Volume 31, Supplement—May 2025
SUPPLEMENT ISSUE
Supplement
Lessons from 5 Years of Routine Whole-Genome Sequencing for Epidemiologic Surveillance of Shiga Toxin–Producing Escherichia coli, France, 2018–2022
Figure 5
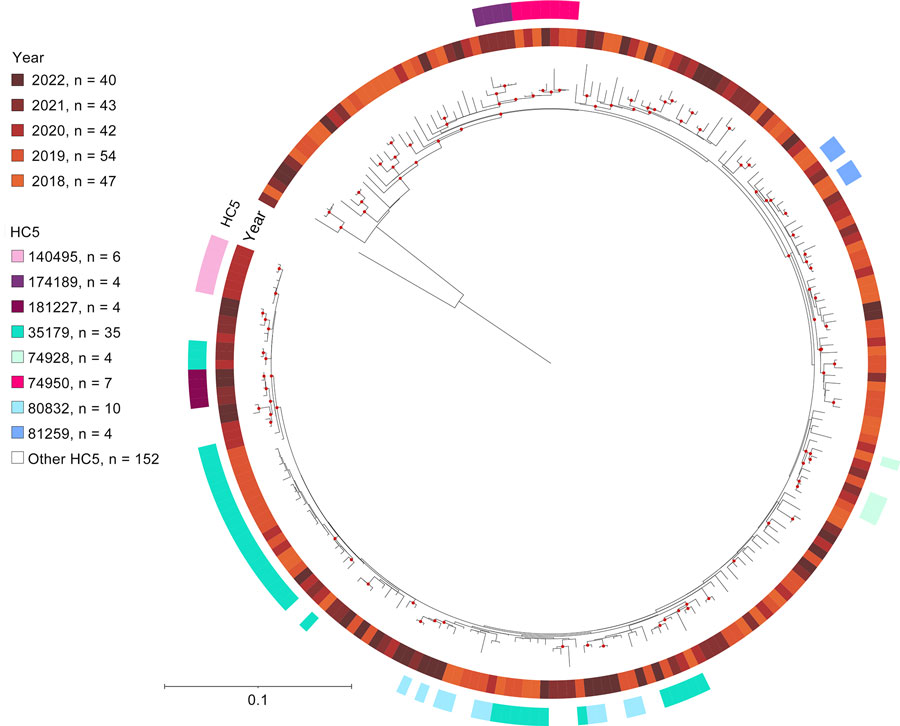
Figure 5. Single-nucleotide polymorphism–based maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of 226 080:H2 isolates from 5 years of routine whole-genome sequencing for epidemiologic surveillance of Shiga toxin–producing Escherichia coli, France, 2018–2022. Tree was built based on the sequence alignment of 3,949 single-nucleotide variant sites of the recombination-free core genome of E. coli strain MOD1-EC6881 (GenBank accession no. GCF_002520045.1). Tree was midpoint-rooted and visualized with iTOL (https://itol.embl.de). Bootstrap support values >90% are indicated with red dots on the branches. Branch lengths and corresponding scale bar indicate numbers of single-nucleotide polymorphisms per base of the final alignment. HC5, hierarchical clustering at a threshold of 5 allelic differences.