Volume 31, Number 10—October 2025
Research
Effect of Seasonal Influenza Vaccines on Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Clade 2.3.4.4b Virus Infection in Ferrets
Figure 6
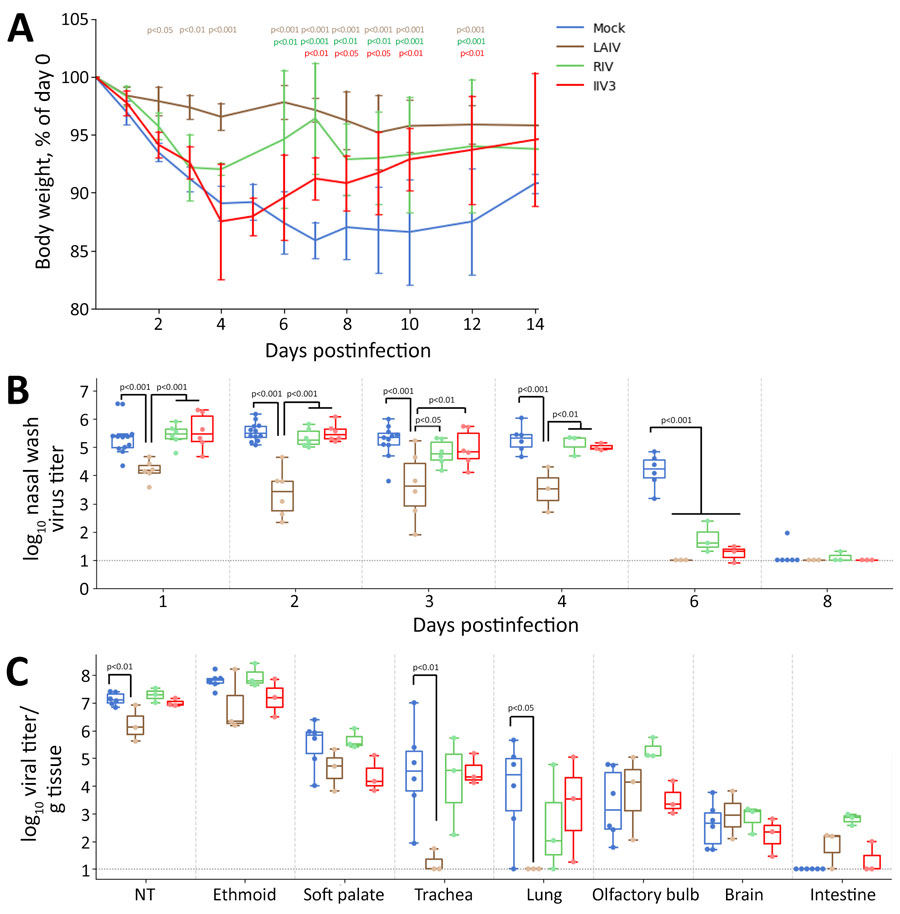
Figure 6. Body weight and influenza A(H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4b viral titers from nasal wash and tissue samples collected during study of the effect of seasonal influenza vaccines on clade 2.3.4.4b H5N1 virus infection in ferrets. n = 6 ferrets per vaccinated group, n = 12 ferrets in the mock vaccinated group. A) Body weights were monitored for 14 days postinfection and scaled to each ferret’s weight on day 0. We assessed p values relative to the mock-infected group by using a linear mixed model with repeated measures in R with lmerTest version 3.1.3 (The R Project for Statistical Computing, https://www.r-project.org); p values are indicated in colors matching the relevant body weight traces. Lines are plotted as means ± SDs. B) We collected nasal washes with phosphate buffered saline and measured the amount of virus by standard plaque formation assays. We assessed p values by using a linear mixed model with repeated measures in R with lmerTest version 3.1.3. C) Three days after infection, we euthanized 3 ferrets per immunized group and 6 ferrets in the mock control group. We measured the amount of virus present in each tissue sample by standard plaque formation assay and assessed p values relative to the mock-infected group. In panels B and C, colored dots indicate individual values, horizontal lines within boxes represent geometric mean titers, box tops and bottoms indicate interquartile ranges, and error bars indicate limits of the distribution. Dotted gray horizontal line indicates limit of detection. IIV3, Fluarix trivalent inactivated influenza vaccine (GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals, https://www.gsk.com); LAIV, FluMist live attenuated influenza vaccine (AstraZeneca, https://www.astrazeneca.com); RIV, Flublok recombinant influenza vaccine (Sanofi, https://www.sanofi.com).
1These first authors contributed equally to this article.