Volume 20, Number 12—December 2014
Research
Geographic Divergence of Bovine and Human Shiga Toxin–Producing Escherichia coli O157:H7 Genotypes, New Zealand1
Figure 3
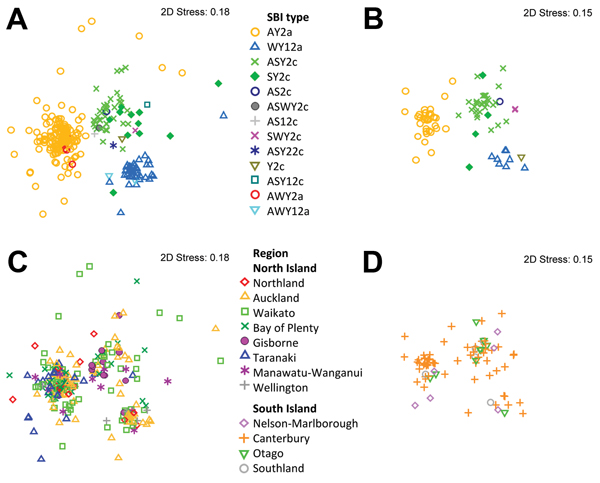
Figure 3. Multidimensional scaling plots showing the genotypic clustering of human Shiga toxin–producing Escherichia coli O157:H7 isolates originating from the North Island (n = 274, 4 isolates excluded) and the South Island (n = 81, 4 isolates excluded), New Zealand. The plots were determined on the basis of the isolates’ pulsed-field gel electrophoresis profiles. Clusters associated with Shiga toxin–encoding bacteriophage insertion (SBI) types (A) and regions (C) for isolates from the North Island. Clusters associated with SBI types (B) and regions (D) for isolates from the South Island. 2D, 2 dimensional.
1Preliminary results from this study were presented at the New Zealand Veterinary Association Conference; June 16–20, 2014, Hamilton, New Zealand.