Volume 31, Supplement—May 2025
SUPPLEMENT ISSUE
Supplement
Lessons from 5 Years of Routine Whole-Genome Sequencing for Epidemiologic Surveillance of Shiga Toxin–Producing Escherichia coli, France, 2018–2022
Figure 3
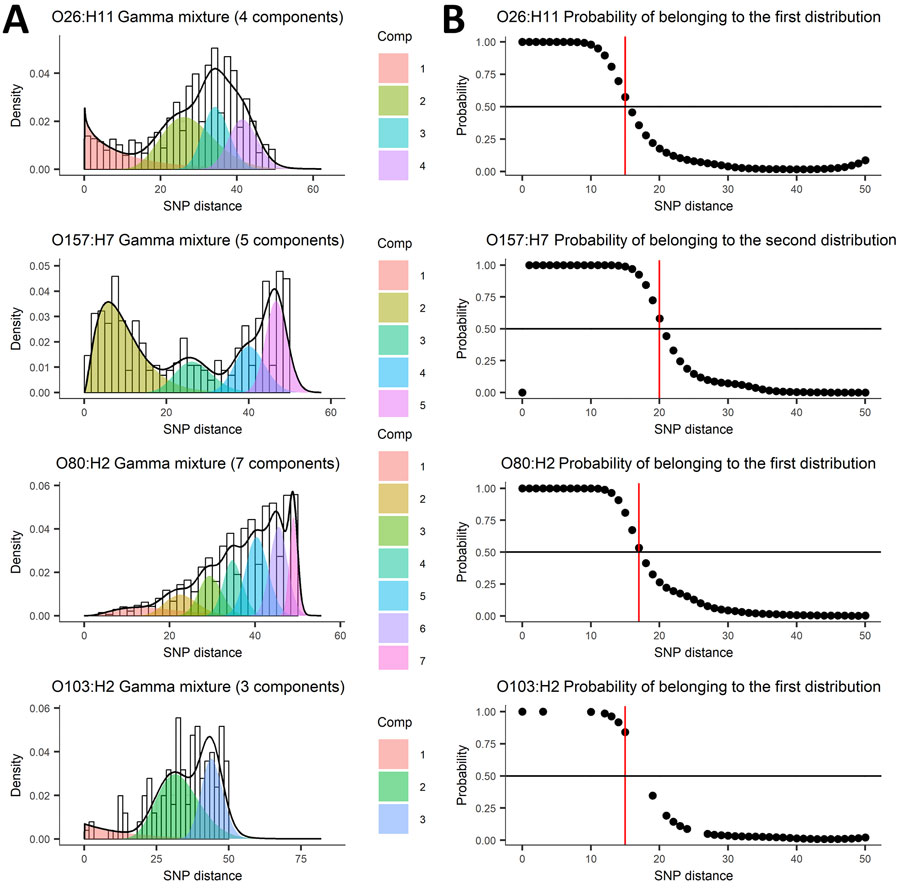
Figure 3. Mixture of distributions model applied to SNP distance data from 5 years of routine whole-genome sequencing for epidemiologic surveillance of Shiga toxin–producing Escherichia coli, France, 2018–2022. A) Number of components fit to the data distribution; B) threshold represented as a probability of belonging to the first or second distribution. Shiga toxin–producing Escherichia coli serotypes are shown for each panel. Comp, component; SNP, single-nucleotide polymorphism.
Page created: April 08, 2025
Page updated: May 12, 2025
Page reviewed: May 12, 2025
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.