Volume 29, Number 7—July 2023
Research
Triplex ELISA for Assessing Durability of Taenia solium Seropositivity after Neurocysticercosis Cure
Figure 7
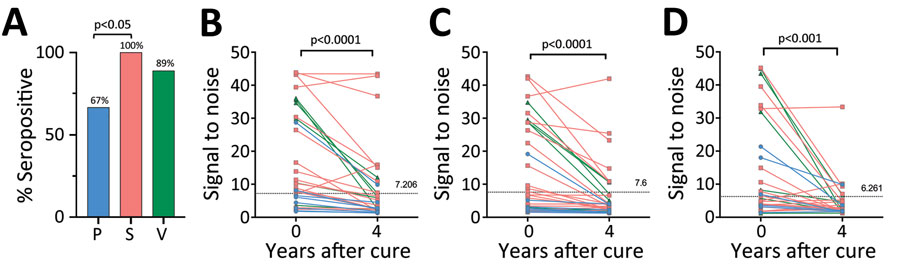
Figure 7. Taenia solium seropositivity over time by a triplex assay to determine durability of T. solium seropositivity after neurocysticercosis cure. The triplex assay combines 3 families of T. solium antigens: T24H, GP50, and Ts18var3. A) Seropositivity at time of cure. B–D) Seropositivity at year 4 by neurocysticercosis disease type: B) parenchymal (n = 9); C) subarachnoid (n = 28); and D) ventricular disease (n = 9). Line colors in panels B–D correspond to bar colors in panel A. Horizonal dotted lines indicate the 100% specificity cutoff used for that protein. Statistically significant differences in seropositivity were seen between patients with parenchymal disease (67%) and subarachnoid disease (100%) (p = 0.011), but not for ventricular disease (89%), at the time of cure. Patients seropositive at time of cure (parenchymal n = 6, subarachnoid n = 28, ventricular n = 8) underwent testing of paired samples at time of cure (day 0) and 4 years after cure. For each subgroup, reactivity to GP50, T24H, and Ts18var3 showed statistically significant decreases by year 4. P, parenchymal; S, subarachnoid; V, ventricular.