Volume 30, Number 8—August 2024
Research
Metagenomic Detection of Bacterial Zoonotic Pathogens among Febrile Patients, Tanzania, 2007–20091
Figure 1
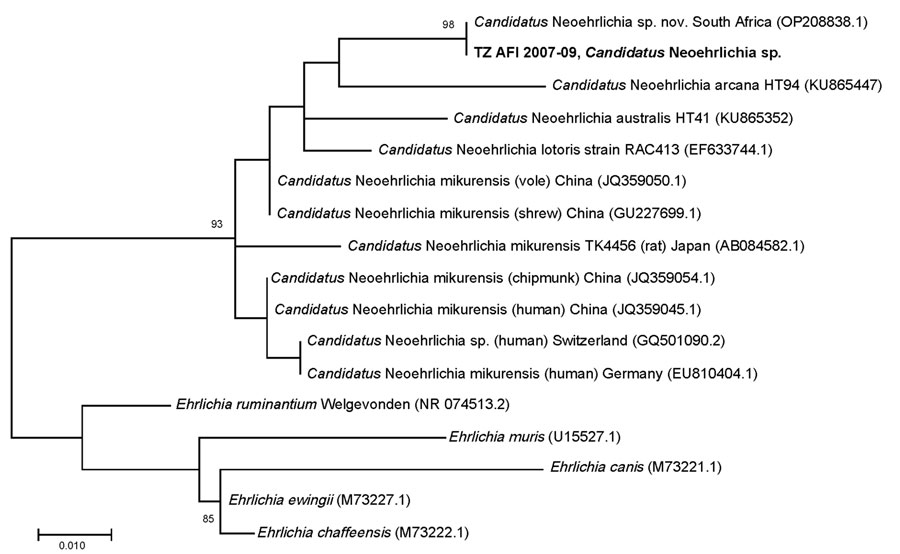
Figure 1. Phylogenetic tree for Candidatus Neoehrlichia spp. identified during metagenomic detection of bacterial zoonotic pathogens among febrile patients, Tanzania, 2007–2009. Bold text indicates the sequence from this study. Numbers in parentheses indicate GenBank accession numbers. A 1,467-bp 16S sequence amplified from a bone marrow aspirate from a patient from South Africa (GenBank accession no. OP208838) matched 100% over the 296-bp variable regions 1 and 2 target sequence amplified in this study (18). Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
References
- Prasad N, Murdoch DR, Reyburn H, Crump JA. Etiology of severe febrile illness in low- and middle-income countries: a systematic review. PLoS One. 2015;10:
e0127962 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Maina AN, Farris CM, Odhiambo A, Jiang J, Laktabai J, Armstrong J, et al. Q fever, scrub typhus, and rickettsial diseases in children, Kenya, 2011–2012. Emerg Infect Dis. 2016;22:883–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dreyfus A, Dyal JW, Pearson R, Kankya C, Kajura C, Alinaitwe L, et al. Leptospira seroprevalence and risk factors in health centre patients in Hoima District, Western Uganda. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016;10:
e0004858 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Prabhu M, Nicholson WL, Roche AJ, Kersh GJ, Fitzpatrick KA, Oliver LD, et al. Q fever, spotted fever group, and typhus group rickettsioses among hospitalized febrile patients in northern Tanzania. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;53:e8–15. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Biggs HM, Bui DM, Galloway RL, Stoddard RA, Shadomy SV, Morrissey AB, et al. Leptospirosis among hospitalized febrile patients in northern Tanzania. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2011;85:275–81. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Crump JA, Morrissey AB, Nicholson WL, Massung RF, Stoddard RA, Galloway RL, et al. Etiology of severe non-malaria febrile illness in Northern Tanzania: a prospective cohort study. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013;7:
e2324 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Maze MJ, Cash-Goldwasser S, Rubach MP, Biggs HM, Galloway RL, Sharples KJ, et al. Risk factors for human acute leptospirosis in northern Tanzania. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018;12:
e0006372 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Pisharody S, Rubach MP, Carugati M, Nicholson WL, Perniciaro JL, Biggs HM, et al. Incidence estimates of acute Q fever and spotted fever group rickettsioses, Kilimanjaro, Tanzania, from 2007 to 2008 and from 2012 to 2014. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2021;106:494–503. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Allan KJ, Maze MJ, Galloway RL, Rubach MP, Biggs HM, Halliday JEB, et al. Molecular detection and typing of pathogenic Leptospira in febrile patients and phylogenetic comparison with Leptospira detected among animals in Tanzania. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020;103:1427–34. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Carugati M, Kilonzo KG, Crump JA. Fever, bacterial zoonoses, and One Health in sub-Saharan Africa. Clin Med (Lond). 2019;19:375–80. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kingry L, Sheldon S, Oatman S, Pritt B, Anacker M, Bjork J, et al. Targeted metagenomics for clinical detection and discovery of bacterial tick-borne pathogens. J Clin Microbiol. 2020;58:e00147–20. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Crump JA, Ramadhani HO, Morrissey AB, Msuya LJ, Yang LY, Chow SC, et al. Invasive bacterial and fungal infections among hospitalized HIV-infected and HIV-uninfected children and infants in northern Tanzania. Trop Med Int Health. 2011;16:830–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Crump JA, Ramadhani HO, Morrissey AB, Saganda W, Mwako MS, Yang LY, et al. Invasive bacterial and fungal infections among hospitalized HIV-infected and HIV-uninfected adults and adolescents in northern Tanzania. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;52:341–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wood DE, Salzberg SL. Kraken: ultrafast metagenomic sequence classification using exact alignments. Genome Biol. 2014;15:R46. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol. 2018;35:1547–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Yoshida K, Bartel A, Chipman JJ, Bohn J, D’Augustino McGowan C, Barrett M, et al. tableone: create ‘Table 1’ to describe baseline characteristics with or without propensity score weights [cited 2023 Dec 13]. https://cloud.r-project.org/web/packages/tableone/tableone.pdf
