Volume 24, Number 1—January 2018
Research
Detection and Circulation of a Novel Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Virus in Australia
Figure 3
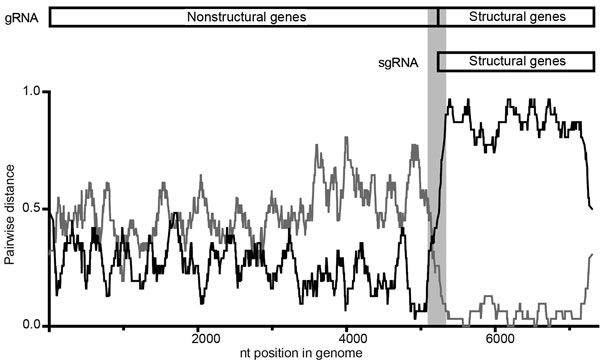
Figure 3. Recombination detection program plot (42) demonstrating recombination in a representative rabbit hemorraghic disease virus type a (RHDVa) strain from Australia. The pairwise identity of the recombinant, KYO-1, with the putative parental strains, RHDVa/AB300693.2/JPN/Hokkaido/2002 (black) and RCV-A1/EU871528.1/AUS/MIC-07(1–4)/2007 (dark gray), is plotted according to genome position (nt). A clear crossover event can be observed at the junction of RNA-dependent RNA polymerase and viral protein 60. The window size was set to 30. A schematic representation of the rabbit lagovirus gRNA and sgRNA is shown above the RDP plot to illustrate the genomic structure. The light gray bar shows the region where recombination was detected. gRNA, RNA genome; RHDV, RCV, rabbit calicivirus; sgRNA, subgenomic RNA.
References
- Abrantes J, van der Loo W, Le Pendu J, Esteves PJ. Rabbit haemorrhagic disease (RHD) and rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV): a review. Vet Res (Faisalabad). 2012;43:12. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Delibes-Mateos M, Ferreira C, Carro F, Escudero MA, Gortázar C. Ecosystem effects of variant rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus, Iberian Peninsula. Emerg Infect Dis. 2014;20:2166–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cooke B, Chudleigh P, Simpson S, Saunders G. The economic benefits of the biological control of rabbits in Australia, 1950–2011. Aust Econ Hist Rev. 2013;53:91–107. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Pedler RD, Brandle R, Read JL, Southgate R, Bird P, Moseby KE. Rabbit biocontrol and landscape-scale recovery of threatened desert mammals. Conserv Biol. 2016;30:774–82. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cooke BD, Fenner F. Rabbit haemorrhagic disease and the biological control of wild rabbits, Oryctolagus cuniculus, in Australia and New Zealand. Wildl Res. 2002;29:689–706. DOIGoogle Scholar
- O’Hara P. The illegal introduction of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus in New Zealand. Rev Sci Tech. 2006;25:119–23. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Eden J-S, Kovaliski J, Duckworth JA, Swain G, Mahar JE, Strive T, et al. Comparative phylodynamics of rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus in Australia and New Zealand. J Virol. 2015;89:9548–58. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wirblich C, Thiel HJ, Meyers G. Genetic map of the calicivirus rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus as deduced from in vitro translation studies. J Virol. 1996;70:7974–83.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Meyers G, Wirblich C, Thiel HJ. Genomic and subgenomic RNAs of rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus are both protein-linked and packaged into particles. Virology. 1991;184:677–86. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Le Gall-Reculé G, Zwingelstein F, Laurent S, de Boisséson C, Portejoie Y, Rasschaert D. Phylogenetic analysis of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus in France between 1993 and 2000, and the characterisation of RHDV antigenic variants. Arch Virol. 2003;148:65–81. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lavazza A, Capucci L. Chapter 2.6.2. Rabbit haemorrhagic disease. In: OIE manual of diagnostic tests and vaccines for terrestrial animals. 2016 [cited 2017 Jan 13]. http://www.oie.int/fileadmin/Home/eng/Health_standards/tahm/2.06.02_RHD.pdf
- Capucci L, Fallacara F, Grazioli S, Lavazza A, Pacciarini ML, Brocchi E. A further step in the evolution of rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus: the appearance of the first consistent antigenic variant. Virus Res. 1998;58:115–26. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Schirrmeier H, Reimann I, Köllner B, Granzow H. Pathogenic, antigenic and molecular properties of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV) isolated from vaccinated rabbits: detection and characterization of antigenic variants. Arch Virol. 1999;144:719–35. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wang X, Hao H, Qiu L, Dang R, Du E, Zhang S, et al. Phylogenetic analysis of rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus in China and the antigenic variation of new strains. Arch Virol. 