Volume 31, Number 10—October 2025
Research
Multidrug-Resistant pESI-Harboring Salmonella enterica Serovar Muenchen Sequence Type 82 in Poultry and Humans, Israel, 2020–2023
Cite This Article
Citation for Media
Abstract
Salmonella enterica serovar Muenchen emerged in Israel in 2018 and became a major public health threat. We aimed to determine the role of poultry in rising human cases, transmission routes within the broiler industry, and genetic similarity to Salmonella Muenchen found globally. We used whole-genome sequencing to compare Salmonella Muenchen isolates from poultry, food, and humans collected in Israel (2020–2023; n = 109) and globally (n = 125). Salmonella Muenchen sequence type 82 isolates from Israel harbored pESI plasmid, exhibited high genetic similarity between human and poultry sources, and closely resembled international pESI-positive strains; we found quinolone-resistance determinants in 58.6% of isolates. Salmonella Muenchen prevalence in commercial broiler flocks was 61.5% (95% CI 51.5%–71.5%); strains could not be traced to breeder flocks, but on-farm persistence existed. The clonal spread of Salmonella Muenchen in poultry contributes to increased incidence in humans. Horizontal transmission in broilers requires control measures to protect public health.
Nontyphoidal Salmonella (NTS) is a major cause of foodborne illness worldwide (1); poultry serve as a reservoir and a source of infection to humans for multiple serotypes (2). Although most serotypes cause little harm to the infected bird (3), controlling NTS infection in poultry is essential for the protection of public health (2). Given the pyramidal structure of the poultry industry (a large number of production flocks [broilers and layers] are descendants of a small number of parent and grandparent breeding flocks), control measures for NTS spread, such as vaccination against specific serotypes (2), are often focused on the parent and grandparent flocks and not on the high number of short-lived production birds.
In Israel, NTS surveillance in humans relies on passive reporting of clinical cases to the national reference laboratory of the Ministry of Health (4), similar to the approach used in Europe (5). In the poultry sector, the Egg and Poultry Board and the Israeli Veterinary Services conduct an active surveillance program for Salmonella only in breeding flocks and layer hen farms, in accordance with international regulations (European Regulation no. 2160/2003).
Since 2018, Salmonella Muenchen and Salmonella Virginia, formerly misclassified as separate serotypes (6) (both referred to as Salmonella Muenchen hereafter), emerged as the dominant serotypes in clinical cases in humans in Israel. These serotypes accounted for 2.0% (101/5,072) of all Salmonella cases in 2017 and 35.4% (1,124/3,171) in 2022 (7). A similar trend was found in Salmonella isolates from poultry: from 3.8% (63/1,672) of the animal and poultry sources in 2017 to 23.6% (202/857) in 2021, and from 4.9% (12/245) of the food industry and ready-to-eat products (most of which are from poultry slaughterhouses) in 2017 to 20.0% (43/215) in 2021 (7).
Another study in Israel (8) reported that Salmonella Muenchen had acquired pESI, a plasmid first identified in Salmonella Infantis (9). pESI is described as a mega-plasmid that contributed to stress tolerance and increased pathogenicity that enabled the rapid spread of Salmonella Infantis in humans and poultry in Israel since 2007 and later in Italy (10) and other locations worldwide (11). The spread in Israel was ultimately controlled by the introduction of mandatory vaccination against Salmonella Infantis in breeder flocks in 2011 (4). However, despite a rapid reduction in the prevalence of Salmonella Infantis in breeder flocks, the success of the vaccination program to reduce the prevalence in broiler flocks was only evident several years after its initiation (A. Wiseman, pers. comm., telephone, 2020 Jul 1). Therefore, we suspected that the persistence of Salmonella Infantis in the farm environment and horizontal transmission between flocks, rather than vertical transmission from parent flocks, played a substantial role in its spread.
We used a large collection of Salmonella Muenchen isolates recovered from broiler flocks in Israel to determine the genetic relatedness among isolates from broilers, humans, and other poultry sources and the presence of relevant genetic determinants such as pESI and antimicrobial resistance (AMR) genes. We also determined the prevalence of Salmonella Muenchen in commercial broiler flocks and the potential transmission routes between different growth stages to observe whether vertical or horizontal transmission play a major role in bacterial spread. Finally, we studied genetic similarities between the emerging Salmonella Muenchen in Israel and global strains to reflect on the potential for its global spread and the risk posed to public health globally.
