Volume 30, Number 8—August 2024
Dispatch
ST913-IVa-t991 Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus among Pediatric Patients, Israel
Figure 2
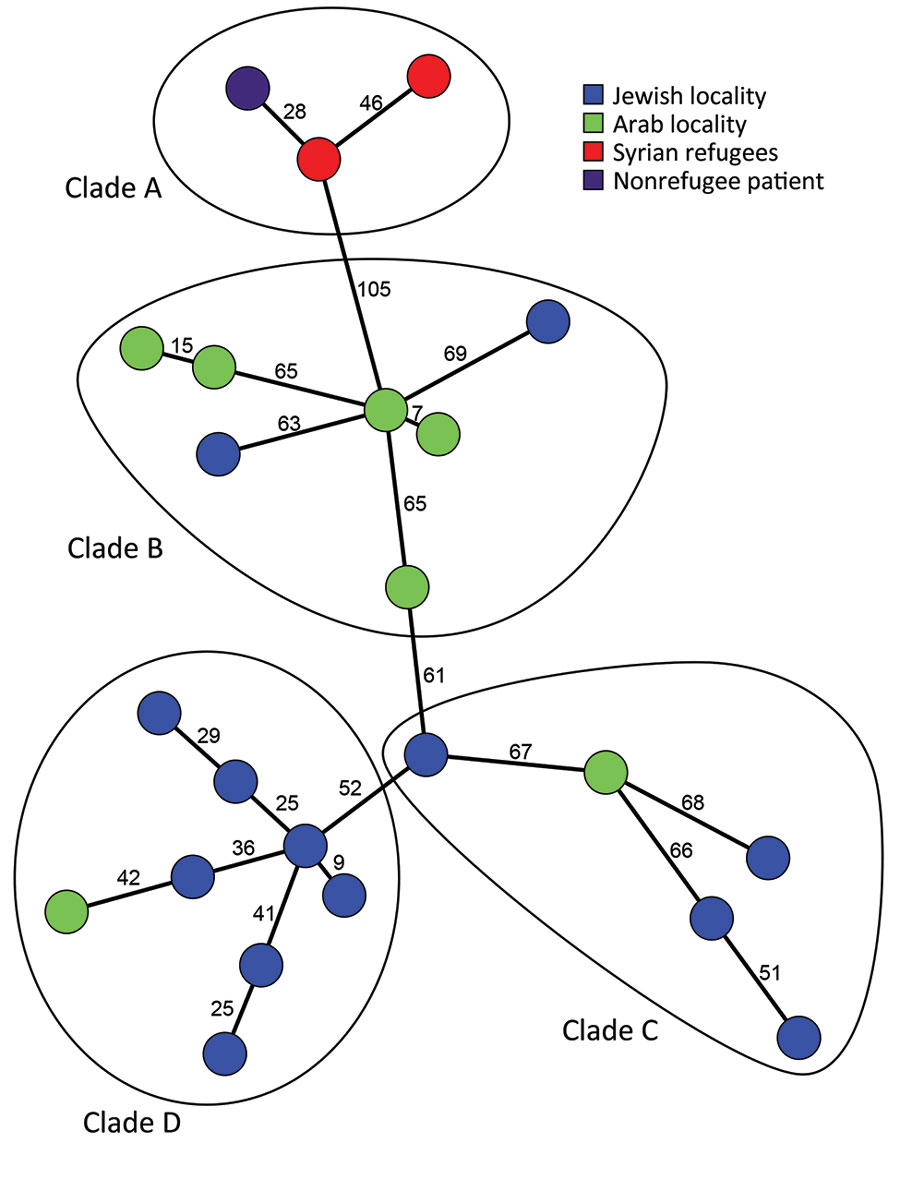
Figure 2. Phylogenetic relationships between 23 t991 MRSA genomes isolated in Israel and Germany. The figure shows a minimum spanning tree, created in Bionumerics software (https://www.bionumerics.com), based on 3,904 wgMLST allele IDs of sequenced t991 MRSA isolates. Each node represents an isolate; numbers along branches connecting nodes indicate the numbers of allelic differences between isolates. The isolates are further divided into 4 clades (A–D). MRSA, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; wgMLST whole-genome multilocus sequence typing.
Page created: July 10, 2024
Page updated: July 21, 2024
Page reviewed: July 21, 2024
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.