Volume 31, Number 9—September 2025
Research
Sporothrix brasiliensis Treatment Failure without Initial Elevated Itraconazole MICs in Felids at Border of Brazil
Figure 3
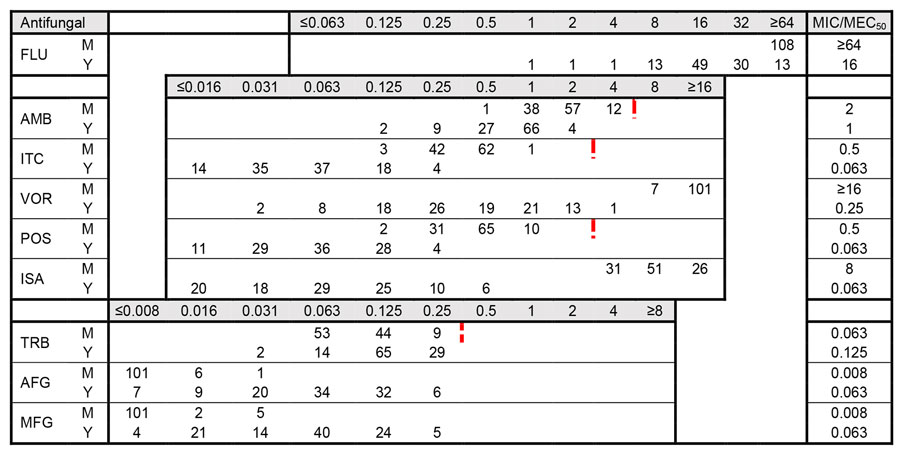
Figure 3. Distribution of MICs for 108 clinical isolates in study of Sporothrix brasiliensis treatment failure without initial elevated itraconazole MICs in felids at border of Brazil. MICs were determined according to Clinical Laboratory and Standards Institute M38 (22) and M27 (24) guidelines. Red dotted lines indicate division of wild-type versus non–wild-type isolates based on ECV values proposed by Espinel-Ingroff (23), when available. The ECV value for voriconazole is 32 µg/mL. MICs are given in µg/mL. For AFG and MFG, the MEC50 (filamentous phase) was determined. AFG, anidulafungin; AMB, amphotericin B; FLU, fluconazole; ISA, isavuconazole; ITC, itraconazole; M, mycelial phase; MEC50, minimal effective concentration that inhibits 50% of isolates; MFG, micafungin; MIC50, MIC that inhibits 50% of isolates; POS, posaconazole; TRB, terbinafine; VOR, voriconazole; Y, yeast phase.
References
- Rossow JA, Queiroz-Telles F, Caceres DH, Beer KD, Jackson BR, Pereira JG, et al. A One Health approach to combatting Sporothrix brasiliensis: narrative review of an emerging zoonotic fungal pathogen in South America. J Fungi (Basel). 2020;6:247. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rodrigues AM, Della Terra PP, Gremião ID, Pereira SA, Orofino-Costa R, de Camargo ZP. The threat of emerging and re-emerging pathogenic Sporothrix species. Mycopathologia. 2020;185:813–42. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rodrigues AM, Gonçalves SS, de Carvalho JA, Borba-Santos LP, Rozental S, Camargo ZP. Current progress on epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment of sporotrichosis and their future trends. J Fungi (Basel). 2022;8:776. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- do Prado CM, Razzolini E, Santacruz G, Ojeda L, Geraldo MR, Segovia N, et al. First cases of feline sporotrichosis caused by Sporothrix brasiliensis in Paraguay. J Fungi (Basel). 2023;9:972. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Etchecopaz A, Toscanini MA, Gisbert A, Mas J, Scarpa M, Iovannitti CA, et al. Sporothrix brasiliensis: a review of an emerging South American fungal pathogen, its related disease, presentation and spread in Argentina. J Fungi (Basel). 2021;7:170. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Thomson P, González C, Blank O, Ramírez V, Río CD, Santibáñez S, et al. Sporotrichosis outbreak due to Sporothrix brasiliensis in domestic cats in Magallanes, Chile: a One-Health-approach study. J Fungi (Basel). 2023;9:226. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gallo S, Arias-Rodriguez C, Sánchez-Cifuentes EA, Santa-Vélez C, Larrañaga-Piñeres I, Gaviria-Barrera ME, et al. First three cases of cat-associated zoonotic cutaneous sporotrichosis in Colombia. Int J Dermatol. 2022;61:1276–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cognialli RCR, Cáceres DH, Bastos FAGD, Cavassin FB, Lustosa BPR, Vicente VA, et al. Rising incidence of Sporothrix brasiliensis infections, Curitiba, Brazil, 2011–2022. Emerg Infect Dis. 2023;29:1330–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rabello VBS, Almeida MA, Bernardes-Engemann AR, Almeida-Paes R, de Macedo PM, Zancopé-Oliveira RM. The historical burden of sporotrichosis in Brazil: a systematic review of cases reported from 1907 to 2020. Braz J Microbiol. 2022;53:231–44. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Etchecopaz AN, Lanza N, Toscanini MA, Devoto TB, Pola SJ, Daneri GL, et al. Sporotrichosis caused by Sporothrix brasiliensis in Argentina: Case report, molecular identification and in vitro susceptibility pattern to antifungal drugs. J Mycol Med. 2020;30:
