Volume 22, Number 5—May 2016
Research
Expansion of Shiga Toxin–Producing Escherichia coli by Use of Bovine Antibiotic Growth Promoters
Figure 6
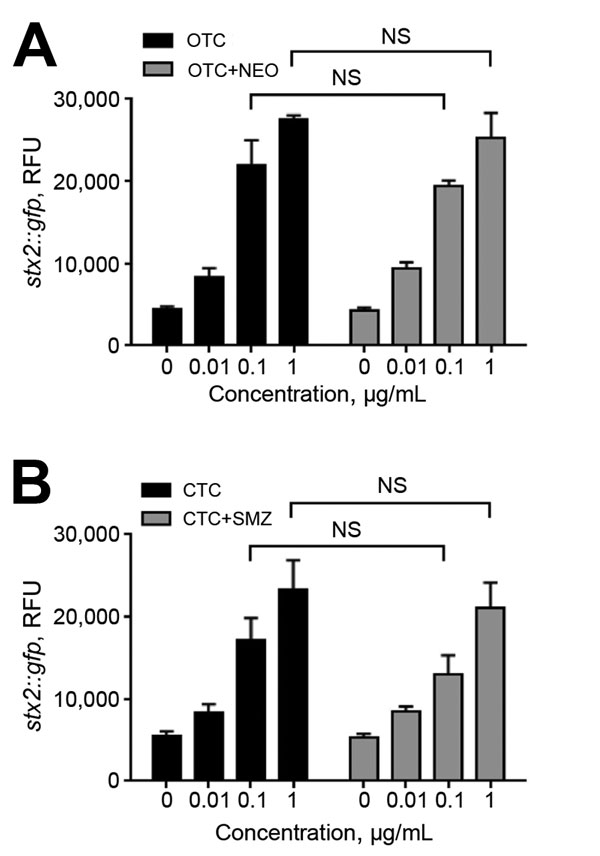
Figure 6. Induction of stx2 expression by treatment of oxytetracycline (OTC) and chlortetracycline (CTC) in combination with other antibiotics. Escherichia coli O157 harboring Pstx2::gfp was exposed to the following antibiotic combinations that are used in cattle for weight gain and feed efficiency: A) OTC/neomycin (NEO), and B) CTC/sulfamethazine (SMZ). The antibiotic combinations were prepared by mixing the indicated concentrations of each antibiotic. The results show means and SDs of a single representative experiment with triplicate samples. The experiment was repeated 3 times, and similar results were observed in all experiments. Statistical analysis was performed by using a Student t-test and GraphPad Prism 6 (http://www.graphpad.com/). NS, not significant; RFU, relative fluorescence units.