Volume 21, Number 3—March 2015
Research
Nanomicroarray and Multiplex Next-Generation Sequencing for Simultaneous Identification and Characterization of Influenza Viruses
Figure 4
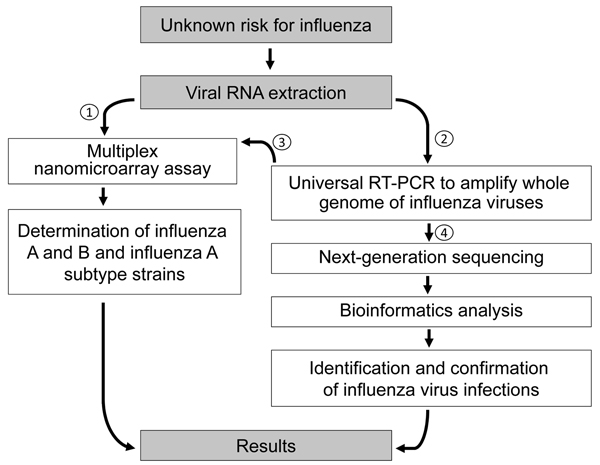
Figure 4. Diagnostic algorithm for identification of an unknown risk for influenza by using nanomicroarray and next-generation sequencing (NGS) assays. To determine the virus type for a suspected influenza virus infection, viral RNA is extracted from a patient sample and initially analyzed in nanomicroarray assay for screening and determining the influenza A and B viruses (1). Once a novel, emerging, or co-infected influenza A and B virus is found, universal reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) is performed to generate whole-genome mega-amplicons (2), which can then be retested on the nanomicroarray assay to confirm the initial finding (3) or sent to the central laboratory performing the NGS assay and data analysis for final sequence confirmation (4).