of results tested by different assays expressed as a heatmap. Dotted lines indicate positive cutoff levels. IC50, 50% inhibitory concentration; N, nucleocapsid; OD, optical density; RBD, receptor-binding domain; S1, spike protein subunit 1; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; VN, virus neutralization.
Page created: February 21, 2021
Page updated: April 20, 2021
Page reviewed: April 20, 2021
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.