Volume 22, Number 3—March 2016
Synopsis
Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Virus in Egypt
Figure 4
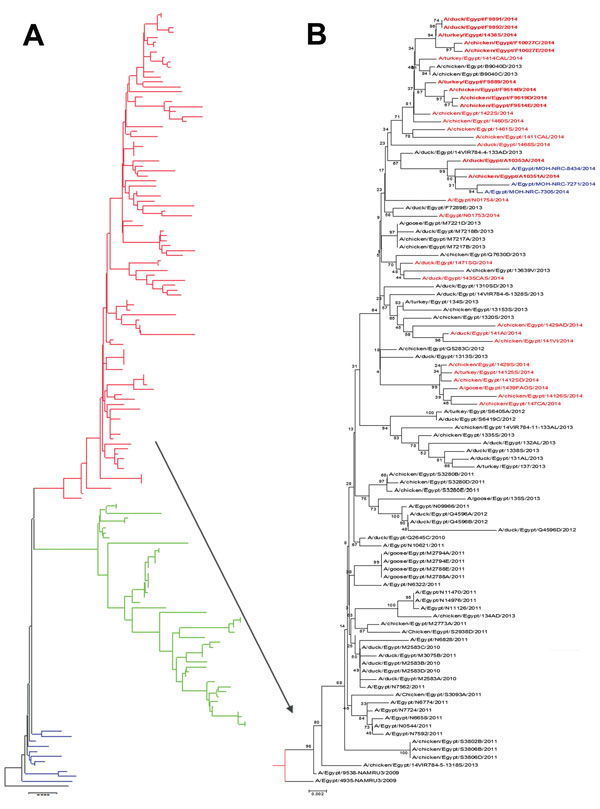
Figure 4. Phylogenetic tree of the hemagglutinin genes of avian influenza subtype H5N1 viruses isolated in Egypt during 2006–2014 and reference isolates from GenBank. Phylogenetic analysis was conducted by using the neighbor-joining algorithm with the Kimura 2-parameter model. Strain A/bar-headed goose/Qinghai/3/2005 was used as the root for the tree, and the reliability of phylogenetic inference at each branch node was estimated by the bootstrap method with 1,000 replications. Evolutionary analysis was conducted by using MEGA6 (http://www.megasoftware.net). A) Clade 2.2 viruses from 2006–2008 are shown in blue, subclade 2.2.1.1 viruses are shown in green, and clade 2.2.1 viruses are shown in red. B) Human viruses sequenced for this study are shown in blue. Boldface red font indicates avian viruses isolated in 2014 and sequenced for this study; lightface red font indicates other viruses from GenBank. *Indicates that 2014 viruses were grouped in 1 lineage. Scale bars indicate nucleotide substitutions per site.