Study Population and Sample Collection
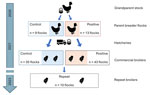
We conducted 3 analyses of Salmonella Muenchen isolates (Appendix 1). We chose study populations and collected samples in accordance with the intention of each analysis. For analysis A, we identified Salmonella Muenchen isolates collected in Israel during June 2020–January 2022 from a broad geographic distribution from broilers (n = 60; see analysis B) and layers (n = 9), poultry slaughterhouses (n = 9) (Appendix 1 Figure 1), and human clinical cases (n = 21). For analysis B, we used isolates from heavy breeders, grandparent flocks and hatcheries that were collected as part of the national Salmonella active surveillance program and were tested for Salmonella in accordance with International Standards Organization protocol ISO-6579–1 (12). Subsequently, we screened all serogroup C isolates for Salmonella Muenchen by multiplex PCR (13). We selected 13 heavy-breeder flocks that tested positive for Salmonella Muenchen on >2 successive collections as the positive group and 9 flocks with >3 successive negative results for Salmonella as the control group. We identified newly hatched broiler flocks (n = 78) and purposely sampled them for detection of Salmonella Muenchen: of those, 43 flocks were descendent from the positive group, and 35 flocks were descendent from the control group (Figure 1). We used those samples to estimate prevalence and assess risk factors for positivity to Salmonella Muenchen in broilers. In addition, 15–20 months after the initial broiler sampling, we resampled 10 new flocks in barns where Salmonella Muenchen was previously detected (hereafter, repeat broilers) (Figure 1). We obtained samples from broiler farms by using environmental drag swabs either inside the barn (interior swabs) or around the exterior of the barn (exterior swabs), or by using chick sampling and testing, conducted independently of this study (Appendix 2 Table 1). We conducted environmental sampling of the barns just before marketing, during marketing time (i.e., when transferred to the slaughterhouse at age 35–42 days), or after marketing when the barn was emptied but before cleaning.
We selected 70 of the Salmonella Muenchen isolates, representing a broad geographic distribution and representative of the different production stages, to undergo whole-genome sampling. That group included isolates from commercial broilers, subdivided into those descendent from the positive (n = 20) and control (n = 18) groups, hatcheries (n = 3), breeder flocks (n = 10), breeder pullets (n = 6), grandparent flocks (n = 3), and repeat broilers (n = 10) (Appendix 2 Table 3).
For analysis C, we chose 11 isolates that had undergone whole-genome sequencing and genetic analysis (from analysis A) to represent the different sources and genetic diversity of Salmonella Muenchen in Israel. In addition, we downloaded paired-end reads of Salmonella Muenchen global isolates (n = 125; i.e., strains collected during 2018–2021 from various sources in other countries) and strains known to contain pESI (8) from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov) (Appendix 2 Table 4).
Genetic Analysis
We generated paired-end reads for all isolates using the NextSeq platform (Illumina, https://www.illumina.com). In addition, we subjected isolate Br19 to long-read sequencing using the Oxford Nanopore platform (Nanopore Technologies, https://nanoporetech.). We used its hybrid assembly, built using Unicycler version 0.5.0 (github.com/rrwick/Unicycler) (14), as a genetically relevant reference genome. We aligned Illumina reads to the reference genome using Snippy version 4.6.0 (https://github.com/tseemann/snippy). We created maximum-likelihood trees using RAxML version 8.2.12 (https://github.com/amkozlov/raxml-ng) (15). We assessed branch support for the trees using 10,000 bootstrap replicates. We conducted de novo genome assemblies using SPAdes version 3.12.0 (16). We used contigs as an input for detection of AMR genes, known point mutations, and genes associated with virulence and resistance; detection of plasmid replicons; detection of a pESI target sequence (8); in silico serotyping; and multilocus sequence typing.
For analyses A and B, we rooted the maximum-likelihood trees to a Salmonella Muenchen sequence type (ST)112 outgroup strain (NCBI Sequence Read Archive accession no. SRR6222324). For analysis C, we rooted the tree to a Salmonella Braenderup strain (accession no. SRR5874793), a closely related yet genetically distinct serotype (17).
