Volume 29, Number 6—June 2023
Research
Evolution of Avian Influenza Virus (H3) with Spillover into Humans, China
Figure 2
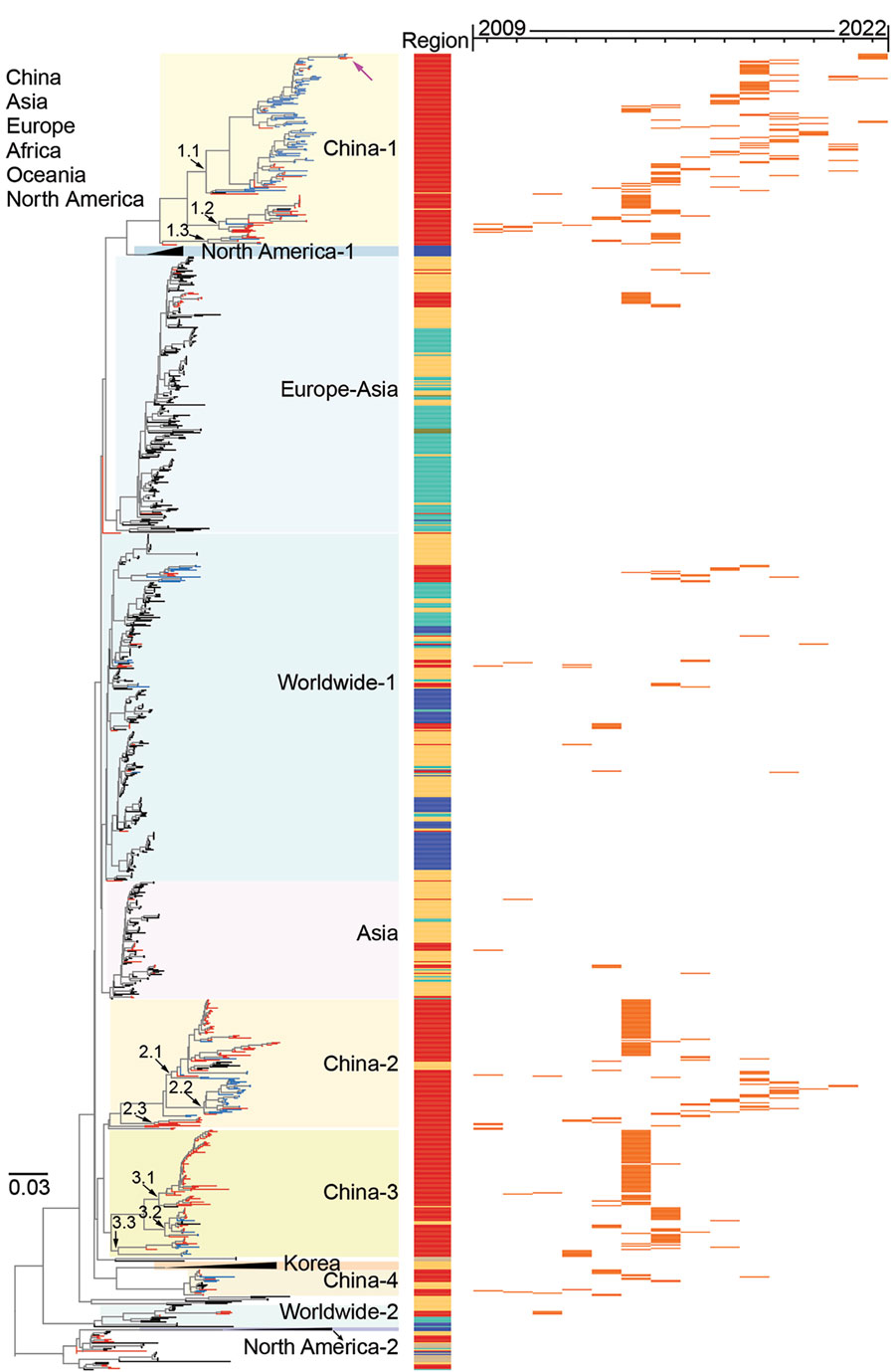
Figure 2. Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree of hemagglutinin genes of avian influenza viruses subtype H3 from China (n = 1,291) and reference sequences from GISAID (https://www.gisaid.org). Blue tree sections indicate sequences reported in this study; red tree sections indicate other H3 sequences from China; violet arrow at top of tree indicates human H3N8 virus. For clarity, some clades are collapsed. Sublineages are shown with different background colors on the phylogenetic tree. Subgroups in sublineages China-1, China-2, and China-3 are marked with black arrows at the nodes. The sampling locations are annotated with colored bars adjacent to the tree. For the H3 viruses sampled in China during 2009–2022, the sampling year of each of these viruses is shown on the right panel with orange horizontal bars. The phylogenetic tree of the H3 genes with more detailed information is shown in Appendix Figure 1. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.