Disclaimer: Early release articles are not considered as final versions. Any changes will be reflected in the online version in the month the article is officially released.
Volume 32, Number 2—February 2026
Research
Pulmonary Complications in Fatal Yellow Fever, Brazil, 2017–2019
Figure 2
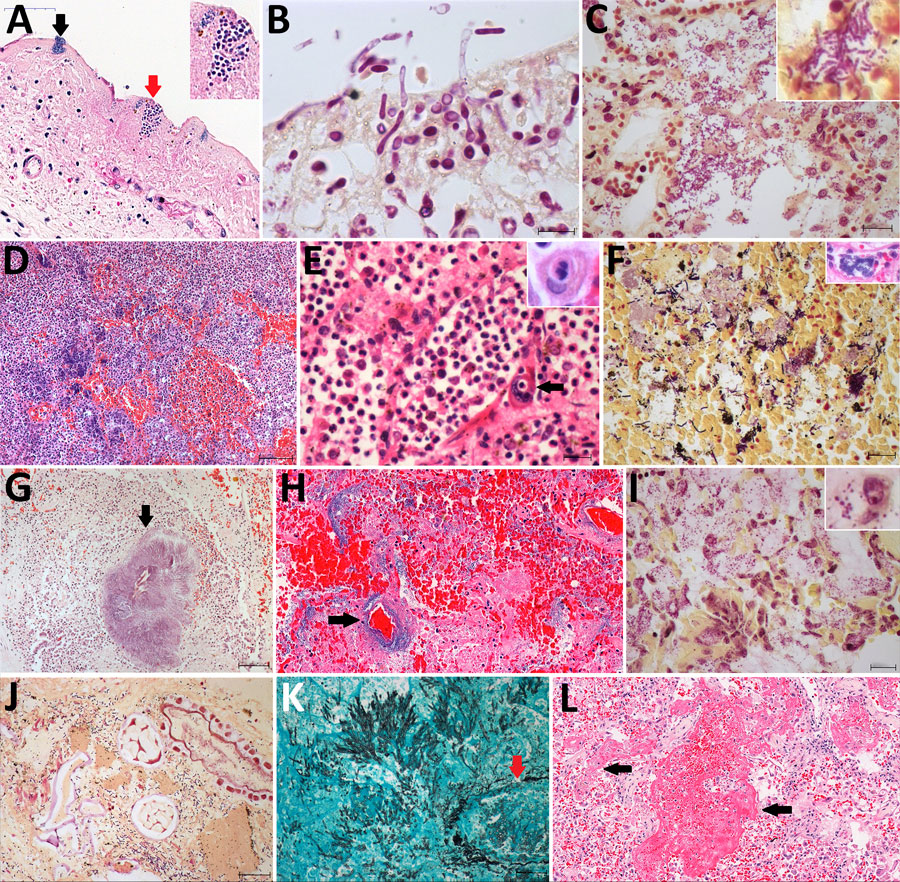
Figure 2. Pulmonary microscopic findings in patients with fatal yellow fever, São Paulo, Brazil, 2017–2019. A) Tracheal necrosis associated with bacilli (black arrow) and yeasts (inset and red arrow). Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) stain; scale bar = 50 µm. B) Candida albicans pseudohyphae and hyphae invading necrotic tracheal mucosa. Gram stain in immersion oil; scale bar = 10 µm. C) Bronchopneumonia associated with gram-negative bacilli. Gram stain; scale bar = 20 µm. D) Hemorrhagic pneumonia with microabscess composed of macrophages, neutrophils and colonies of coccus. HE stain; scale bar = 100 µm. E) Suppurative pneumonia showing hemophagocytosis (left inset) and a megakaryocyte in a septal vessel (arrow), with emperipolesis. HE stain; scale bar = 20 µm. Inset: megakaryocyte labeled by VIII factor antigen detected by immunohistochemistry. Peroxidase stain. F) Polymicrobial aspirative pneumonia with gram-positive cocci and gram-positive and gram-negative bacilli with different morphologies; the inset show a colony of bacilli in a septal vessel corresponding to agonal bacteremia. Gram stain; scale bar = 20 µm. Inset: HE stain. G) Actynomyces granule (arrow) with degenerated squamous cells in the center in an area of aspirative pneumonia. HE stain; scale bar = 100 µm. H) Pseudomonas hemorrhagic pneumonia, with numerous bacilli surrounding a septal vessel (arrow). HE stain; scale bar = 50 µm. I) Mycoplasma salivarium pneumonia, showing tiny gram-negative bacilli (inset) in the cytoplasm of intrabronchial macrophages. Gram stain; scale bar = 20 µm. J) Bronchoaspiration of vegetal alimentary material, associated with gram-negative bacilli, in the alveolar space. Gram stain; scale bar = 20 µm. K) Pulmonary angioinvasive aspergillosis, with typical hyphae invading pulmonary vessel (arrow), with associated necrosis and mild neutrophilic reaction. Grocott-Gomori methenamine silver stain; scale bar = 20 µm. L) Exudative diffuse alveolar damage, with congestion, alveolar edema, and hyaline membranes (arrow). HE stain; scale bar = 100 µm. Insets: original magnification ×400.