Volume 31, Number 10—October 2025
Research
Multidrug-Resistant pESI-Harboring Salmonella enterica Serovar Muenchen Sequence Type 82 in Poultry and Humans, Israel, 2020–2023
Figure 2
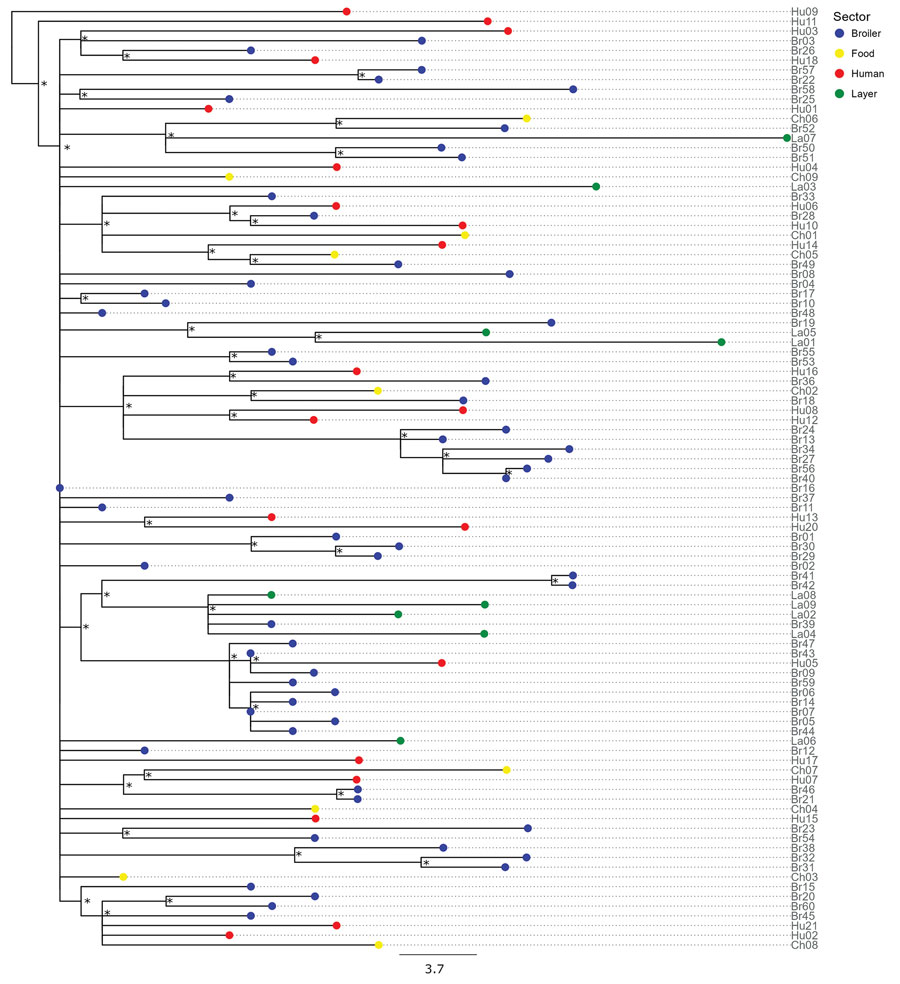
Figure 2. Maximum-likelihood tree reconstructed using whole-genome sequences of Salmonella enterica serovar Muenchen isolates collected from broilers (n = 60), layers (n = 9), food products of poultry origin (whole chicken carcasses sampled in poultry slaughterhouses; n = 9), and humans (n = 21) in study of Salmonella Muenchen in poultry and humans, Israel, June 2020–January 2022. We used a hybrid assembly of Salmonella Muenchen sequence type 82 (Br19) as a reference genome and used Salmonella Muenchen sequence type 112 (National Center for Biotechnology Information Sequence Read Archive accession no. SRR6222324) to root the tree (not shown). The analysis included 1,227 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the alignment (0–69 pairwise SNPs, median 31). Because isolates Hu19 and Br35 were duplicates of isolate Br16, we removed them from the analysis. Tip colors indicate sector. Asterisks (*) indicate nodes with >70% bootstrap support. Additional data (Appendix 1 Figure 2) include a heatmap and show the presence of acquired antimicrobial resistance genes and point mutations and indicate the isolates in which antimicrobial sensitivity was tested in vitro and the presence of a pESI genetic marker, hyp_pESI, and plasmid replicons. Scale bar represents SNP difference.