Volume 24, Number 12—December 2018
Research
Survey of Ebola Viruses in Frugivorous and Insectivorous Bats in Guinea, Cameroon, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo, 2015–2017
Figure 2
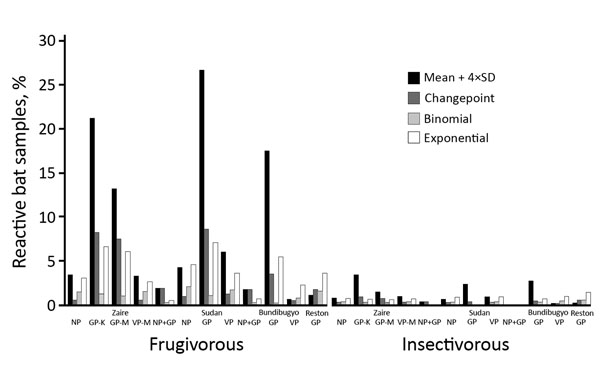
Figure 2. Bat blood samples reactive to Ebola virus antigens, by statistical method used to determine cutoff, Guinea, Cameroon, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo, 2015–2017. Samples from frugivorous bats (n = 1,736) and insectivorous bats (n = 2,199) were tested by Luminex assay with GP, NP, and VP of the Zaire and Sudan lineages; GP and VP of the Bundibugyo lineage; and GP of the Reston lineage. GP, glycoprotein; K, Kissoudougou strain; M, Mayinga strain; NP, nucleoprotein; VP, viral protein 40.
1These first authors contributed equally to this article.
2These senior authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: November 20, 2018
Page updated: November 20, 2018
Page reviewed: November 20, 2018
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.