Volume 23, Number 8—August 2017
Synopsis
Added Value of Next-Generation Sequencing for Multilocus Sequence Typing Analysis of a Pneumocystis jirovecii Pneumonia Outbreak1
Figure 1
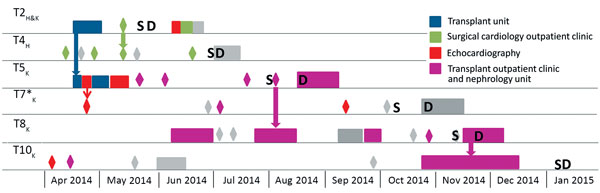
Figure 1. Transmission map illustrating space and time events for cluster patients sharing the clonal C2a genotype identified in a study of a Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia outbreak at a university hospital in France, 2009–2015. Rectangles indicate hospitalization periods of >1 day; diamonds indicate 1-day presence in the institution (e.g., emergency services, imaging, laboratory, outpatient clinics). Places involved in the transmission network are shown in color, whereas units not involved are shown in gray. Thick arrow refers to probable nosocomial transmission of P. jirovecii between 2 patients who were present in the same place (same floor and same corridor) on the same day. Thin arrow represents possible nosocomial transmission of P. jirovecii between T5 and T7 (patients were in perpendicular corridors). Subscript letters on patient labels indicate type of transplant (H, heart; K, kidney). D, date of diagnosis and treatment initiation; S, date of symptoms onset. Asterisk indicates that patient was carrying the C2a genotype as a minor strain.
1Preliminary results from this study were presented at the American Society for Microbiology Microbe 2016 Conference, June 16–20, 2016, Boston, Massachusetts, USA.
2Current affiliation: Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Limoges, Limoges, France.