Volume 28, Number 2—February 2022
CME ACTIVITY - Synopsis
Clinical and Laboratory Characteristics and Outcome of Illness Caused by Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus without Central Nervous System Involvement
Figure 2
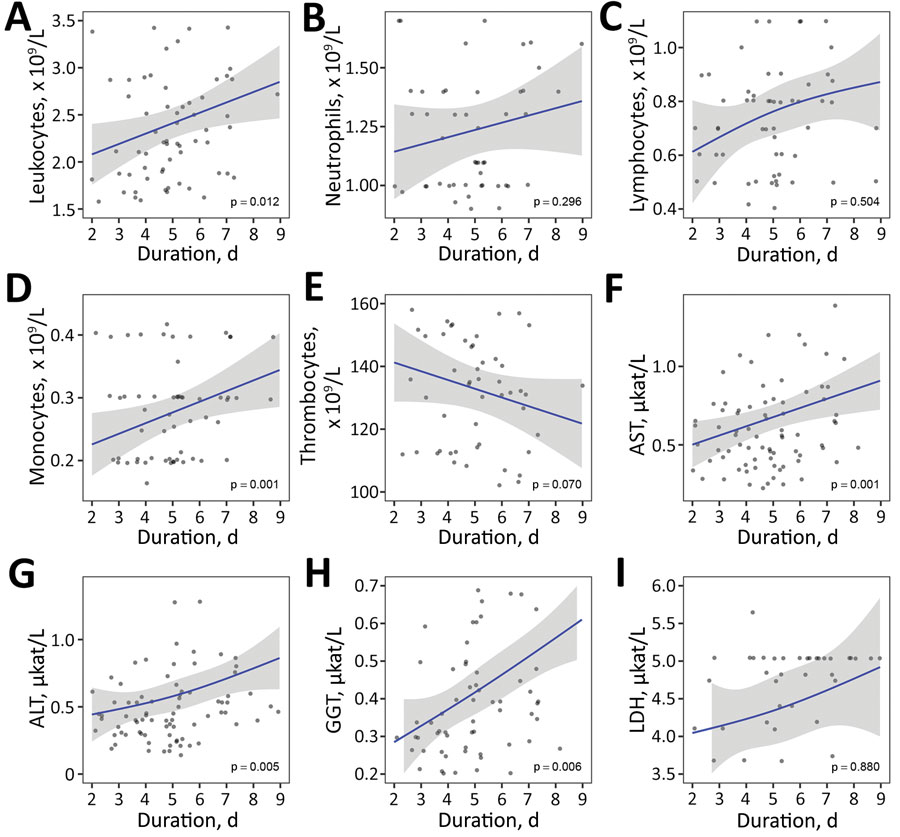
Figure 2. Laboratory findings according to illness duration in cases of febrile illness caused by tick-borne encephalitis virus without central nervous system involvement at the time of evaluations, Slovenia. A) Leukocytes, B) neutrophils, C) lymphocytes, D) monocytes, E) thrombocytes, F) AST, G) ALT, H) GGT, and I) LDH. Blue lines indicate loess regression lines; shaded areas indicate 95% CIs. Relationships between variables in panels C, G, and I were modeled by using restricted cubic splines with 3 knots (25). ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; GGT, gamma-glutamyl transferase; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase.
References
- Demina TV, Dzhioev YP, Verkhozina MM, Kozlova IV, Tkachev SE, Plyusnin A, et al. Genotyping and characterization of the geographical distribution of tick-borne encephalitis virus variants with a set of molecular probes. J Med Virol. 2010;82:965–76. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kozlova IV, Demina TV, Tkachev SE, Doroschenko EK, Lisak OV, Verkhozina MM, et al. Characteristics of the Baikal subtype of tick-borne encephalitis virus circulating in Eastern Siberia. Acta Biomedicia Scientifica. 2018;3:53–60. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Marvik Å, Tveten Y, Pedersen AB, Stiasny K, Andreassen ÅK, Grude N. Low prevalence of tick-borne encephalitis virus antibodies in Norwegian blood donors. Infect Dis (Lond). 2021;53:44–51. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tomažič J, Pikelj F, Schwartz B, Kunze M, Kraigher A, Matjašič M, et al.; Slovenian TBE study group. The clinical features of tick-borne encephalitis in Slovenia. A study of 492 cases in 1994. Antibiot Monitor. 1996;12:115–20.