- Wickham H, Averick M, Bryan J, Chang W, McGowan LDA, François R, et al. Welcome to the tidyverse. J Open Source Softw. 2019;4:1686. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Bamford C, Blumberg LH, Bosman M, Frean J, Hoek KGP, Miles J, et al. Neoehrlichiosis in symptomatic immunocompetent child, South Africa. Emerg Infect Dis. 2023;29:407–10. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bitam I, Dittmar K, Parola P, Whiting MF, Raoult D. Fleas and flea-borne diseases. Int J Infect Dis. 2010;14:e667–76. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Leulmi H, Socolovschi C, Laudisoit A, Houemenou G, Davoust B, Bitam I, et al. Detection of Rickettsia felis, Rickettsia typhi, Bartonella species and Yersinia pestis in fleas (Siphonaptera) from Africa. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014;8:
e3152 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Theonest NO, Carter RW, Amani N, Doherty SL, Hugho E, Keyyu JD, et al. Molecular detection and genetic characterization of Bartonella species from rodents and their associated ectoparasites from northern Tanzania. PLoS One. 2019;14:
e0223667 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Badiaga S, Brouqui P. Human louse-transmitted infectious diseases. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2012;18:332–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fournier PE, Jensenius M, Laferl H, Vene S, Raoult D. Kinetics of antibody responses in Rickettsia africae and Rickettsia conorii infections. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2002;9:324–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Harrison N, Burgmann H, Forstner C, Ramharter M, Széll M, Schötta AM, et al. Molecular diagnosis of African tick bite fever using eschar swabs in a traveller returning from Tanzania. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2016;128:602–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jensenius M, Fournier PE, Raoult D, Raoult D. Rickettsioses and the international traveler. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;39:1493–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Yoshikawa H, Kimura M, Ogawa M, Rolain J-M, Raoult D. Laboratory-confirmed Mediterranean spotted fever in a Japanese traveler to Kenya. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2005;73:1086–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rutherford JS, Macaluso KR, Smith N, Zaki SR, Paddock CD, Davis J, et al. Fatal spotted fever rickettsiosis, Kenya. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004;10:910–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mutai BK, Wainaina JM, Magiri CG, Nganga JK, Ithondeka PM, Njagi ON, et al. Zoonotic surveillance for rickettsiae in domestic animals in Kenya. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2013;13:360–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zemtsova GE, Apanaskevich DA, Reeves WK, Hahn M, Snellgrove A, Levin ML. Phylogeography of Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato and its relationships with climatic factors. Exp Appl Acarol. 2016;69:191–203. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lynen G, Zeman P, Bakuname C, Di Giulio G, Mtui P, Sanka P, et al. Cattle ticks of the genera Rhipicephalus and Amblyomma of economic importance in Tanzania: distribution assessed with GIS based on an extensive field survey. Exp Appl Acarol. 2007;43:303–19. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Schwameis M, Auer J, Mitteregger D, Simonitsch-Klupp I, Ramharter M, Burgmann H, et al. Anaplasmataceae-specific PCR for diagnosis and therapeutic guidance for symptomatic neoehrlichiosis in immunocompetent host. Emerg Infect Dis. 2016;22:281–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Motto SK, Shirima GM, de Clare Bronsvoort BM, Cook EAJ. Epidemiology of leptospirosis in Tanzania: A review of the current status, serogroup diversity and reservoirs. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021;15:
e0009918 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Hagedoorn NN, Maze MJ, Carugati M, Cash-Goldwasser S, Allan KJ, Chen K, et al. Global distribution of Leptospira serovar isolations and detections from animal host species: A systematic review and online database. Trop Med Int Health. 2024;29:161–72. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
1Preliminary results of this study were presented at the 72nd American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene Annual Meeting; October 18–22, 2023; Chicago, Illinois, USA.
Page created: June 15, 2024
Page updated: July 20, 2024
Page reviewed: July 20, 2024
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.