Volume 31, Number 9—September 2025
Research Letter
Characterization of Emerging Human Dirofilaria repens Infections, Estonia, 2023
Figure 2
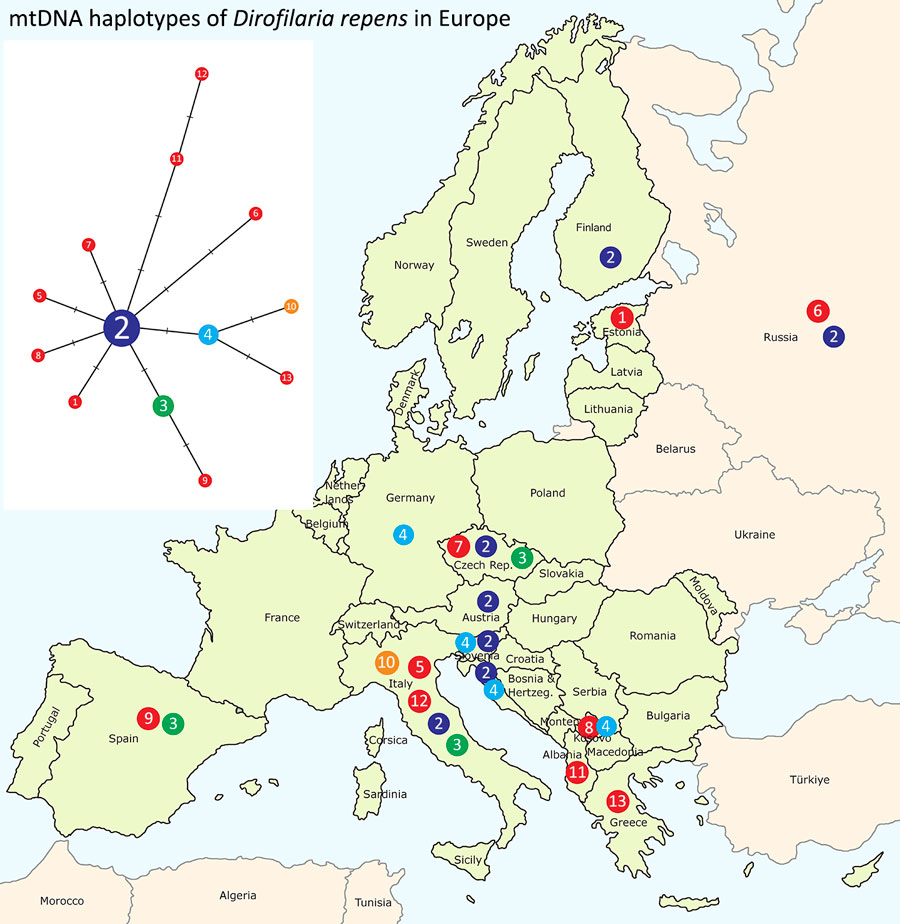
Figure 2. Distribution map of emerging Dirofilaria repens haplotypes (n = 13) in Europe, including samples from Estonia, 2023. Haplotypes were derived from the median joining network analysis (left), illustrating relationships of D. repens isolates (n = 39) from Estonia and other countries. We established relationships on the basis of partial mtDNA cox1 gene sequence variation (570 bp). The circled number is the haplotype identification number. Red circles represent haplotypes with unique sequences. Haplotypes represented by >2 are in different colors. Each crossed bar equates to a single-nucleotide polymorphism differentiating the haplotypes. Of note, the human isolate In2 from Estonia has a unique haplotype 1, which is closely related to the central haplotype 2, reported previously in D. repens isolates from humans, dogs, and mosquitoes in various countries (Appendix Table 2). mtDNA, mitochondrial DNA.