100908 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Barnacle JR, Chow YJ, Borman AM, Wyllie S, Dominguez V, Russell K, et al. The first three reported cases of Sporothrix brasiliensis cat-transmitted sporotrichosis outside South America. Med Mycol Case Rep. 2022;39:14–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kaadan MI, Dennis M, Desai N, Yadavalli G, Lederer P. One Health education for future physicians: a case report of cat-transmitted sporotrichosis. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2020;7:ofaa049. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Queiroz-Telles F, Cognialli RC, Salvador GL, Moreira GA, Herkert PF, Hagen F. Cutaneous disseminated sporotrichosis in immunocompetent patient: Case report and literature review. Med Mycol Case Rep. 2022;36:31–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bastos F, Farias M, Monti F, Cognialli R, Lopuch L, Gabriel A, et al. Spread of Sporothrix brasiliensis from the sneeze of infected cats: a potential novel route of transmission. Med Mycol. 2022;60(Supplement_1):myac072P462. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Gremião IDF. Martins da Silva da Rocha E, Montenegro H, Carneiro AJB, Xavier MO, de Farias MR, et al. Guideline for the management of feline sporotrichosis caused by Sporothrix brasiliensis and literature revision. Braz J Microbiol. 2021;52:107–24. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Spruijtenburg B, Bombassaro A, Meijer EFJ, Rodrigues AM, Grisolia ME, Vicente VA, et al. Sporothrix brasiliensis genotyping reveals numerous independent zoonotic introductions in Brazil. J Infect. 2023;86:610–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Roldán Villalobos W, Monti F, Ferreira T, Sato S, Telles F, Farias M. Therapeutic efficacy of isavuconazole and potassium iodide in a cat with refractory sporotrichosis. Vet Dermatol. 2023;34:624–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nakasu CCT, Waller SB, Ripoll MK, Ferreira MRA, Conceição FR, Gomes ADR, et al. Feline sporotrichosis: a case series of itraconazole-resistant Sporothrix brasiliensis infection. Braz J Microbiol. 2021;52:163–71. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ribeiro Dos Santos A, Gade L, Misas E, Litvintseva AP, Nunnally NS, Parnell LA, et al. Bimodal distribution of azole susceptibility in Sporothrix brasiliensis isolates in Brazil. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2024;68:
e0162023 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Ramos MLM, Almeida-Silva F, de Souza Rabello VB, Nahal J, Figueiredo-Carvalho MHG, Bernardes-Engemann AR, et al. In vitro activity of the anthelmintic drug niclosamide against Sporothrix spp. strains with distinct genetic and antifungal susceptibility backgrounds. Braz J Microbiol. 2024;55:1359–68. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Waller SB, Ripoll MK, Pierobom RM, Rodrigues PRC, Costa PPC, Pinto FDCL, et al. Screening of alkaloids and withanolides isolated from Solanaceae plants for antifungal properties against non-wild type Sporothrix brasiliensis. J Mycol Med. 2024;34:
101451 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Reference method for broth dilution antifungal susceptibility testing of filamentous fungi. CLSI standard M38. 3rd edition. Wayne (PA): The Institute; 2017.
- Espinel-Ingroff A, Abreu DPB, Almeida-Paes R, Brilhante RSN, Chakrabarti A, Chowdhary A, et al. Multicenter, international study of MIC/MEC distributions for definition of epidemiological cutoff values for Sporothrix species identified by molecular methods. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017;61:e01057–17. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Reference method for broth dilution antifungal susceptibility testing of yeasts. CLSI standard M27. 4th edition. Wayne (PA): The Institute; 2017.
