Volume 31, Number 9—September 2025
Dispatch
Related Melioidosis Cases with Unknown Exposure Source, Georgia, USA, 1983–2024
Figure 1
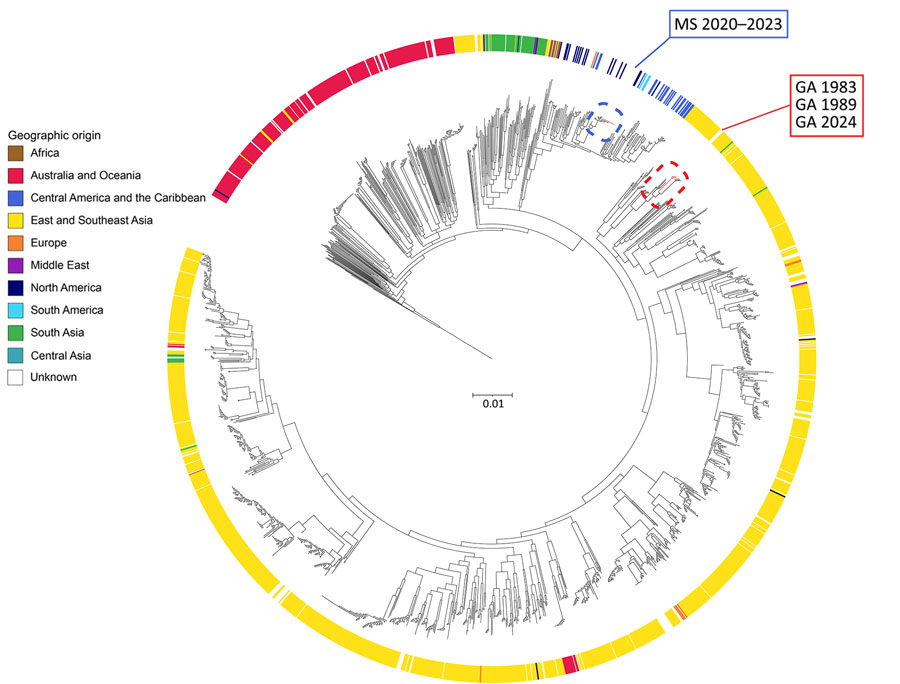
Figure 1. Global maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree of core-genome single-nucleotide polymorphisms comparing new isolate genomes from 4 related melioidosis cases with unknown exposure source, Georgia, USA, 1983–2024 (red dashed red rectangle), with all B. pseudomallei genomes from the Center for Disease Control and Prevention’s internal and National Center for Biotechnology Information’s worldwide RefSeq databases as of August 6, 2024 (n = 1,976 genomes). Strain MSHR668 was used as an outgroup. New isolate genomes are distinct from B. pseudomallei genomes isolated from the environment in Mississippi (dashed blue rectangle). Isolates with a reported geographic origin are associated with their country of origin and rings are colored according to definitions listed in The World Factbook (https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook). Scale bar units represent substitutions per site from a 22% core alignment against B. pseudomallei strain 110 (7.78 Mbp size, RefSeq accession no. GCF_001905265.1).
1These first authors contributed equally to this article.