Volume 24, Number 12—December 2018
Research
Rat Hepatitis E Virus as Cause of Persistent Hepatitis after Liver Transplant
Figure 4
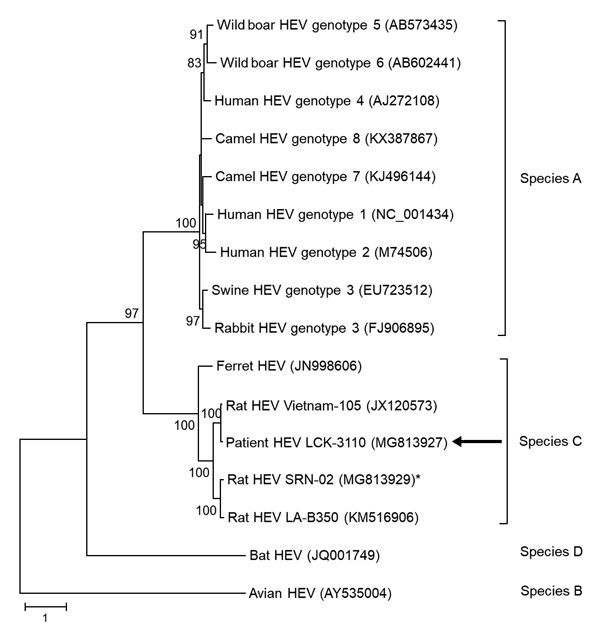
Figure 4. Phylogenetic analysis using complete open reading frame 2 nucleotide sequences of LCK-3110 and other hepatitis E virus strains. The tree was constructed using maximum-likelihood method with bootstrap values calculated from 1,000 trees. Only bootstrap values >70% are shown. GenBank accession numbers are provided. Arrows indicate strain LCK-3110; asterisk indicates strain SRN-02 detected in a street rodent in the epidemiologic investigation. Scale bar indicates mucleotide substitutions per site.
Page created: November 20, 2018
Page updated: November 20, 2018
Page reviewed: November 20, 2018
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.