- Rodrigues AM, de Melo Teixeira M, de Hoog GS, Schubach TM, Pereira SA, Fernandes GF, et al. Phylogenetic analysis reveals a high prevalence of Sporothrix brasiliensis in feline sporotrichosis outbreaks. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013;7:
e2281 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Silva CE, Valeriano CA, Ferraz CE, Neves RP, Oliveira MM, Silva JC, et al. Epidemiological features and geographical expansion of sporotrichosis in the state of Pernambuco, northeastern Brazil. Future Microbiol. 2021;16:1371–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Alzuguir CLC, Pereira SA, Magalhães MAFM, Almeida-Paes R, Freitas DFS, Oliveira LFA, et al. Geo-epidemiology and socioeconomic aspects of human sporotrichosis in the municipality of Duque de Caxias, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, between 2007 and 2016. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2020;114:99–106.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- IBGE–Instituto Brasileiro De Geografia E Estatística. Cidades: Foz do Iguaçu. Rio de Janeiro: IBGE, 2022 [cited 2024 Nov 1]. https://cidades.ibge.gov.br/brasil/pr/foz-do-iguacu/panorama
- Review WP. Ciudad del Este, Paraguay population 2024 [cited 2024 Nov 1]. https://worldpopulationreview.com/cities/paraguay/ciudad-del-este
- do Prado CM, Svoboda WK, Chiyo L, Queiroz-Telles F. Fundamentos de Saúde Única (One Health) e Planejamento Estratégico Situacional para Implementação de Política Pública de Saúde para Prevenção e Controle da Esporotricose na Região da Tríplice Fronteira (Brasil, Paraguai, Argentina). In: Zilly A, da Silva RMM, editors. Saúde Pública Na Região Da Fronteira Brasil-Paraguai-Argentina. São Carlos: Pedro & João Editores; 2022. p. 101–18.
- Pereira SA, Gremião IDF, Kitada AAB, Boechat JS, Viana PG, Schubach TMP. The epidemiological scenario of feline sporotrichosis in Rio de Janeiro, State of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2014;47:392–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- de Miranda LHM, Meli M, Conceição-Silva F, Novacco M, Menezes RC, Pereira SA, et al. Co-infection with feline retrovirus is related to changes in immunological parameters of cats with sporotrichosis. PLoS One. 2018;13:
e0207644 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Araújo AA, Codeço C, F S Freitas D, M de Macedo P, A Pereira S, D F Gremião I, et al. Mathematical model of the dynamics of transmission and control of sporotrichosis in domestic cats. PLoS One. 2023;18:
e0272672 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Lloret A, Hartmann K, Pennisi MG, Ferrer L, Addie D, Belák S, et al. Sporotrichosis in cats: ABCD guidelines on prevention and management. J Feline Med Surg. 2013;15:619–23. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fernandez NB, Spruijtenburg B, Tiraboschi IN, Meis JF, Lugo A, López Joffre MC, et al. Genotyping and clonal origin of Sporothrix brasiliensis in human sporotrichosis cases in Argentina. Med Mycol Case Rep. 2024;43:
100633 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Fichman V, Almeida-Silva F, Francis Saraiva Freitas D, Zancopé-Oliveira RM, Gutierrez-Galhardo MC, Almeida-Paes R. Severe sporotrichosis caused by Sporothrix brasiliensis: antifungal susceptibility and clinical outcomes. J Fungi (Basel). 2022;9:49. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Reis EGD, Pereira SA, Miranda LHM, Oliveira RVC, Quintana MSB, Viana PG, et al. A randomized clinical trial comparing itraconazole and a combination therapy with itraconazole and potassium iodide for the treatment of feline sporotrichosis. J Fungi (Basel). 2024;10:101. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Waller SB, Dalla Lana DF, Quatrin PM, Ferreira MRA, Fuentefria AM, Mezzari A. Antifungal resistance on Sporothrix species: an overview. Braz J Microbiol. 2021;52:73–80. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fernández-Silva F, Capilla J, Mayayo E, Guarro J. Modest efficacy of voriconazole against murine infections by Sporothrix schenckii and lack of efficacy against Sporothrix brasiliensis. Mycoses. 2014;57:121–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lecca LO, Paiva MT, de Oliveira CSF, Morais MHF, de Azevedo MI, Bastos CVE, et al. Associated factors and spatial patterns of the epidemic sporotrichosis in a high density human populated area: A cross-sectional study from 2016 to 2018. Prev Vet Med. 2020;176:
104939 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Schubach TM, Schubach A, Okamoto T, Barros MB, Figueiredo FB, Cuzzi T, et al. Evaluation of an epidemic of sporotrichosis in cats: 347 cases (1998-2001). J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2004;224:1623–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Boechat JS, Oliveira MME, Almeida-Paes R, Gremião IDF, Machado ACS, Oliveira RVC, et al. Feline sporotrichosis: associations between clinical-epidemiological profiles and phenotypic-genotypic characteristics of the etiological agents in the Rio de Janeiro epizootic area. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2018;113:185–96. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chen Y, Ma F, Lu T, Budha N, Jin JY, Kenny JR, et al. Development of a physiologically based pharmacokinetic model for itraconazole pharmacokinetics and drug-drug interaction prediction. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2016;55:735–49. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Prentice AG, Glasmacher A. Making sense of itraconazole pharmacokinetics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005;56(Suppl 1):i17–22. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
1These first authors contributed equally to this article.
2These senior authors contributed equally to this article.