Volume 23, Number 6—June 2017
Research
Invasive Serotype 35B Pneumococci Including an Expanding Serotype Switch Lineage, United States, 2015–2016
Figure 2
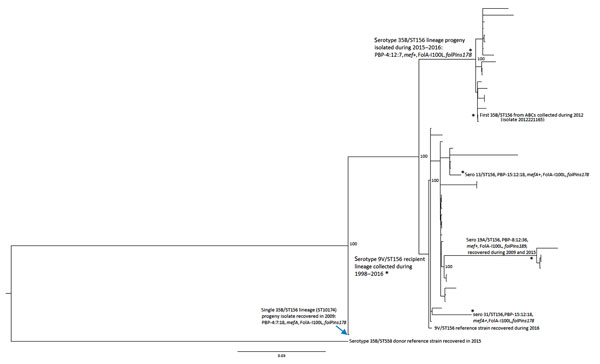
Figure 2. Phylogenetic analysis of potential recipient and serotype switch pneumococcal progeny strains within the ST56 lineage based upon a total alignment of 10,409 core single-nucleotide polymorphisms, United States, 2015–2016. All 20 serotype 35B progeny shown were recovered through Active Bacterial Core surveillance, and all but 2 indicated strains were obtained during 2015–2016. Isolate features are depicted for the 2 major nodes, with exceptions indicated by asterisks within the tree. Bootstrap values are indicated at key nodes. The serotype 9V isolate that was used for the reference recipient sequences described in Figure 3 is indicated as the third isolate from bottom. All isolates above the 9V recipient reference within this major cluster, except where indicated, are also 9V/ST156. Three additional serotype switch ST156 strain types detected by Active Bacterial Core surveillance during 2015–2016 are indicated by asterisks (single isolates of serotypes 31 and 13 and 4 serotype 19A isolates). Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.