Volume 31, Number 11—November 2025
Research
Monkeypox Virus Partial-Genome Amplicon Sequencing for Improvement of Genomic Surveillance during Mpox Outbreaks
Figure 4
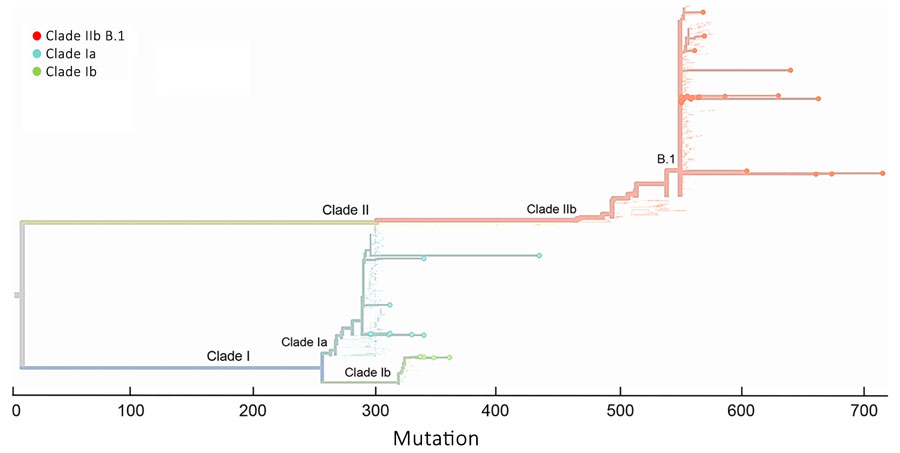
Figure 4. Amplicon-based phylogenetic assignment of monkeypox virus by 10-kb and 15-kb regions in Nextclade 3.10.0 (https://clades.nextstrain.org) for study of partial-genome amplicon sequencing for improvement of genomic surveillance during mpox outbreaks. Sixteen clinical specimens from Democratic Republic of the Congo were assigned to clade Ia or Ib, and 33 clinical specimens from United States were assigned to clade IIb lineage B.1.
Page created: November 18, 2025
Page updated: December 10, 2025
Page reviewed: December 10, 2025
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.