Phenotypic Analysis
We assessed antimicrobial resistance of a selection of broiler isolates (n = 15), representing the diversity of genetic elements present that might confer resistance, using Sensititre susceptibility plates (Thermo Fisher Scientific, https://www.thermofisher.com). We used human clinical breakpoints for MIC value interpretation.
Criteria for the Presence of the pESI Plasmid
We determined that the pESI plasmid was present if the plasmid replicon IncFIB (pN55391) or hyp_pESI, a 559bp target sequence (8), were present, together with >1 of 3 groups of genes previously described in pESI (8,18). Those gene groups included 4 AMR genes, sul1, tetA, aadA1, and qacEdelta1; yersiniabactin genes ybtP and ybtQ; or genes associated with the mer operon, merC, merP, merT, and merR.
Statistical Analysis
For statistical analysis, we used WINPEPI version 11.65 (19). We calculated Pearson χ2, Fisher exact test, and odds ratios (ORs) with 95% CIs, as appropriate.
Ethics Statement
Isolates used for the purpose of this research were collected as part of mandatory routine surveillance programs that were conducted according to the ethical standards and in compliance with Israel law. Clinical isolates from humans were obtained anonymously from the Ministry of Health, Public Health Laboratories, Jerusalem, Israel. Additional sampling was limited to environmental sampling of poultry farms.
Analysis A—Genetic Variability of Salmonella Muenchen in Poultry and Humans
We identified Salmonella Muenchen from all sources (n = 99) as ST82. Clustering according to source was not evident in the reconstructed maximum-likelihood tree (Figure 2). We identified 19 acquired AMR genes. We found the combination of aadA1, sul1, tetA, and qacE genes, associated with pESI and conferring resistance to streptomycin, sulfonamides, tetracyclines, and quaternary ammonium, in 92/99 (92.9%) isolates. We found that 86/99 (86.9%) isolates harbored the dfrA14 gene, conferring resistance to trimethoprim, and 16/99 (16.2%) isolates harbored the blaTEM gene, conferring resistance to β-lactams. In addition, 1 isolate from a chicken carcass harbored the blaOXA-808 gene. Genetic determinants associated with quinolone resistance were present in 58/99 (58.6%) isolates. We found the qnrB19 gene, associated with the presence of the Col (pHAD28) plasmid replicon, in 40/99 (40.4%) isolates, and the qnrS1 gene in 13/99 (13.1%) isolates. We found the S83A or S83F mutation in the DNA gyrase A (gyrA) gene in 6.1% (6/99) of isolates (Appendix 1 Figure 2; Appendix 2 Table 5). We further verified our findings using the Br19 hybrid assembly (Appendix 1). We found no significant difference in the presence of AMR genes across the different sources (Table 1). We identified the plasmid replicon IncFIB (pN55391), hyp_pESI, and the yersiniabactin genes ybtP and ybtQ, indicating the presence of pESI plasmid, in all but 1 strain, a human clinical isolate (Appendix 2 Table 5).
Phenotypic analysis of broiler isolates (n = 15) showed that all were resistant to tetracycline and sulfisoxazole (Appendix 2 Table 2). Despite a few minor exceptions, we observed an overall alignment between phenotype and the genotype (Table 2). The presence of either the qnrB19 or qnrS1 gene or gyrA S83F mutation alone conferred decreased susceptibility to ciprofloxacin (MICs >0.12 and <1 µg/mL) in 9/11 (81.8%) and clinical resistance (MIC = 1 µg/mL) in 1/11 of the tested isolates. The gyrA S83F mutation was associated with resistance to nalidixic acid; the presence of the gyrA mutation together with the qnrS1 gene (n = 1) conferred clinical resistance to ciprofloxacin (MIC = 1 µg/mL).
Analysis B—Salmonella Muenchen Transmission in the Broiler Production Industry
We determined Salmonella Muenchen prevalence of 64.0% (412/644) in group C samples collected as part of the active surveillance program from heavy-breeder flocks in 2021. We estimated Salmonella Muenchen prevalence in broiler flocks at 61.5% (95% CI 51.5%–71.5%; 48/78 isolates). We found no significant difference (p = 0.83) in prevalence between the broilers descendent from positive (26/43) and control (22/35) breeding groups. Moreover, we recovered Salmonella Muenchen isolates in 8/10 (80.0%) of the broiler barns in which it was previously detected, 15–20 months after the initial sampling; we referred to the poultry in those barns as repeat broilers.
