Volume 28, Number 7—July 2022
Research
Measuring Basic Reproduction Number to Assess Effects of Nonpharmaceutical Interventions on Nosocomial SARS-CoV-2 Transmission
Figure 1
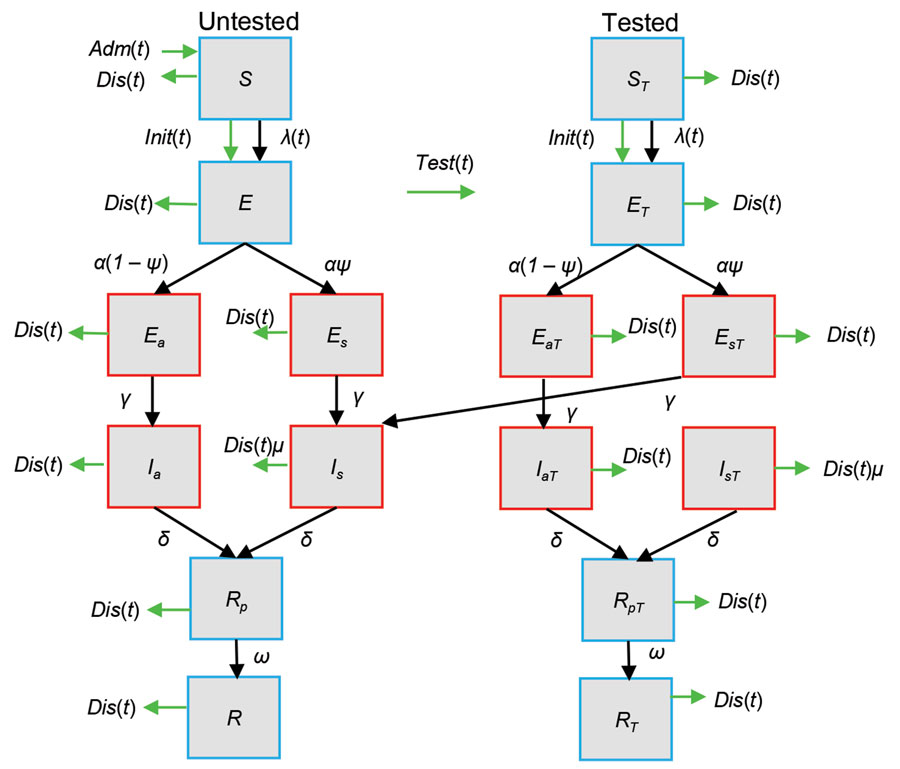
Figure 1. Compartmental susceptible-exposed-infectious-recovered model used to estimate nosocomial SARS-CoV-2 transmission rates on the basis of data for a long-term care facility in France. Red boxes indicate SARS-CoV-2 infectious compartments and blue boxes indicate noninfectious compartments. The left side shows the trajectory of untested persons, the right side shows tested persons. If untested persons are tested at any point in state X, they will enter the equivalent tested compartment (XT, right panel), which is epidemiologically identical except for the testing rate. Patients in the susceptible state (S) can become infected by contact with infectious patients. When infected, patients move to the noninfectious incubation (E) compartment, after which they can either enter an asymptomatic or a symptomatic pathway of infectiousness. Each pathway has an infectious incubation period (Ea, Es) before asymptomatic (Ia) or symptomatic (Is) infection begins. After full infection, patients recover into a noninfectious state (Rp) where they are still likely to test positive before full recovery (R) when the probability of testing positive diminishes to (1 – test specificity). Green arrows refer to processes, initiation (Init), admission (Adm), discharge (Dis), and testing (Test), that occur a specified number of times on a given day according to model inputs. Black arrows indicate processes that are natural for infection and are entirely stochastic (Appendix Methods, Figure 1). E, exposed; Ea, asymptomatic exposed; EaT, asymptomatic exposed and tested; Es, symptomatic exposed; EsT, symptomatic exposed and tested; ET, exposed and tested; I, infectious; Ia, asymptomatic infectious; IaT, asymptomatic infectious and tested; Is, symptomatic infectious; IsT, symptomatic infectious and tested; IT, infectious and tested; R, recovered; Rp, recovered to noninfectious state; RpT, recovered to noninfectious state and tested; RT, recovered and tested; S, susceptible; t, time; α, rate of progression from noninfectious incubation; ψ, proportion of patients entering symptomatic pathway; λ(t), force of infection at time t; γ, rate of progression from infectious incubation; δ, rate of progression from symptomatic infection; μ, relative rate of discharge for symptomatic patients relative to any nonsymptomatic patient; ω, rate at which viral shedding ceases during recovery.
1These authors were co-principal investigators.
2Members of the workgroup are listed at the end of this article.