2012;157:1523–30. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Oem JK, Lee KN, Roh IS, Lee KK, Kim SH, Kim HR, et al. Identification and characterization of rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus genetic variants isolated in Korea. J Vet Med Sci. 2009;71:1519–23. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Burmakina G, Malogolovkina N, Lunitsin A, Titov I, Tsybanov S, Malogolovkin A. Comparative analysis of rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus strains originating from outbreaks in the Russian Federation. Arch Virol. 2016;161:1973–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Abrantes J, Lopes AM, Dalton KP, Parra F, Esteves PJ. Detection of RHDVa on the Iberian Peninsula: isolation of an RHDVa strain from a Spanish rabbitry. Arch Virol. 2014;159:321–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Le Gall-Reculé G, Lavazza A, Marchandeau S, Bertagnoli S, Zwingelstein F, Cavadini P, et al. Emergence of a new lagovirus related to Rabbit Haemorrhagic Disease Virus. Vet Res (Faisalabad). 2013;44:81. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dalton KP, Nicieza I, Balseiro A, Muguerza MA, Rosell JM, Casais R, et al. Variant rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus in young rabbits, Spain. Emerg Infect Dis. 2012;18:2009–12. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Abrantes J, Lopes AM, Dalton KP, Melo P, Correia JJ, Ramada M, et al. New variant of rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus, Portugal, 2012-2013. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013;19:1900–2. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Baily JL, Dagleish MP, Graham M, Maley M, Rocchi MS. RHDV variant 2 presence detected in Scotland. Vet Rec. 2014;174:411. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Duarte M, Henriques M, Barros SC, Fagulha T, Ramos F, Luís T, et al. Detection of RHDV variant 2 in the Azores. Vet Rec. 2015;176:130. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hall RN, Mahar JE, Haboury S, Stevens V, Holmes EC, Strive T. Emerging rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus 2 (RHDVb), Australia. Emerg Infect Dis. 2015;21:2276–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dalton KP, Nicieza I, Abrantes J, Esteves PJ, Parra F. Spread of new variant RHDV in domestic rabbits on the Iberian Peninsula. Vet Microbiol. 2014;169:67–73. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lopes AM, Correia J, Abrantes J, Melo P, Ramada M, Magalhães MJ, et al. Is the new variant RHDV replacing genogroup 1 in Portuguese wild rabbit populations? Viruses. 2014;7:27–36. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Westcott DG, Frossard JP, Everest D, Dastjerdi A, Duff JP, Steinbach F, et al. Incursion of RHDV2-like variant in Great Britain. Vet Rec. 2014;174:333. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Puggioni G, Cavadini P, Maestrale C, Scivoli R, Botti G, Ligios C, et al. The new French 2010 Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Virus causes an RHD-like disease in the Sardinian Cape hare (Lepus capensis mediterraneus). Vet Res (Faisalabad). 2013;44:96. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Camarda A, Pugliese N, Cavadini P, Circella E, Capucci L, Caroli A, et al. Detection of the new emerging rabbit haemorrhagic disease type 2 virus (RHDV2) in Sicily from rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) and Italian hare (Lepus corsicanus). Res Vet Sci. 2014;97:642–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lopes AM, Marques S, Silva E, Magalhães MJ, Pinheiro A, Alves PC, et al. Detection of RHDV strains in the Iberian hare (Lepus granatensis): earliest evidence of rabbit lagovirus cross-species infection. Vet Res. 2014;45:94.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hall RN, Peacock DE, Kovaliski J, Mahar JE, Mourant R, Piper M, et al. Detection of RHDV2 in European brown hares (Lepus europaeus) in Australia. Vet Rec. 2017;180:121. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mahar JE, Nicholson L, Eden JS, Duchêne S, Kerr PJ, Duckworth J, et al. Benign rabbit caliciviruses exhibit evolutionary dynamics similar to those of their virulent relatives. J Virol. 2016;90:9317–29. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Office International des Epizooties. Rabbit haemorrhagic disease, Australia—immediate notification report. Ref OIE = 14719. 2014 [cited 2017 Jan 16]. http://www.oie.int/wahis_2/public/wahid.php/Reviewreport/Review?page_refer=MapFullEventReport&reportid=14719
