Disclaimer: Early release articles are not considered as final versions. Any changes will be reflected in the online version in the month the article is officially released.
Volume 32, Number 2—February 2026
Research
Pulmonary Complications in Fatal Yellow Fever, Brazil, 2017–2019
Figure 3
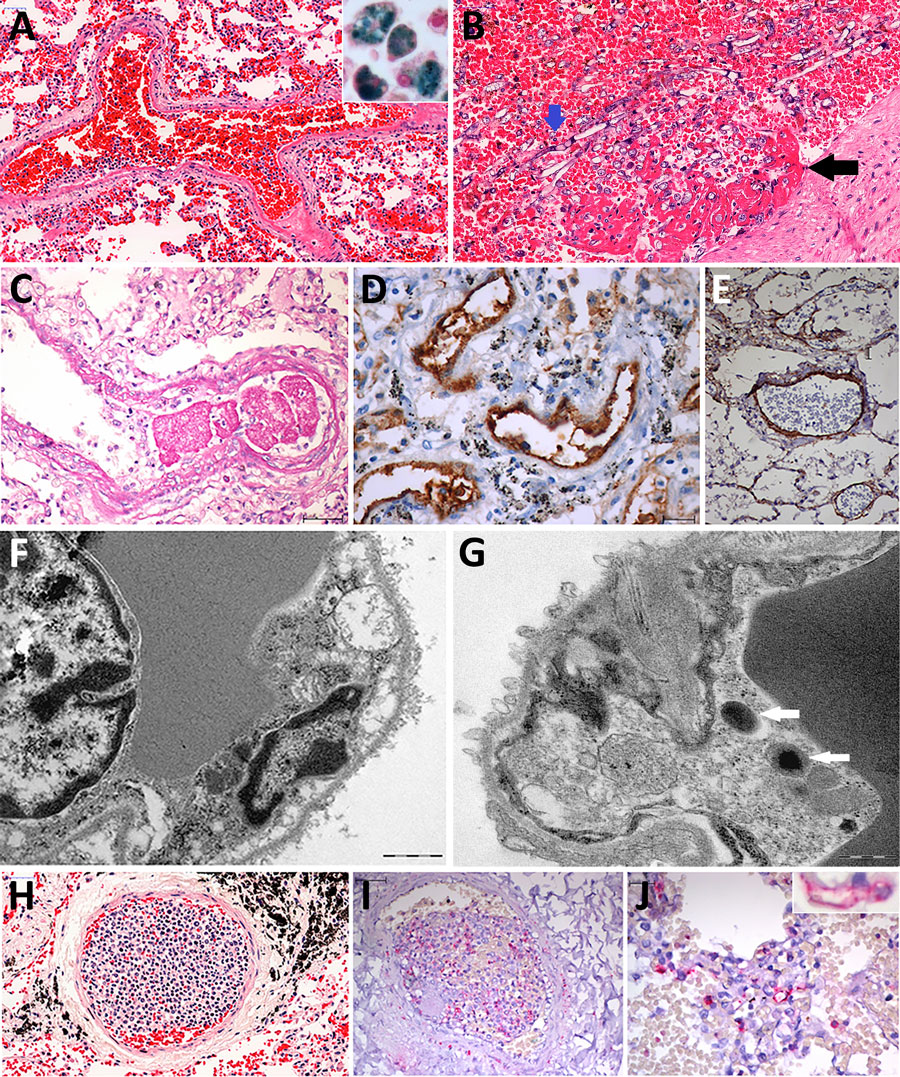
Figure 3. Pulmonary vascular damage in fatal yellow fever cases, 2017–2019 epidemic, São Paulo, Brazil. A) Medium-sized artery with fibrinoid necrosis of the endothelial layer, marginated leukocytes, wall edema, septal congestion, alveolar hemorrhage. Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) stain; scale bar represents 50 µm. Inset shows a group of hemosiderin-laden alveolar macrophages stained for iron. Perls stain; original magnification ×200. B) Pulmonary artery showing angioinvasion by Aspergillus spp. forming fibrinous thrombus on the endothelial vascular layer (black arrow). HE stain; scale bar (top) represents 50 µm. C) A small fibrin clot and the artery fibrinoid necrosis and wall edema. Periodic acid–Schiff stain; scale bar represents 50 µm. D) Positive detection of VIII coagulation factor in the entire wall of pulmonary arteries. Peroxidase stain; scale bar represents 20 µm. E) The VCAM is detected in the endothelial and muscular pulmonary artery layers. Peroxidase stain; scale bar represents 20 µm. F) Septal capillaries showing mitochondrial dilation with loss of cristae. Ultrathin section; scale bar represents 1 µm. G) Bacilli (arrows) within septal pulmonary vessel. Ultrathin section; scale bar represents 500 nm. H) Histologic leukostasis in a septal pulmonary artery, showing immature myeloid cells, lymphocytes, and neutrophils. HE stain; scale bar represents 50 µm. I) Intravascular cells expressing yellow fever virus antigens in their cytoplasm. Alkaline phosphatase stain; scale bar represents 50 µm. J) The yellow fever virus antigen is detected in the cytoplasm of septal endothelial cells (inset) and in interstitial and alveolar inflammatory cells. Alkaline phosphatase stain; scale bar represents 20 µm. Inset original magnification ×400.