Volume 19, Number 2—February 2013
Dispatch
Human Granulocytic Anaplasmosis, Japan
Figure 1
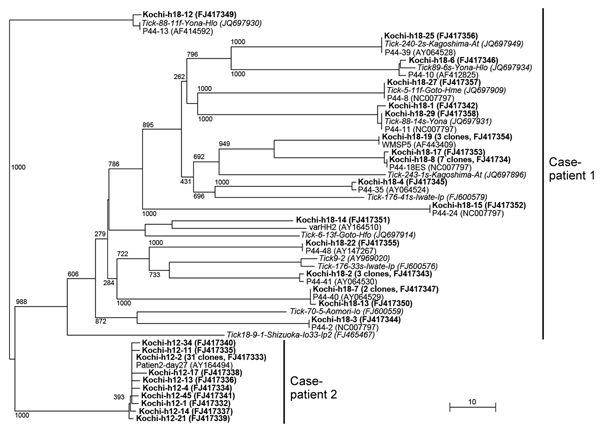
Figure 1. . . Phylogenetic analysis of Anaplasma phagocytophilum p44/msp2 multigenes detected in blood from 2 men in Kochi Prefecture, Japan. Each p44/msp2 PCR product was cloned (TA Cloning Kit; Life Technologies, Grand Island, NY, USA) into the PCR2.1 vector, after which recombinant clones were randomly selected and the DNA inserts were sequenced. The tree was constructed on the basis of the 117–133 aa sequences of the p44/msp2 genes by using the neighbor-joining method. The closest relatives to sequences for the 2 case-patients are included in the tree. Those sequences have been published in GenBank: patient2-day27 (obtained from a US patient); P44-2, P44-8, P44-10, P44-11, P44-13, P44-18E, P44-28, P44-35, P44-39, P44-40, P44-41, P44-48, varHH2, and WMSP5 are from human isolates; and 44-kDa outer membrane proteins are from ticks collected in Japan. Boldface font indicates the 28 p44/msp2 genes from case-patient 1 and the 40 from case-patient 2. Numbers on the tree indicate bootstrap values for branch points. Scale bar indicates the percent of sequence divergence. Data in parentheses indicate the number of p44/msp2 clones with identical sequences and the sequence accession numbers.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
2Current affiliation: Ehime Prefectural Central Hospital, Matsuyama, Ehime, Japan.
3Current affiliation: Kochi Medical School, Nankoku, Kochi, Japan.