Volume 14, Number 5—May 2008
Dispatch
Spread of Streptococcus suis Sequence Type 7, China
Figure 1
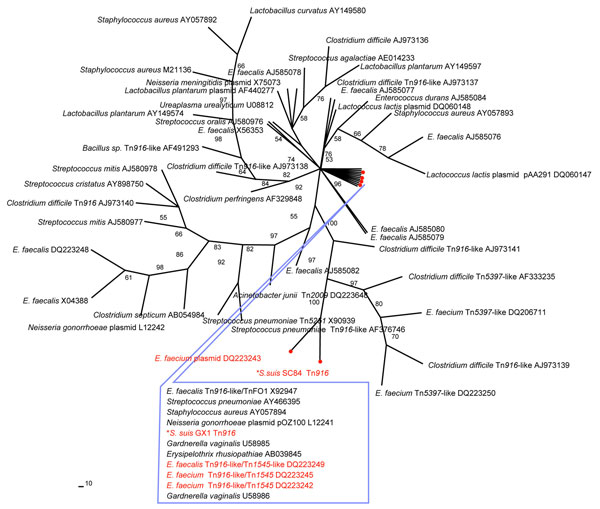
Figure 1. Phylogenetic relationship of the tetM sequences of Streptococcus suis. An unrooted maximum-parsimony tree was based on multiple aligned partial tetM sequences of 2 S. suis (asterisk) and 53 reference sequences retrieved from GenBank. The alignment length for the analysis was 1,415 bp. If available, the designation of the tetM-carrying plasmid or transposon is indicated, followed by the GenBank accession number. Percent bootstrap support at each internal node was based on 200 replicate trees. The sequences of known pig origin are marked in red.
Page created: July 08, 2010
Page updated: July 08, 2010
Page reviewed: July 08, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.