We found no significant association between positivity in the breeder farm and detection of Salmonella Muenchen in chick samples (Table 3) or environmental swab samples collected in the barn (Table 4) and around the barn (Table 5). Positivity in the chicks was significantly associated with older age of chicks (OR = 8.1; p < 0.05). Positivity in the interior swab samples was associated with positivity in the exterior swabs collected at the same time (OR = 123; p < 0.01). In addition, positivity in the exterior swab samples was associated with sampling time, sampling after versus before marketing (OR = 8.25; p < 0.05).
Clustering of strains collected from parent breeding flocks and the descendant broiler flocks was not evident in the reconstructed phylogeny tree (Figure 3). In addition, we observed no genetic similarity between grandparents, pullets, hatcheries, and the breeder flocks, except for an instance of an isolate from a pullet flock (Br46) persisting (difference of 2 single-nucleotide polymorphisms [SNPs]) in the same flock when we sampled it 10 months later as a heavy-breeder flock (Br21). We observed evidence of clustering of samples collected by various sampling techniques (chicks, interior swabs, and exterior swabs) from the same barn in 7/13 barns (Figure 3). Repeat sampling of the broiler barns produced isolates that were closely related in 6/10 (60.0%) of the cases; 4 of those were highly genetically similar (4–8 SNPs) to the previous isolates from the same farm (Figure 3).
Although the samples we collected in various production stages were genetically heterogeneous, we found the frequencies of AMR gene presence in different production stages to be similar, based on a limited number of samples compared between sources (Table 6). We found similar frequencies of AMR genes in the positive and control groups (p>0.05) Table 7).
Analysis C—Global Distribution of Salmonella Muenchen Harboring pESI
We reconstructed a maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree from 11 isolates chosen from our study and 125 isolates from elsewhere globally (Appendix 1 Figure 3). We noted that Salmonella Muenchen was genetically diverse globally, represented by 11 different STs in our analysis. We distinguished 2 main genetic subpopulations; 1 genetic subpopulation consisted of ST83 (n = 38), and the other contained predominantly ST112 (n = 25) and ST82 (n = 49). ST83 was detected in the United States, Canada, and the United Kingdom from both human and food-animal sources. ST112 had a broader distribution, including strains from the United States, Canada, Mexico, United Kingdom, and Australia. We identified pESI exclusively in ST82 isolates. ST82, which also included isolates without pESI, was found in most of the countries represented. The pESI-positive ST82 isolates formed a clade and included all the isolates from our study and an additional 18 strains from other countries including the United States (n = 12), United Kingdom (n = 5), and South Africa (n = 1). Apart from the isolates collected in Israel representing both human and poultry sources, pESI-positive isolates were from human samples (n = 15) or from isolates from the NCBI database that lacked detailed information about source (n = 3) (Appendix 2 Table 4,6).
Salmonella Muenchen has become the dominant serovar in Israel; a surge in human clinical cases was associated with an increased prevalence in the poultry industry (7). We demonstrated genetic similarity, including the presence of the pESI megaplasmid, in isolates collected from poultry and chicken meat and from humans. Furthermore, we estimated a high prevalence (61.5% [95% CI 51.5%–71.5%]) of the emerging Salmonella Muenchen in broilers, and by tracing transmission pathways within the broiler industry we demonstrated that horizontal transmission plays a major role in its spread. Finally, we found that the emerging multidrug-resistant Salmonella Muenchen strain in Israel closely resembles pESI-positive Salmonella Muenchen isolates from other countries, underscoring the potential for clonal expansion and the risk to public health.
Various sources, such as food (21) and animal hosts (22), are associated with NTS infections, and circulation between animal hosts, which could potentially form additional transmission pathways to humans, have been described previously (23). Salmonella Muenchen has been detected in a wide range of foods of animal origin, including beef, seafood, and pork (24), and in plant-based foods (25). Chicken meat has rarely been documented as a source of infection; the last reported outbreak in the United States occurred in 2015 (26). However, our findings strongly suggest that poultry broilers are an important source of human infections caused by Salmonella Muenchen in Israel. The high genetic similarity between strains collected from broiler flocks and layer flocks may indicate that eggs serve as an additional source for human infections, however their role as a route of transmission to humans needs to be further explored.
