Volume 30, Number 6—June 2024
Dispatch
Concurrent Infection with Clade 2.3.4.4b Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza H5N6 and H5N1 Viruses, South Korea, 2023
Figure 1
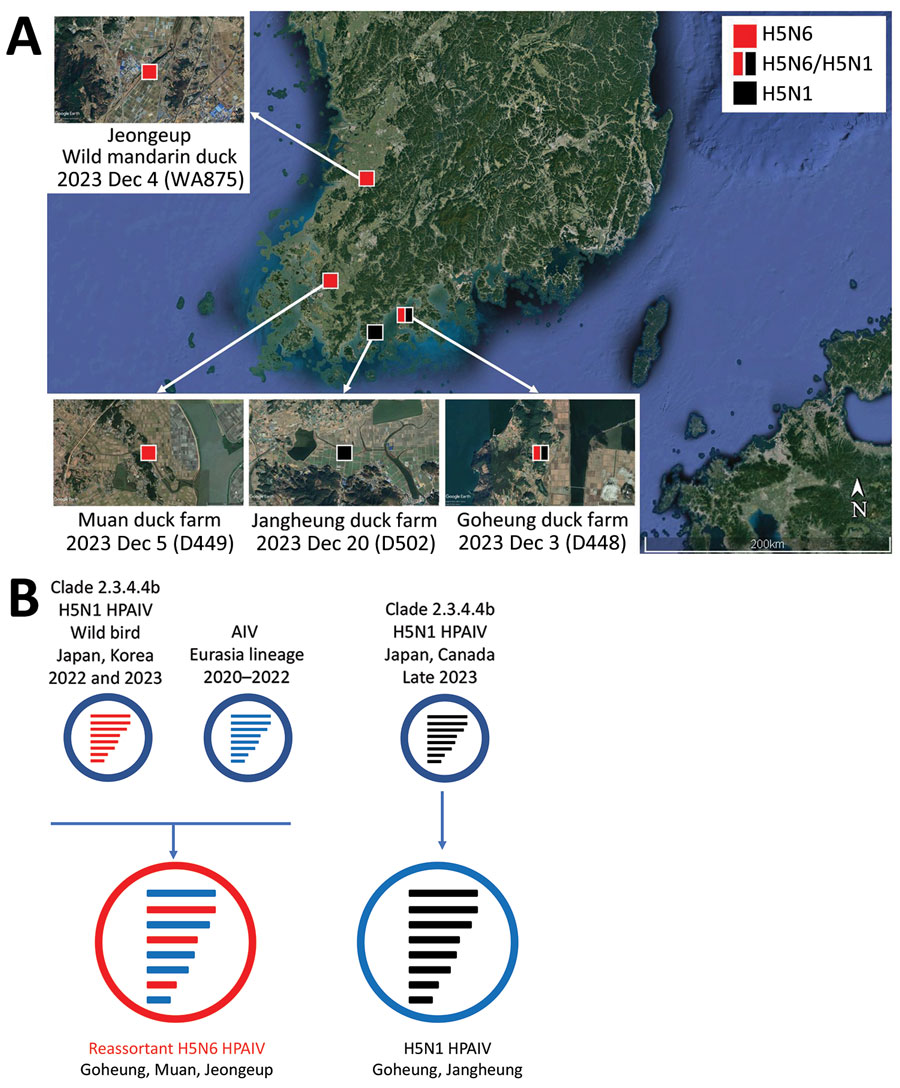
Figure 1. Locations of duck farms and of wild ducks infected with clade 2.3.4.4b HPAIV H5, South Korea, 2023, and their viral genotypes. A) Each square indicates the location of the infected farms or wild birds where the samples were collected. Red indicates H5N6 virus and black H5N1 virus. Satellite image is from Google Earth (https://earth.google.com). B) Genetic constellation of H5N6 and H5N1 viruses concurrently detected in December 2023. The bars represent 8 gene segments of the avian influenza virus in the following order (from top to bottom): polymerase basic 2, polymerase basic 1, polymerase acidic, hemagglutinin, nucleoprotein, neuraminidase, matrix, and nonstructural. The 8 genes of each virus are represented by colored bars, indicating presumed recent donors. HPAIV, highly pathogenic avian influenza virus.