Volume 20, Number 12—December 2014
Dispatch
Novel Amdoparvovirus Infecting Farmed Raccoon Dogs and Arctic Foxes
Figure 2
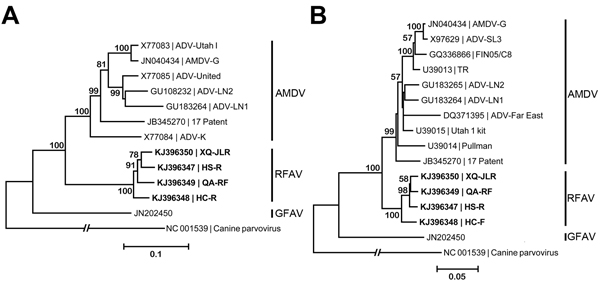
Figure 2. Phylogenetic analyses of amdoparvoviruses. A) Phylogenetic tree based on the viral NS1 gene. B) A phylogenetic tree based on the major capsid VP2. RFAV and other published amdoparvovirus sequences were aligned by using the MUSCLE program in MEGA5.2 (9), which used a P-distance model with 1,000 bootstrap replicates to generate phylogenetic trees of NS1 and VP2 aa sequences. GenBank accession numbers of isolates or strains are shown on the tree. Canine parvovirus was used as an outgroup. AMDV, Aleutian mink disease virus; GFAV, gray fox amdoparvovirus; RFAV, raccoon dog and fox amdoparvovirus; NS, nonstructural protein; VP, viral structural protein. Sequences obtained from this study are shown in bold. Scale bars indicate nucleotide substitutions per site.
References
- Cotmore SF, Agbandje-McKenna M, Chiorini JA, Mukha DV, Pintel DJ, Qiu J, The family Parvoviridae. Arch Virol. 2014;159:1239–47. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Li L, Pesavento PA, Woods L, Clifford DL, Luff J, Wang C, Novel amdovirus in gray foxes. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17:1876–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Farid AH. Aleutian mink disease virus in furbearing mammals in Nova Scotia, Canada. Acta Vet Scand. 2013;55:10–55. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Porter DD, Larsen AE, Porter HG. The pathogenesis of Aleutian disease of mink. 3. Immune complex arteritis. Am J Pathol. 1973;71:331–44 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cho HJ, Greenfield J. Eradication of Aleutian disease of mink by eliminating positive counterimmunoelectrophoresis test reactors. J Clin Microbiol. 1978;7:18–22 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Henson JB, Gorham JR, Leader RW. A field test for Aleutian disease. Natl.Fur.News. 1962;34:8–9.
- Djikeng A, Halpin R, Kuzmickas R, Depasse J, Feldblyum J, Sengamalay N, Viral genome sequencing by random priming methods. BMC Genomics. 2008;9:5–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Oleksiewicz MB, Costello F, Huhtanen M, Wolfinbarger JB, Alexandersen S, Bloom ME. Subcellular localization of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus proteins and DNA during permissive infection of Crandell feline kidney cells. J Virol. 1996;70:3242–7 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol. 2011;28:2731–9 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar