Volume 29, Number 10—October 2023
Research
Posttransfusion Sepsis Attributable to Bacterial Contamination in Platelet Collection Set Manufacturing Facility, United States
Figure 4
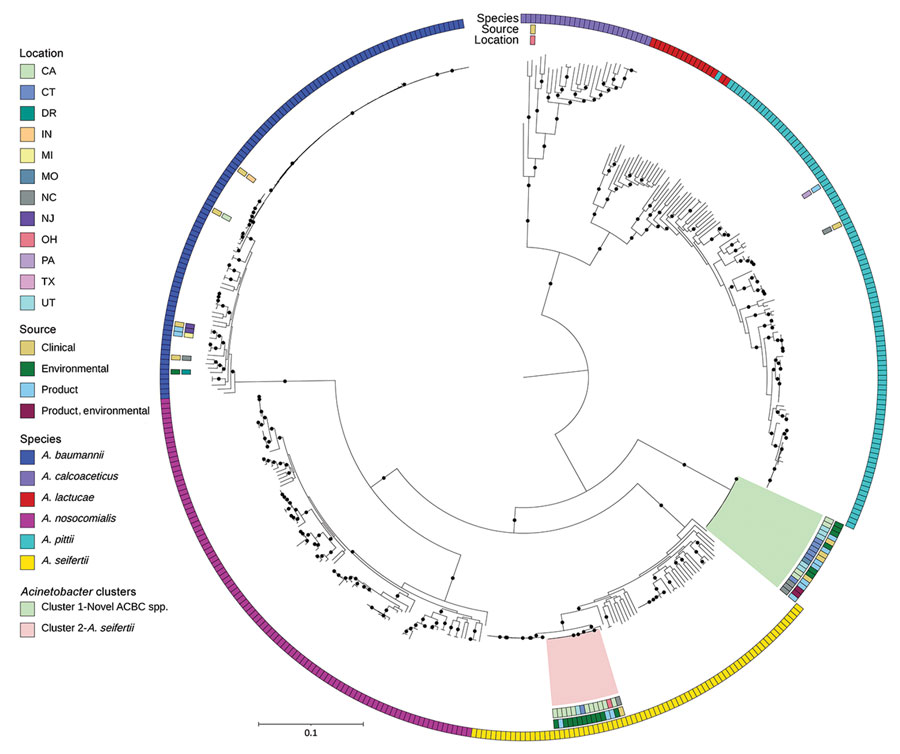
Figure 4. Public ACBC shown with study isolates from investigation of bacterial contamination of platelet blood products, United States, 2018–2022. Shown is a RaxML (https://cme.h-its.org)‒generated phylogeny based on core genes of genomes from ACBC isolates from this study compared with all A. calcoaceticus, A. lactucae, and A. seifertii and a subsampled set of A. baumannii, A. nosocomialis, and A. pittii genomes from the National Center for Biotechnology Information RefSeq (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/refseq) database, along with all Staphylococcus saprophyticus from the RefSeq database. Isolate location, isolate source, and species from National Center for Biotechnology Information database along with all S. saprophyticus isolates or by average nucleotide identity were layered onto the phylogeny. Pink and green indicate the 2 clusters from Figure 3, panel B. Black circles on branches indicate 100% support for the branch of 100 bootstraps. US states are identified by 2-letter postal codes. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site. ACBC, Acinetobacter calcoaceticus-baumannii; DR, Dominican Republic.