- Collins BJ, White JR, Lenghaus C, Morrissy CJ, Westbury HA. Presence of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus antigen in rabbit tissues as revealed by a monoclonal antibody dependent capture ELISA. J Virol Methods. 1996;58:145–54. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gall A, Hoffmann B, Teifke JP, Lange B, Schirrmeier H. Persistence of viral RNA in rabbits which overcome an experimental RHDV infection detected by a highly sensitive multiplex real-time RT-PCR. Vet Microbiol. 2007;120:17–32. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Strive T, Wright JD, Robinson AJ. Identification and partial characterisation of a new Lagovirus in Australian wild rabbits. Virology. 2009;384:97–105. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jahnke M, Holmes EC, Kerr PJ, Wright JD, Strive T. Evolution and phylogeography of the nonpathogenic calicivirus RCV-A1 in wild rabbits in Australia. J Virol. 2010;84:12397–404. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Elsworth P, Cooke BD, Kovaliski J, Sinclair R, Holmes EC, Strive T. Increased virulence of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus associated with genetic resistance in wild Australian rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus). Virology. 2014;464-465:415–23. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hall RN, Capucci L, Matthaei M, Esposito S, Kerr PJ, Frese M, et al. An in vivo system for directed experimental evolution of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0173727. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kearse M, Moir R, Wilson A, Stones-Havas S, Cheung M, Sturrock S, et al. Geneious Basic: an integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics. 2012;28:1647–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Guindon S, Gascuel O, Rannala B. A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst Biol. 2003;52:696–704. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Posada D. jModelTest: phylogenetic model averaging. Mol Biol Evol. 2008;25:1253–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Martin DP, Murrell B, Golden M, Khoosal A, Muhire B. RDP4: Detection and analysis of recombination patterns in virus genomes. Virus Evol. 2015;1:vev003 .
- Liu J, Kerr PJ, Strive T. A sensitive and specific blocking ELISA for the detection of rabbit calicivirus RCV-A1 antibodies. Virol J. 2012;9:182. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Liu J, Kerr PJ, Wright JD, Strive T. Serological assays to discriminate rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus from Australian non-pathogenic rabbit calicivirus. Vet Microbiol. 2012;157:345–54. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cooke BD, Robinson AJ, Merchant JC, Nardin A, Capucci L. Use of ELISAs in field studies of rabbit haemorrhagic disease (RHD) in Australia. Epidemiol Infect. 2000;124:563–76. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lopes AM, Dalton KP, Magalhães MJ, Parra F, Esteves PJ, Holmes EC, et al. Full genomic analysis of new variant rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus revealed multiple recombination events. J Gen Virol. 2015;96:1309–19. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bergin IL, Wise AG, Bolin SR, Mullaney TP, Kiupel M, Maes RK. Novel calicivirus identified in rabbits, Michigan, USA. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009;15:1955–62. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- MacLachlan NJ. Parvoviridae A2. In: Dubovi EJ, editor. Fenner’s veterinary virology. 5th edition. Boston: Academic Press; 2017. p. 245–57.
- Cox TE, Liu J, de Ven RV, Strive T. Different serological profiles to co-occurring pathogenic and non-pathogenic caliciviruses in wild European rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus) across Australia. J Wildl Dis. 2017;53:472–81. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Matthaei M, Kerr PJ, Read AJ, Hick P, Haboury S, Wright JD, et al. Comparative quantitative monitoring of rabbit haemorrhagic disease viruses in rabbit kittens. Virol J. 2014;11:109. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
1Current affiliation: University of Alabama at Birmingham School of Medicine, Birmingham, Alabama, USA.