Controlling Salmonella Muenchen in the poultry industry in Israel will be crucial to curb the incidence of infections in the human population. Vaccinating breeder flocks can be effective (2), assuming that the transmission of the pathogen is mainly vertical from the parent to the production flocks. A previous study (27) examining the transmission of Salmonella within vertically integrated poultry operations suggested, on the basis of serologic and molecular methods, that transmission pathways are varied and might depend on the serotype; certain serotypes, including Salmonella Muenchen, transmitted horizontally to broiler flocks after hatching. Our findings, supported by advanced large-scale genetic analysis, further support that route of transmission in the emerging Salmonella Muenchen spread. Our conclusion is based on the lack of clustering of isolates from broiler flocks with their parent breeding flocks and lack of significant risk for Salmonella Muenchen positivity in broiler flocks descending from Salmonella Muenchen–positive breeder flocks. Additional findings supported on-site infection and horizontal transmission, such as the significantly increased risk for Salmonella Muenchen positivity in older chicks, genetic clustering of isolates within and between broiler farms, and evidence of strains persisting in broiler barns over time. Therefore, we suspect that the initiation of mandatory vaccination of breeder flocks in Israel against Salmonella Muenchen as of March 2024 (Bulletin notice, Ministry of Agriculture, 2023 Aug) may result in a limited reduction in the prevalence of Salmonella Muenchen, because Salmonella persists in the farm soil or barn litter (28). Other possible measures that can be employed on the farms or along the production chain (e.g., during transport) to decrease the prevalence of Salmonella Muenchen include increasing biosecurity by different measures, such as controlled farm access and thorough cleaning and disinfection between flocks. Sources for Salmonella contamination, including poultry feed and pests (29–31), may also be controlled. In addition, techniques such as fecal microbiota transplants to chicks to prevent colonization of Salmonella spp. via competitive exclusion and the use of probiotics are potential methods to reduce gastrointestinal colonization (31,32). Increased surveillance and control of this serotype along the production chain, such as during transport, in the slaughterhouse, and during processing, might also reduce transmission to the human consumer.
The public health risk associated with transmission of multidrug-resistant Salmonella is considered one of the biggest threats to global health (33). Surveillance data from the Ministry of Health reported that 30/77 (39.0%) of Salmonella Muenchen isolates collected in 2021 from humans and 21/41 (51.2%) from nonhuman sources had reduced susceptibility to ciprofloxacin (7), which is critical for treatment of invasive salmonellosis in humans (34). In our study, 11/21 (52.4%) of human and 47/78 (60.3%) of poultry isolates contained chromosomal point mutations on the gyrA gene, or harbored qnr genes known to be involved in conferring resistance to quinolones (35). Phenotypic testing revealed that all isolates exhibiting decreased susceptibility or resistance to ciprofloxacin had >1 of those resistance determinants present. The presence of the transmissible blaOXA-808 gene in an isolate recovered from poultry meat was unusual. That gene, belonging to the blaOXA-23 family, a group of carbapenem-hydrolyzing β-lactamases, was previously reported in Acinetobacter species (36). Although Salmonella has been known to harbor blaOXA genes (37), this specific variant had not been previously reported. Potential carbapenem resistance is an alarming finding because carbapenem is a broad-spectrum antimicrobial drug reserved as a last-resort treatment for bacterial infections in humans (34).
Phenotypic resistance aligned with genotype with a few exceptions: tetracycline, chloramphenicol, ampicillin, sulfisoxazole, and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole. We observed 3 MDR isolates exhibiting resistance to >1 of those antimicrobial drugs with no known AMR gene present. Such discordances may be the result of various potential mechanisms, such as AMR determinants yet to be described (38).