- Günther G, Haglund M, Lindquist L, Forsgren M, Sköldenberg B. Tick-bone encephalitis in Sweden in relation to aseptic meningo-encephalitis of other etiology: a prospective study of clinical course and outcome. J Neurol. 1997;244:230–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kaiser R. The clinical and epidemiological profile of tick-borne encephalitis in southern Germany 1994-98: a prospective study of 656 patients. Brain. 1999;122:2067–78. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kaiser R, Holzmann H. Laboratory findings in tick-borne encephalitis—correlation with clinical outcome. Infection. 2000;28:78–84. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mickiene A, Laiskonis A, Günther G, Vene S, Lundkvist A, Lindquist L. Tickborne encephalitis in an area of high endemicity in lithuania: disease severity and long-term prognosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;35:650–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kaiser R. Tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) in Germany and clinical course of the disease. Int J Med Microbiol. 2002;291(Suppl 33):58–61. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Logar M, Bogovic P, Cerar D, Avsic-Zupanc T, Strle F. Tick-borne encephalitis in Slovenia from 2000 to 2004: comparison of the course in adult and elderly patients. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2006;118:702–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Misić Majerus L, Daković Rode O, Ruzić Sabljić E. [Post-encephalitic syndrome in patients with tick-borne encephalitis] [in Croatian]. Acta Med Croatica. 2009;63:269–78.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Radzišauskienė D, Urbonienė J, Kaubrys G, Andruškevičius S, Jatužis D, Matulytė E, et al. The epidemiology, clinical presentation, and predictors of severe Tick-borne encephalitis in Lithuania, a highly endemic country: A retrospective study of 1040 patients. PLoS One. 2020;15:
e0241587 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Barp N, Trentini A, Di Nuzzo M, Mondardini V, Francavilla E, Contini C. Clinical and laboratory findings in tick-borne encephalitis virus infection. Parasite Epidemiol Control. 2020;10:
e00160 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Bogovič P, Lotrič-Furlan S, Avšič-Županc T, Korva M, Kastrin A, Lusa L, et al. Comparison of clinical, laboratory and immune characteristics of the monophasic and biphasic course of tick-borne encephalitis. Microorganisms. 2021;9:796. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kohlmaier B, Schweintzger NA, Sagmeister MG, Švendová V, Kohlfürst DS, Sonnleitner A, et al.; The Eu-Tick-Bo Study Group. Clinical characteristics of patients with tick-borne encephalitis (TBE): a European multicentre study from 2010 to 2017. Microorganisms. 2021;9:1420. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mansfield KL, Johnson N, Phipps LP, Stephenson JR, Fooks AR, Solomon T. Tick-borne encephalitis virus - a review of an emerging zoonosis. J Gen Virol. 2009;90:1781–94. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bogovic P, Strle F. Tick-borne encephalitis: A review of epidemiology, clinical characteristics, and management. World J Clin Cases. 2015;3:430–41. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Taba P, Schmutzhard E, Forsberg P, Lutsar I, Ljøstad U, Mygland Å, et al. EAN consensus review on prevention, diagnosis and management of tick-borne encephalitis. Eur J Neurol. 2017;24:1214–e61. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bogovič P, Stupica D, Rojko T, Lotrič-Furlan S, Avšič-Županc T, Kastrin A, et al. The long-term outcome of tick-borne encephalitis in Central Europe. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2018;9:369–78. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Granström M. Tick-borne zoonoses in Europe. Clin Microbiol Infect. 1997;3:156–69. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dumpis U, Crook D, Oksi J. Tick-borne encephalitis. Clin Infect Dis. 1999;28:882–90. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Borde JP, Zajkowska J. TBE in adults. In: Dobler G, Erber W, Bröker M, Schmitt HJ, editors. The TBE Book, 2nd ed. Singapore: Global Health Press; 2019. p. 105–24.
- Schultze D, Dollenmaier G, Rohner A, Guidi T, Cassinotti P. Benefit of detecting tick-borne encephalitis viremia in the first phase of illness. J Clin Virol. 2007;38:172–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lotrič-Furlan S, Avsic-Zupanc T, Strle F. Is an isolated initial phase of a tick-borne encephalitis a common event? Clin Infect Dis. 2000;30:987–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Saksida A, Jakopin N, Jelovšek M, Knap N, Fajs L, Lusa L, et al. Virus RNA load in patients with tick-borne encephalitis, Slovenia. Emerg Infect Dis. 2018;24:1315–23. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- van Buuren S. Multiple imputation of discrete and continuous data by fully conditional specification. Stat Methods Med Res. 2007;16:219–42. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Perperoglou A, Sauerbrei W, Abrahamowicz M, Schmid M. A review of spline function procedures in R. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2019;19:46. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- R Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing [cited 2021 May 18]. http://www.r-project.org
- Lotrič-Furlan S, Bogovič P, Avšič-Županc T, Jelovšek M, Lusa L, Strle F. Tick-borne encephalitis in patients vaccinated against this disease. J Intern Med. 2017;282:142–55. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bogovič P, Lotrič-Furlan S, Avšič-Županc T, Lusa L, Strle F. Factors associated with severity of tick-borne encephalitis: A prospective observational study. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2018;26:25–31. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Anić K, Soldo I, Perić L, Karner I, Barac B. Tick-borne encephalitis in eastern Croatia. Scand J Infect Dis. 1998;30:509–12. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lotric-Furlan S, Petrovec M, Avsic-Zupanc T, Strle F. Clinical distinction between human granulocytic ehrlichiosis and the initial phase of tick-borne encephalitis. J Infect. 2000;40:55–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lotric-Furlan S, Petrovec M, Avsic-Zupanc T, Logar M, Strle F. Epidemiological, clinical and laboratory distinction between human granulocytic ehrlichiosis and the initial phase of tick-borne encephalitis. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2002;114:636–40.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lotric-Furlan S, Strle F. Thrombocytopenia, leukopenia and abnormal liver function tests in the initial phase of tick-borne encephalitis. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1995;282:275–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lotric-Furlan S, Strle F. Thrombocytopenia—a common finding in the initial phase of tick-borne encephalitis. Infection. 1995;23:203–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Saksida A, Duh D, Lotric-Furlan S, Strle F, Petrovec M, Avsic-Zupanc T. The importance of tick-borne encephalitis virus RNA detection for early differential diagnosis of tick-borne encephalitis. J Clin Virol. 2005;33:331–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ackermann R, Krüger K, Roggendorf M, Rehse-Küpper B, Mörtter M, Schneider M, et al. [Spread of early-summer meningoencephalitis in the Federal Republic of Germany] [in German]. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1986;111:927–33. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: December 02, 2021
Page updated: January 21, 2022
Page reviewed: January 21, 2022
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.