Volume 14, Number 7—July 2008
Dispatch
AIDS Patient Death Caused by Novel Cryptococcus neoformans × C. gattii Hybrid
Figure 1
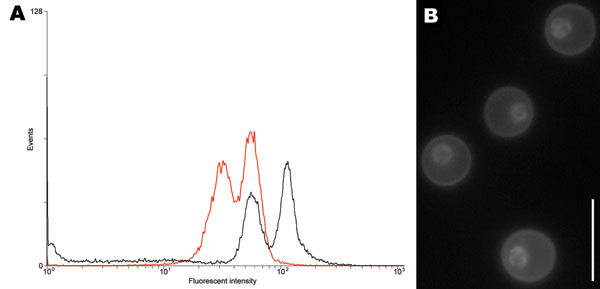
Figure 1. A) Determination of ploidy of the novel Cryptococcus neoformans × C. gattii serotype AB hybrid isolate CBS10496 by flow cytometry. The first peak corresponds to the G1 phase; the second peak corresponds to the G2 phase. Haploid reference strain CBS10510 is shown by the red line; CBS10496 is shown by the black line. The G1 peak of CBS10496 coincided with the G2 peak of strain CBS10510, which indicated that strain CBS10496 has approximately twice the amount of DNA than CBS10510. B) Nuclear staining of isolate CBS10496 with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole, showing that cells are monokaryotic. Scale bar = 10 μm.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
2Current affiliation: Netherlands Commission on Genetic Modification, Bilthoven, the Netherlands.