The surge in prevalence of Salmonella Muenchen in poultry since 2018 correlated with a marked increase in the frequency of pESI-positive isolates: from 146 Salmonella Muenchen isolates collected by the EPB during 2009–2021, pESI was detected in only 3/50 (6.0%) of isolates before 2018 but in 85/96 (88.5%) of isolates since January 2018 (E. Elnekave, unpub. data). In this study, we demonstrated the continuation of the trend; 100.0% (88/88) of poultry isolates harbored the plasmid. The pESI plasmid provides fitness advantages to the bacterial host, such as increased tolerance to mercury and oxidative stress, and AMR (9). Those advantages might contribute to the high prevalence and spread of the pESI-harboring Salmonella Muenchen; further studies are required to determine which of the specific advantages and under what conditions enable Salmonella Muenchen propagation in the broiler industry in Israel.
We found that the Israel Salmonella Muenchen strains were genetically similar to strains collected in the United Kingdom, South Africa, and the United States. All belonged to ST82 and harbored pESI. Such clonality might suggest travel-associated transmission of Salmonella Muenchen or might be a result of a common origin and global dissemination of contaminated poultry breeding stock, as suggested previously with this serotype (8) and others (39). In addition, the strain was recently reported from the West Bank (40), which suggests regional spread. The relatively rare identification of pESI in strains other than Salmonella Infantis ST32 and Salmonella Muenchen ST82 (18) might indicate an adaptation mechanism to the plasmid that has not been determined. Given the vast global spread of Salmonella Infantis harboring pESI (11) since its detection (9), it is highly possible that a pESI-harboring Salmonella Muenchen ST82 will be the next Salmonella to emerge globally.
Dr. Perry is a PhD student specializing in molecular epidemiology, focusing on the epidemiology and genetic characterization of emerging zoonotic pathogens. Her research on Salmonella serotypes contributes to preventing future infections, improving public and animal health and welfare.
Acknowledgments
We thank the poultry farm owners and poultry veterinarians for their collaboration.
The Hebrew University of Jerusalem internal fund supported this work in a seed fund to E.E. The Israeli Ministry of Agriculture supported the work (grant no. 12-11-0001 to E.E., A.W. and A.R.).
Raw reads from isolates sequenced in this study (n = 109) are available in the Sequence Read Archive database of NCBI under Bioproject PRJNA1192251, accession nos. SRR31558526–SRR31558634 (short reads) and SRR31558786 (long reads). Metadata and accession numbers are provided in Appendix 2 Table 4.
Author contributions: E.E. and A.W. initiated and designed the study. A.W., C.S., Y.P., G.M., I.M., E.Y., and A.R. contributed samples and data. K.A., T.R., and J.P. performed laboratory work and data analysis. T.R. and J.P. collected samples. J.P. drafted the manuscript. All authors contributed to the scientific discussion and have read and approved the final manuscript.
References
- Kirk MD, Pires SM, Black RE, Caipo M, Crump JA, Devleesschauwer B, et al. World Health Organization estimates of the global and regional disease burden of 22 foodborne bacterial, protozoal, and viral diseases, 2010: a data synthesis. PLoS Med. 2015;12:
e1001921 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Koutsoumanis K, Allende A, Alvarez-Ordóñez A, Bolton D, Bover-Cid S, Chemaly M, et al.; EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards (EFSA BIOHAZ Panel). Salmonella control in poultry flocks and its public health impact. EFSA J. 2019;17:
e05596 .PubMedGoogle Scholar - Gast RK, Porter RE. Salmonella infections. In: Swayne DE Boulianne M, Logue CM, McDougald LR, Nair V, Suarez DL, et al., editors. Diseases of poultry. 14th ed. Hoboken (NJ, USA): Wiley-Blackwell; 2020. p. 719–53.
- Bassal R, Davidovich-Cohen M, Yakunin E, Rokney A, Ken-Dror S, Strauss M, et al. Trends in the epidemiology of non-typhoidal salmonellosis in Israel between 2010 and 2021. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20:5626. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Introduction to the annual epidemiological report. 2022 [cited 2024 Sep 20]. https://ecdc.europa.eu/en/annual-epidemiological-reports/methods
- Mikoleit M, Van Duyne MS, Halpin J, McGlinchey B, Fields PI. Variable expression of O:61 in Salmonella group C2. J Clin Microbiol. 2012;50:4098–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Israel Ministry of Health. Jerusalem Central Laboratories annual reports [in Hebrew] [cited 2024 Oct 9]. https://www.gov.il/he/collectors/publications?officeId=104cb0f4-d65a-4692-b590-94af928c19c0&limit=10&UnitId=d46cf637-e0b1-4b56-ae75-4e58f67ca8bf.
