Volume 21, Number 5—May 2015
Research
Protective Antibodies against Placental Malaria and Poor Outcomes during Pregnancy, Benin
Figure 4
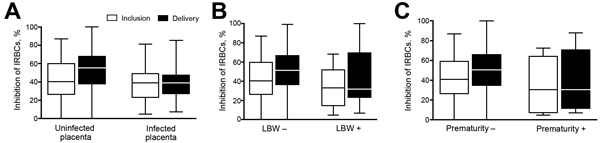
Figure 4. Binding inhibitory capacity of plasma, by adverse outcomes, in pregnant women with documented Plasmodium falciparum infection during follow-up, Benin. Binding inhibition was assessed according to adverse outcomes in the subgroup of women who had ≥1 parasitemia documented between study inclusion and delivery. A) Placental infection (52 infected placentas and 214 uninfected placentas). B) Low birthweight (LBW) (36 with LBW and 254 without LBW). C) Preterm birth (29 preterm and 269 not preterm). Horizontal lines indicate medians, boxes indicate interquartile ranges, and error bars indicate ranges. Plasma binding inhibitory capacity was significantly higher at delivery in women without adverse outcomes (p<0.05, by Fisher exact test), and the increase between inclusion and delivery was also significant (p<0.05, by paired-Wilcoxon test). No associations were observed at inclusion. IRBCs, infected red blood cells.