- Cohen E, Kriger O, Amit S, Davidovich M, Rahav G, Gal-Mor O. The emergence of a multidrug resistant Salmonella Muenchen in Israel is associated with horizontal acquisition of the epidemic pESI plasmid. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2022;28:1499 e7–e14.
- Aviv G, Tsyba K, Steck N, Salmon-Divon M, Cornelius A, Rahav G, et al. A unique megaplasmid contributes to stress tolerance and pathogenicity of an emergent Salmonella enterica serovar Infantis strain. Environ Microbiol. 2014;16:977–94. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Franco A, Leekitcharoenphon P, Feltrin F, Alba P, Cordaro G, Iurescia M, et al. Emergence of a clonal lineage of multidrug-resistant ESBL-producing Salmonella Infantis transmitted from broilers and broiler meat to humans in Italy between 2011 and 2014. PLoS One. 2015;10:
e0144802 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Alvarez DM, Barrón-Montenegro R, Conejeros J, Rivera D, Undurraga EA, Moreno-Switt AI. A review of the global emergence of multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica Serovar Infantis. Int J Food Microbiol. 2023;403:
110297 .PubMedGoogle Scholar - International Organization for Standardization. ISO 65791:2017 + A1:2020. Microbiology of the food chain—horizontal method for the detection, enumeration and serotyping of Salmonella. Part 1: detection of Salmonella spp. Geneva: The Organization; 2017 [cited 2024 Oct 2]. https://www.iso.org/standard/56712.html
- Arnold K, Lim S, Rakler T, Rovira A, Satuchne C, Yechezkel E, et al. Using genetic markers for detection and subtyping of the emerging Salmonella enterica subspecies enterica serotype Muenchen. Poult Sci. 2022;101:
102181 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Wick RR, Judd LM, Gorrie CL, Holt KE. Unicycler: Resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. PLoS Comput Biol. 2017;13:
e1005595 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Kozlov AM, Darriba D, Flouri T, Morel B, Stamatakis A. RAxML-NG: a fast, scalable and user-friendly tool for maximum likelihood phylogenetic inference. Bioinformatics. 2019;35:4453–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nurk S, Bankevich A, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Korobeynikov A, Lapidus A, et al. Assembling single-cell genomes and mini-metagenomes from chimeric MDA products. J Comput Biol. 2013;20:714–37. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Elnekave E, Hong SL, Lim S, Johnson TJ, Perez A, Alvarez J, et al. Comparing serotyping with whole-genome sequencing for subtyping of non-typhoidal Salmonella enterica: a large-scale analysis of 37 serotypes with a public health impact in the USA. Microb Genom. 2020;6:mgen000425. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Dos Santos AMP, Panzenhagen P, Ferrari RG, Conte-Junior CA. Large-scale genomic analysis reveals the pESI-like megaplasmid presence in Salmonella Agona, Muenchen, Schwarzengrund, and Senftenberg. Food Microbiol. 2022;108:
104112 .PubMedGoogle Scholar - Abramson JH. WINPEPI updated: computer programs for epidemiologists, and their teaching potential. Epidemiol Perspect Innov. 2011;8:1. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. 33rd edition. Wayne (PA): The Institute; 2023.
- Pires SM, Vieira AR, Hald T, Cole D. Source attribution of human salmonellosis: an overview of methods and estimates. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2014;11:667–76. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- DE Knegt LV, Pires SM, Hald T. Attributing foodborne salmonellosis in humans to animal reservoirs in the European Union using a multi-country stochastic model. Epidemiol Infect. 2015;143:1175–86. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Perry J, Arnold K, Satuchne C, Koren O, Kenigswald G, Elnekave E. Accumulation of resistance genes in Salmonella Typhimurium transmitted between poultry and dairy farms increases the risk to public health. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024;90:
e0229723 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Ferrari RG, Rosario DKA, Cunha-Neto A, Mano SB, Figueiredo EES, Conte-Junior CA. Worldwide epidemiology of Salmonella serovars in animal-based foods: a meta-analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019;85:e00591–19. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Danyluk MD, Jones TM, Abd SJ, Schlitt-Dittrich F, Jacobs M, Harris LJ. Prevalence and amounts of Salmonella found on raw California almonds. J Food Prot. 2007;70:820–7.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Marshall KE, Cui Z, Gleason BL, Hartley C, Wise ME, Bruce BB, et al. An approach to describe Salmonella serotypes of concern for outbreaks: using burden and trajectory of outbreak-related illnesses associated with meat and poultry. J Food Prot. 2024;87:
100331 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Crabb HK, Allen JL, Devlin JM, Firestone SM, Wilks CR, Gilkerson JR. Salmonella spp. transmission in a vertically integrated poultry operation: Clustering and diversity analysis using phenotyping (serotyping, phage typing) and genotyping (MLVA). PLoS One. 2018;13:
e0201031 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Dunn LL, Sharma V, Chapin TK, Friedrich LM, Larson CC, Rodrigues C, et al. The prevalence and concentration of Salmonella enterica in poultry litter in the southern United States. PLoS One. 2022;17:
e0268231 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Wales AD, Carrique-Mas JJ, Rankin M, Bell B, Thind BB, Davies RH. Review of the carriage of zoonotic bacteria by arthropods, with special reference to Salmonella in mites, flies and litter beetles. Zoonoses Public Health. 2010;57:299–314.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jones FT. A review of practical Salmonella control measures in animal feed. J Appl Poult Res. 2011;20:102–13. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Obe T, Boltz T, Kogut M, Ricke SC, Brooks LA, Macklin K, et al. Controlling Salmonella: strategies for feed, the farm, and the processing plant. Poult Sci. 2023;102:
103086 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Maurer JJ, Cheng Y, Pedroso A, Thompson KK, Akter S, Kwan T, et al. Peeling back the many layers of competitive exclusion. Front Microbiol. 2024;15:
1342887 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Antunes P, Mourão J, Campos J, Peixe L. Salmonellosis: the role of poultry meat. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2016;22:110–21.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kariuki S, Gordon MA, Feasey N, Parry CM. Antimicrobial resistance and management of invasive Salmonella disease. Vaccine. 2015;33(Suppl 3):C21–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chang M-X, Zhang J-F, Sun Y-H, Li R-S, Lin X-L, Yang L, et al. Contribution of different mechanisms to ciprofloxacin resistance in Salmonella spp. Front Microbiol. 2021;12:
663731 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Zong G, Zhong C, Fu J, Zhang Y, Zhang P, Zhang W, et al. The carbapenem resistance gene blaOXA-23 is disseminated by a conjugative plasmid containing the novel transposon Tn6681 in Acinetobacter johnsonii M19. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2020;9:182. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bolzoni L, Scaltriti E, Bracchi C, Angelone S, Menozzi I, Taddei R, et al. Emergence of Salmonella enterica carrying bla OXA-181 carbapenemase gene, Italy, 2021 to 2024. Euro Surveill. 2025;30:
2500175 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Rebelo AR, Bortolaia V, Leekitcharoenphon P, Hansen DS, Nielsen HL, Ellermann-Eriksen S, et al. One day in Denmark: comparison of phenotypic and genotypic antimicrobial susceptibility testing in bacterial isolates from clinical settings. Front Microbiol. 2022;13:
804627 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Miller EA, Elnekave E, Flores-Figueroa C, Johnson A, Kearney A, Munoz-Aguayo J, et al. Emergence of a novel Salmonella enterica serotype reading clonal group is linked to its expansion in commercial turkey production, resulting in unanticipated human illness in North America. mSphere. 2020;5:e00056–20. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Abukhattab S, Hosch S, Abu-Rmeileh NME, Hasan S, Vonaesch P, Crump L, et al. Whole-genome sequencing for One Health surveillance of antimicrobial resistance in conflict zones: a case study of Salmonella spp. and Campylobacter spp. in the West Bank, Palestine. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023;89:
e0065823 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Figures
Tables
Cite This ArticleOriginal Publication Date: September 22, 2025
Table of Contents – Volume 31, Number 10—October 2025
| EID Search Options |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|


Please use the form below to submit correspondence to the authors or contact them at the following address:
Ehud Elnekave, Koret School of Veterinary Medicine, The Robert H. Smith Faculty of Agriculture, Food and Environment, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Herzl St 229, Rehovot 7610001, Israel
Top